Search Engine Optimization 101: What is SEO and How it Works?

Intro: What is Search Engine Optimization?
Search engine optimization (SEO) refers to a series of processes and techniques used by internet marketers to drive targeted traffic from the search engines to a website. If you’re an internet marketer, then you probably know how important search engine optimization is for a business. If your website isn’t among the top search engine results, then you’re missing out on a huge chunk of organic traffic from Google and other search engines.
The problem with SEO is that it is constantly evolving. A number of SEO tactics that were used to drive traffic until few years back may get your site penalized in 2019. There are also a number of myths surrounding SEO tactics that may or may not work, making it necessary to revisit the basics of how search engines work before formulating your SEO strategy.
SEO Tip
Internet marketers must focus their efforts on producing and repurposing high quality content in text, image, audio, video, slides and other formats to get powerful backlinks.
Search Engines
Search engine are used to look up information. Google receives more than 3 billion search requests every day. In less than 0.5 seconds, the search engine gives the most relevant results for a search query after scouring more than a billion websites.
Crawling and Indexing
The process by which search engines return relevant results is known as crawling and indexing. It involves:
-
making an index of the pages on the Web
-
accessing the list instantly
-
deciding the most relevant pages for any search term
In order to perform these functions, search engines use crawlers or bots that scan domains hosted on the Web. After making a list of the websites hosted on the servers, the crawlers then systematically crawl every accessible page on the website and look for information on the page as well as links to other pages that are then added to the list of pages to scour.
In this way, the search engine bots make a web of indexed pages and keep adding new pages to this index every day. In order to store the massive amounts of information indexed by the crawlers, search engines employ large data centers scattered across the world.
Features of Search Engine Results Page
Search results used to be snippets of plain text and a link to the webpage. Today, the standard search results are supplemented by powerful and enriched features that offer supplementary information.
Some ways of landing your website on the SERP features include:
-
Optimizing a site structure for search engines and users
-
Offering content that is accessible to both search engines and users
-
Using structured code to assist crawlers in understanding a website
An organic SERP feature includes:
Rich Snippet: A visual component is added to the standard result, for instance hotel rating stars.
People Also Ask: It is an expandable block of related queries made by searchers.
How does a Search Engine Show Relevant Search Results?
Google is capable of showing hundreds of thousands of search results from its index for any search query. So, how does it determine the best order of displaying these results to a user?
It would be impossible for a team of humans to sift through so many search results in such a short period of time. Instead, Google relies on algorithms, a set of mathematical rules and equations, to understand the intent of user, look for most relevant results to the query, and rank the results on the basis of popularity and authority.
There are more than 200 factors that are considered by the ranking algorithms. These include:
Type of Content: There are different types of content, including news, images and videos. Google prioritizes content on the basis of user intent.
Quality of Content: Content that is useful and informative is prioritized by Google. In internet marketing, this refers to content that is concise, original, thorough and helpful.
Freshness of Content: Google prefers fresh content over outdated one. So if two pieces rank the same for quality, then Google may give priority to the page with fresher content.
Popularity of Page: Google employs a variation of the original PageRank algorithm to determine a webpage’s popularity by the number of other pages linking to it as well as the quality of those links.
Quality of Website: Spammy and low quality websites are penalized by Google and downgraded in the search results.
Search Language: Many non-English users search information on Google in their native languages. In such case, Google may display results in those languages.
Location: A number of users perform local searches, such as “flower shops near me.” In this case, Google is most likely to prioritize local search results.
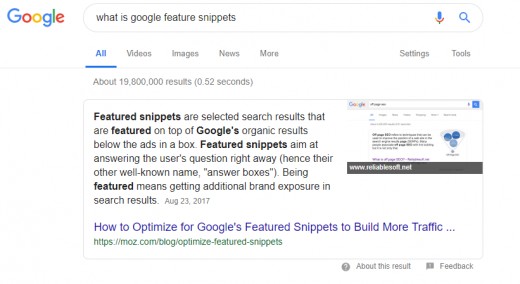
Featured Snippet: It is characterized by a highlighted block at the top of search results with a brief answer to the query and a link to the source URL.
