Benefits of Digital TV


The arrival of digital TV is a change as radical as it marked the transition from black and white to color. It is getting better images, but does not stop there, but also will open the doors to the future introduction of services never before imagined, such as mobile TV reception, interactivity, video on demand services or multimedia so fashionable nowadays with the Internet explosion.
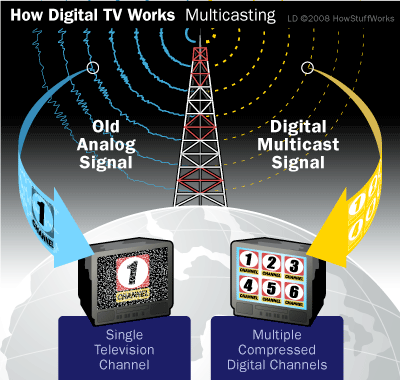
The main problem is that analog TV does not take advantage of the fact that in most cases, video signals vary little in going from one picture element (pixel) to its neighbors, or at least there is a dependence. In short, electromagnetic spectrum is wasted.
In addition to increasing the number of broadcasting stations, the interference goes on to become a serious problem.
The radio channels of digital television occupy the same bandwidth (8MHz) the channels used by analogue television, but due to the use of compression techniques for audio and video signals (MPEG) have capacity for a number television variable depending on baud rate, can range from a single program of high definition TV (great picture and sound) to five programs with similar technical quality to the current (emission standard system G with color PAL), or even more programs similar to video quality. However, initially, it is expected that each multiple channel (multiple channel refers to the ability of a radio channel to host various television programs) or autonomous national coverage will include at least four programs.
The use of digital terrestrial television as a medium for television broadcasting provides a number of advantages over other possible options:
1. When used as a means of distributing the terrestrial network allows us to a reception at home easier and more affordable, as it uses the same system of analog TV reception, even with the previous antenna, without sacrificing quality.
2. Allows for portable reception and moving.
3. You can use single frequency networks, which means using fewer frequencies.
4. Requires less transmission power.
5. Increases the number of programs with respect to the current analog television, allowing multiple multimedia programs and services in each radio channel.
6. Improving the quality of picture and sound (avoiding the effects of snow and dual analog TV picture) in the area of coverage, due to the robustness of the digital signal to noise, interference and propagation multi path.
7. The high spatial resolution of a digital television system allows greater realism, which can be seen in a larger screen.
8. Allows the increased aspect ratio. The conventional format is 4:3, whereas digital television allows 16:9 wide screen formats.
9. It can deliver multichannel audio with CD quality. Besides the multiplicity of audio channels can get the surround sound effect used in cinemas. Besides, these channels could be used to transmit different languages with the same video program.
10. Opens the doors of the home to the Information Society because it allows TV-PC convergence. The TV will become a multimedia terminal that can accept data from telecommunications services, providing value added services such as stock quotes, email, video phone, electronic program guides (EPG), video on demand, pay per view, advanced teletext, home banking, shop at home, etc.
11. Provides varied services, for example at national, regional and local levels.
12. Allows the balanced development between open services (Universal Service) and payment services.


Current TVs do not allow the reception of the new digital signal to obtain a viewable image, so there are two solutions:
1. The obvious solution is to buy a digital TV, but until the system is not fully inserted, the big-screen digital televisions capable of digital television will be expensive.
2. The cheapest solution is to add the current television receiver decoder apparatus, which converts the digital signal into an analog signal. Although the viewer does not perceive the high quality of digital television, the image quality would exceed the same program broadcasted on an analog channel.
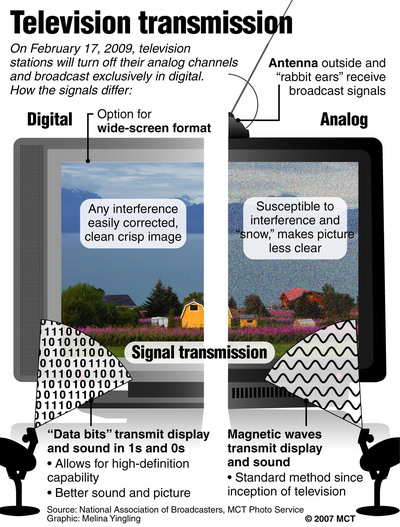
Digital TV versus Analog TV
The main problem with analog TV is that it does not take advantage of the fact that in most cases, video signals vary little in going from one picture element (pixel) to its neighbors, or at least there is a dependence. In short, electromagnetic spectrum is wasted.
In addition to increasing the number of broadcasting stations, the interference goes on to become a serious problem.
In analog television, the parameters of the picture and sound are represented by the analog magnitude of an electrical signal. The transport of this analog signal into the homes takes many resources. In the digital world, these parameters are represented by numbers, in a system of base two, i.e., using only the digits "1" and "0".
The process of digitizing an analog signal is performed by the analog/digital converter. This representation, numerical bit enables the television signal subject to very complex processes without degradation of quality. They offer many advantages and open up a range of possibilities for new services in the home. However, the digital television signal provided directly by the analog/digital converter contains a large amount of bits that are not viable to transport and store without excessive consumption of resources.
The number of bits generated by the process of digitizing a television signal is so high that it takes a lot of storage capacity and resources for transportation.

Groups and forums dedicated to the development and operation of Digital Television (especially in Europe)
European DVB Project (Digital Video Broadcasting), has set standards for digital broadcasting that apply to all forms of broadcast (satellite, terrestrial cable and others).
Forum Digitag (Digital Terrestrial Action Group), which is responsible for unifying criteria of service requirements of the receiver functions of regulatory issues with all the nuances of each country and foster the rapid introduction of digital television.
Project VALIDATE (Verification and Launch of Integrated Digital Advanced Television in Europe), which is the working group that validates all digital television experience, as to the compatibility of different receptors.
MOTIVATE project, examines the possibility of mobile reception of digital television.
The standards for digital television in Europe have been developed by the DVB Project, which consists of over 200 organizations. Because of its lower complexity, the rules for satellite and cable have preceded one or two years to the standard of terrestrial TV, and this has been reflected in their respective implementation.
Examples of the number of bits generated by the digitization of 3 different television formats:
In standard format, a digital television image is formed by 720x576 dots (pixels). Storing an image requires 1 Mbyte. Transmitting a second worth of continuous images requires a transmission speed of 170 Mbits/s.
For widescreen, digital television picture consists of 960x 576 dots (pixels) and requires 30% more capacity than others.
In format digital high definition television image is 1920 x1080 dots (pixels). Storing an image requires more than 4 MB per image. Transmitting a second worth of continuous images requires a transmission speed of 1Gbit/s. Fortunately, television signals have more information than the human eye needs to perceive correctly a picture. That is, have considerable redundancy. This redundancy is exploited by digital compression techniques to reduce the amount of "numbers" generated in the digitization to adequate levels that allow transport with a high quality and resource economics.
These and other techniques were all factors that have driven definitely the digital television development, enabling storage and transport of the digital TV signal with minimum resource use.