Facts About Hepatitis C
Introduction
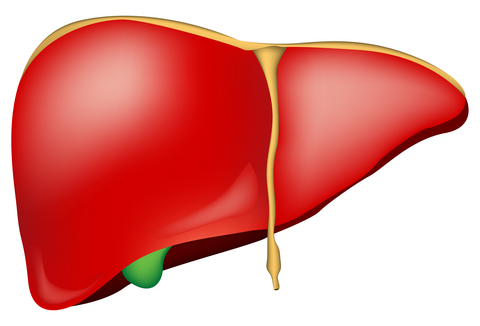
Hepatitis C virus is a contagious, blood borne disease that affects the liver, and causes it to become inflamed and swollen. The liver is the second largest organ in the human body. It performs several important tasks: removes harmful chemicals from the bloodstream, fights infection, is an aid in the digestion of food, and stores nutrients and vitamins as well as energy. A person cannot live without a liver.
There are two forms of Hepatitis C. The initial manifestation is acute Hepatitis C, and occurs within six months of exposure to the virus. Chronic Hepatitis C is the long term illness that occurs as a result of the Hepatitis C virus remaining in the body. Many people with acute Hepatitis C exhibit no symptoms, and some people with chronic Hepatitis C will be largely asymptomatic for as long as 10-30 years. Some people only show symptoms after cirrhosis of the liver has occurred.
There is no treatment for the acute form of Hepatitis C. 75-85% of those thus affected will go on to develop the chronic form. 15-25% of people who contract acute Hepatitis C will recover completely and without treatment. Medical science does not fully understand why these people recover while others go on to develop chronic Hepatitis C. 25% of people who with chronic Hepatitis C will develop cirrhosis (scarring) of the liver, and 10% will develop liver cancer. An estimated 4 million people in the United States have Hepatitis C today, and approximately half of them don't know they are infected. 8,000 to 10,000 people die annually from complications related to Hepatitis C.
Cause and Spread
Hepatitis C is caused by the Hepatitis C virus, or HCV. It is spread from person to person via blood. Those who may be infected or who are at risk for infection include current or past injection drug users, anyone who received a blood transfusion prior to 1992, or blood products for clotting produced prior to 1987, hemodialysis patients, health care workers who may have improperly handled blood or been stuck with an infected needle, HIV infected persons, babies born to mothers with Hepatitis C, anyone who has ever been in or worked in a prison, and anyone who received a tattoo or piercing where sterile practices were not followed. Less commonly, Hepatitis C can be spread through sex and through the sharing of personal items, such as a razor or toothbrush, that may have had contact with an infected person's blood. Hepatitis C is not spread by mosquitoes, eating utensils, breast feeding, kissing, coughing, sneezing or by food or water.
Symptoms
Symptoms for the acute and chronic form are largely the same, although they may be so mild in the acute form that they pass unnoticed. Symptoms include pain in the upper right abdominal area, tiredness and fatigue, abdominal and/or ankle swelling, dark urine, fever, itching, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and/or the whites of the eyes), loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, pale or clay colored stools, and (in the chronic form only), bleeding from the esophagus or stomach.
Diagnosis
The FDA just recently approved OraSure Technologies OraQuick HCV Rapid Antibody test which detects the presence of HCV antibodies in just twenty minutes with a simple finger stick text. Traditionally, Hepatitis C is diagnosed with an EIA assay that detects the Hepatitis C antibodies. If that test is positive, a Hepatitis C RNA assay will measure the amount of virus, or viral load, in the blood. A Hepatitis C genotype test will determine what genotype infection a person has; most Americans have the genotype 1 infection, which unfortunately is the hardest to treat. Various other tests, including a liver biopsy might be performed in an attempt to establish the progression of the disease and the amount of damage done to the liver.
Prognosis
The hope of removing HCV from the blood with treatment is as high as 90% for some people. Those who do not receive a "cure" often do reduce their potential risk of cirrhosis and liver cancer through the reduction of their viral load. Unfortunately, not everyone is able to tolerate the treatment. Hepatitis C is one of the most common causes of chronic liver disease. Sometimes the last resort for a person with a diseased liver is a transplant, and even then, the Hepatitis C generally returns.
Treatment
The goal of treatment is to remove the virus from the blood, thus reducing the risk of cirrhosis and liver cancer. The most common medical treatment today is a combination of pegylated interferon (which is a synthetic version of the interferon the body produces to fight infection) and ribavirin. The treatment typically consists of weekly interferon injections and twice daily capsules of ribavirin, for a 24-48 weeks. This treatment can have severe side effects: anemia, depression, fatigue, fever, flu-like symptoms, headache, irritability, loss of appetite, low white blood cell count, nausea, vomiting and thinning hair. In clinical trials, it is about 50% effective, however in real life, doctors find that less than a third of patients have a sustained response once treatment has ended, and most have significant side effects. There are two new drugs on the horizon, Merck's Boceprevir and Vertex's Telaprevir, which are scheduled for approval process review by the FDA's Antiviral Drug Advisory Committee at the end of April, 2011. Clinical trial data suggests that when one of these drugs is added to the interferon/ribavirin regimen, the likelihood of a sustained virologic resonse is significantly increased in both new patients, and patients who previously did not respond to the treatment. The interferon and ribavirin must still be taken for the first three months of treatment, but this is a shorter length of treatment than when interferon and ribavirin are used alone. Another drug that has shown promise in treating Hepatitis C is the antiviral drug Amantadinel. Alternative treatments include Ozone therapy, which has been quite successful in reversing Hepatitis C, sometimes after just a few sessions, and various dietary and supplementation regimens. The most often mentioned and highly touted herbal supplement in alternative literature is milk thistle.
Conclusion
Persons with Hepatitis C should not drink alcohol. Even a small amount of alcohol exacerbates the inflammation and progression of the disease. Affected individuals should also exercise caution in taking both legal and illegal drugs, prescription and over the counter, as most drugs are metabolized in the liver. Before taking drugs or even supplements, persons with Hepatitis C should consult with their health care providers.
Links
Pub Med on Hepatitis C: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0001329/
CDC on Hepatitis C: http://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/C/
National Institute of Health: http://health.nih.gov/topic/HepatitisC
Medline Plus: http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/hepatitisc.html