Types of 3D Printers
Introduction
There are different kinds of technologies used by 3D Printers. Every printer is said to have a different purpose. Depending on the requirement, we must choose what type to be used based on each printer’s pros and cons. There's always a trade-off among many parameters such as strength, quality, and cost. Hence, choosing the right printer for your requirements is essential.

Few of the various technologies involved in 3D printing are:
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) or Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF)
- Stereolithography Apparatus (SLA)
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
- Digital Light Processing (DLP)
- PolyJet
- Multi Jet Fusion (MJF)
3D printers are usually classified based on the input material used. In the beginning, 3D printers could print solely with plastic, which caused the decline of the product quality. The necessity to improve performance and efficiency led to the invention of different types of printers. Let's dive deeper and learn more about each type of printer.
1. Fused Deposition Modelling
FDM is the most popularly used 3D printer where they use plastic filaments to print products. For example toys, cup holders, project demonstrations, etc.
The plastic is heated to a particular temperature where the plastic begins to melt, giving it the ability to flow. A tapered tip (nozzle) is attached to one end of the extruder which works as a tip of a pen.
The process starts with the printing of the base cross-section according to the design of the model. The movement of the nozzle and process of extrusion are highly coordinated to draw the entire cross-section. After printing one complete layer, the platform is lowered and the next layer is printed. These steps are repeated until the object is complete.

Manufacturing brands like Prusa, Ultimaker, and Stratasys produce top-notch FDM printers.
Note: Patent rights of FDM belong to Stratasys. Due to this reason, FDM is also called Fused Filament Fabrication.

2. Stereolithography
Stereolithography (SLA) is the pro-version of FDM. It can ace minute details in objects along with speed. It is preferably used for artworks and in areas where detailing the object is the top priority. So, you could say that stereolithography is like the handsome guy in the class.
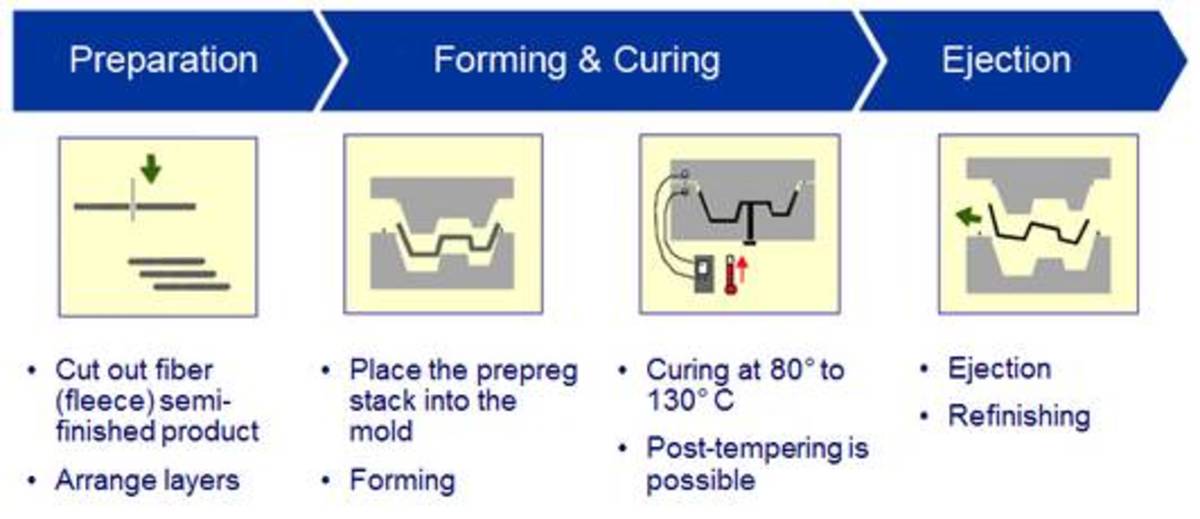
SLA printers use a special kind of liquid polymer resin to print. This resin is capable of transforming into solid when exposed to UV light. This phenomenon is called curing, and the resins are called photocurable resins.
The setup is similar to the extruder in FDM printers but includes a laser and movable mirrors. The laser can be incident onto any point of the plane. The resin is filled in a tank above or below the laser, depending on the design of the printer.
Then, the laser scans a cross-sectional view of the corresponding layer, which cures the cross-section of the object. The platform then descends, making another layer of uncured resin available for the next layer. The bonding of layers takes place during the curing of the successive layer.
Unlike FDM, the print is not ready to use after curing all the layers. Another stage of resin curing is done to make the bonding between layers stronger.
The best desktop SLA printers are produced by FormLabs, 3D Systemes, and EnvisionTEC.
3. Digital Light Processing
DLP and SLA belong to the same class of printers that use curing techniques to print. So, where do we use DLP? Before answering the question, let us see how DLP works.
Digital Light Processing printers have a projector similar to ones in a movie theatre. The cross-section of a layer is projected onto the resin. So the entire projected area is cured at once.
This technique significantly decreases the curing time of a layer. DLP is used to print at high rates. Post printing processes of DLP are identical to SLA.
There’s another type of printer which has a high resemblance to DLP printers. They use LCD screens instead of a projector. However, LCD printers have some issues in terms of usage and maintenance.
According to the working, DLP and LCD printers can be called siblings and SLA is their cousin.
4. Selective Laser Sintering
This type of printer uses a technique called ‘sintering’ to manufacture. When a high powered laser beam is incident on a powdered material, the powder turns into a solid. Hence, SLS printers use powdered metal as input material for 3D printing.
Although sintering provides high strength to the objects printed, it fails to provide high geometrical accuracy and requires high profile tuning before use. SLS also requires knowledge in additive manufacturing and real-time tracking during printing.

In SLS, a thin, uniform layer of powder is laid on the print bed. You might have guessed that the high powered laser scans the cross-sectional area layer after layer to form a solid. The laser used in SLS is never sighted directly. SLS is very complex and sophisticated among all other kinds. A series of processes like machining, heating (to remove internal stresses), and polishing are done to obtain the finished product. SLS can also print metal objects.
5. PolyJet
PolyJet printers use tiny photocurable particles and UV light to carry out 3D printing. PolyJet printers are best used to manufacture compound parts. Parts with varying properties can be printed with ease. These printers can print parts containing fine details with extreme precision. And the best thing about PolyJet printers is that they can print at a very high rate.
6. Multi Jet Fusion
MJF printers also use powder to manufacture parts. It uses jets to lay powder in desired areas and fuses the powder to form a solid. This printer is the best among all other types in terms of performance. It is used if mechanical properties are the topmost priority.
Summing up
The above mentioned are not the only 3D printers present, but they are popular and most widely used printers. Remember that there is always a trade-off. MJF and PolyJet have a lot of capabilities, but the cost is a trade-off. They cost more than an FDM printer. Whereas FDM printers can't produce great quality, but they are easy to use, less expensive, and robust. SLA and DLP printers cost twice as much as FDM and need care and maintenance.
© 2020 Vijayendra Vemula