Knowledge Cards: These are displayed in a panel to the right of the standard results and offer useful information about a search query.
Image Packs: A row of images displayed where visual content is relevant to a query.
Instant Answers: Google displays these results when it can instantly reply to a user’s query. You’ll see these results if you search your location or the weather.
Types of SEO
By optimizing your website, you too can dominate the standard and featured organic search results for keywords that are relevant to your business. This will help you drive a lot of targeted traffic to your website.
In order to optimize your website, you need an effective SEO strategy that focuses on three different types of SEO:
- Technical SEO
- On-Page SEO
- Off-Page SEO
Technical SEO
This involves optimizing your website for crawling and indexing by the search engine bots. This is the foundation of your SEO. The objective is to structure your website in a way that facilitates the crawling and indexing of information.
Technical SEO focuses on the infrastructure and architecture of your website. It involves the following:
Structure and Hierarchy of Website URLs
Make sure that your website uses a site-wide URL structure that is optimized for both search engines and users. There must be a well-defined flow of URLs from domain to category to sub-category. Keep adding any new pages to this hierarchy.
www.example.com/category/subcategory/product
Websites that lack URL structure and hierarchy make it confusing for crawlers and users to find the information they are looking for. This in turn affects your website’s search ranking.
Page Speed
This is a another major ranking factor. Users expect web pages to load instantly and 40% of all searchers abandon pages that fail to load in three seconds. Use widgets, plugins and tracking codes to a minimum. Also, compress any images and videos before using them on your website.
XML Sitemaps
It is a file with a list of every website page. Search engines use a sitemap to discover a website’s internal pages. Make sure that your website sitemap does not have any pages that you don’t want to show in the search results.
HTTP or HTTPS
Whenever you access and interact with a web page, you are relaying information across the Web. Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is a fast but insecure way of transmitting data over the Web. Data is relayed using a connection that is not encrypted and can be accessed by third parties.
For this reason, Google announced in 2014 that it will offer a small ranking benefit to websites running on Secure Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTPS), which encrypts data using an extra layer of Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocol. While some people may disagree, it makes sense for website owners to make a timely transition to HTTPS.
Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP)
AMP is an open-source platform sponsored by Google. It allows website content to load instantly on mobile devices. AMP-optimized websites are known to enjoy better search rankings. The number of mobile users ditching your webpage because of slow loading time will also reduce, further impacting your search results.
On-Page SEO
On-Page SEO is the process of optimizing every element on a website. It involves tweaking and optimizing the front end elements of your website for the search engines. Website owners have complete control over on-page SEO.
Meta Tags
Meta tags are on-page SEO elements that define the structure of a webpage. For instance, an H1 tag describes a page’s title. Proper use of meta tags makes it easier for search engine crawlers to understand the structure of a webpage.
Keep titles up to 70 characters long or they may be truncated in the search results. Meta descriptions are snippets that provide a brief summary of the information on the web page. Avoid stuffing the title and description tags with keywords and focus on providing useful information.
Image Optimization
Since images cannot be read by search engine crawlers, you should use the ALT text to describe what the image is about. It may include a relevant search query but should also provides information to a user about the image.
Internal Links
Linking internally to other website pages helps the search engine crawlers in better understanding what the page is about and determining its relevance to other pages of the website. Internal links also keep users surfing your website longer, which is another positive indicator of a useful website.
Off-site SEO
Off-site SEO involves working with SEO elements that are outside of your website but still impact your ranking. Off-site SEO mainly focuses on building links from authoritative websites to your website. This practice is also known as link building.
Link Building
Link building is the process of getting high quality links from external sites to your website. When an authoritative website links to your website, it is essentially showing the search engines that your website is also reputable and hence deserves to be ranked higher in the search results.
Keep in mind that not all backlinks offer the same ‘link juice.’ The value of a backlink is determined on several factors, including:
-
Authority of linking site
-
Anchor text of link
-
Dofollow or nofollow link
-
Number of links of the backlinking site
Link Building Tip
If you want to determine if a website can provide high quality backlinks, simply visit the Alexa website and look up the website’s Alexa score. The lower a website’s Alexa rank, the more valuable its backlink.








