SAP - An ERP Overview
What is an ERP software.
Consider a large enterprise like PepsiCo, which has number of divisions under it. There is a financial department, logistics section, HR, Warehousing, Sales and distribution etc. All these need to be integrated together, for effective functioning. This is done by a specific software known as Enterprise Resource Planning or ERP.
There is n number of ERP softwares in market today, of which SAP is used in medium to large enterprises.
SAP was the brainchild of five IBM employees who in 1972, setup an ERP enterprise in Germany. The first releases were R1 and R2 which were mainframe only applications. Each functional division within an organization is divided into modules. SAP started with financial application. Modules such as Logistics, HR were added later on.
Modules present in SAP
- Financial Accounting
- Financial Supply Chain Management.
- Controlling.
- Material Management.
- Sales and Distribution.
- Logistic Execution.
- Production Planning.
- Quality Management.
- Plant Maintenance.
- Project system.
- Human Resources.
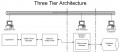
SAP Architecture
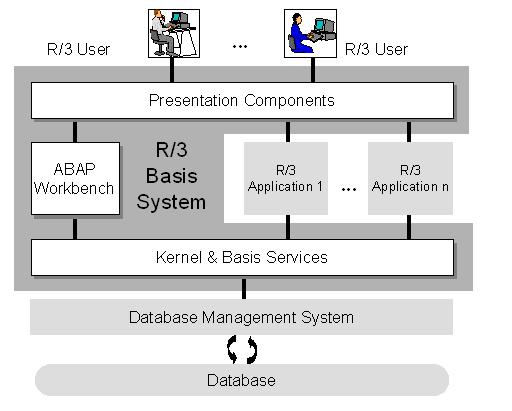
SAP R/3 Architecture
SAP R/3 Architecture can be divided into three main divisions depending on their functionality. The classification include
1. Database Layer
This layer stores all the data that moves through the SAP architecture. The Database layer is further divided into
- Database Management System (DBMS)
- Database Server.
Database management System or DBMS, is a set of software programs used to store, update or delete data from the server. The user can view and organize information according to one’s criteria and also enable security features to prevent unauthorized access
SAP is compatible with any database system, be it Oracle or IBM. In addition SAP has developed its own database known as HANA, if needed.
The database layer may be combined with the application layer onto a single host or both layers may exist independently. It is always better to implement the latter, as this reduces bottleneck in traffic flow.
2. Application Layer
Whenever a user sends a request from the presentation layer, the logical operation is provided by the Application Layer. In theory, only one application server is required to process requests. But in practise, there will be n number of application servers running on various systems. The load distribution between the application servers is provided by the message servers. The message servers contain data of how many application servers are currently online and the distribution of load between them.
3. Presentation layer
The Presentation Layer consists of the SAP GUI (Graphical User Interface) which acts as an interface between the user and the other two layers. User sends request from the Presentation Layer which in turn, gets processed by the Application Layer. Data is then retrieved from the Database layer and passed back to the Presentation Layer in the reverse order.
The control of a program switches from one layer to another during each operation. When the Presentation Layer is ready, the user can enter input in the screen. At that time, the Application Layer will not be accessible. Once the data gets entered, control switches over to the Application Layer. Until the Application layer completes the processing and initiates a new screen, user cannot input any data. The procedure, in which a new screen is presented before the user, is called a dialog step.
Application Server
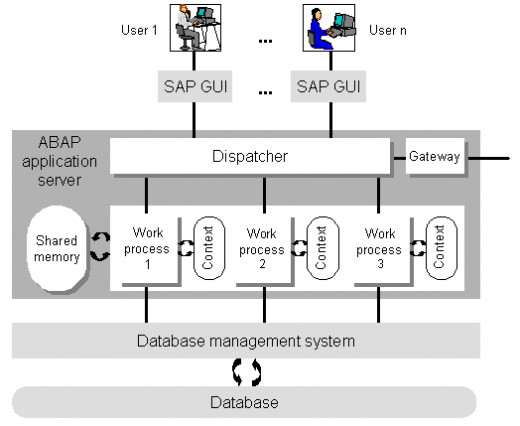
Now let us look a little bit closer to the working of the Application Layer. As told before, it is divided into two sections
- Application Server
- Message Server
The application server is used to connect the Presentation layer with the Database layer. Work process, dispatcher all comes under this. Application server communicates with each other using the message server.
- Work Process: A process initiated by the system, to execute user’s request. There can be n number of work processes, linked to running a program. Work process uses two memory areas. One is User Context, which contains information about the user. Another is known as the Roll Area, which contains the data for program execution.
- Dispatcher: The request that reaches the Application Layer, first comes to the Dispatcher. From here, it is routed to different work processes depending upon their availability. The dispatcher operates on the principle of First come - First server basis.
- Gateway: Acts as an interface for communication medium. RFC protocol is used for communication between SAP system.
- Shared Memory: Represents the common memory in Application Server. All work process has access to this shared memory.

Benefits of SAP
- Improves productivity
- Reduces cost by increasing flexibility.
- Supports additional extensions in an organisation, if required.
- Optimize IT spending.
- Provide immediate access to enterprise information.