- HubPages»
- Technology»
- Computers & Software»
- Computer Hardware
Functional Units of A Computer
Input Unit
The input unit accepts coded information from human operators or from other computers.
Examples: Keyboard, joystick, mouse, input pen, touch screen, trackball, scanner, bar code readers, microphone, floppy disks, magnetic tapes, compact disks.
Memory Unit – Primary Storage
Primary Storage or Main Memory (MM). This is where programs are stored during their execution. The MM is a fast memory capable of operating at electronic speeds.
The information in MM is often processed in groups of fixed size called words. The number of bits in a word is the word length of the computer. Typical word lengths range from 16 to 64 bits. The MM is organized so that the contents of one word, containing n bits, can be stored or retrieved in one basic operation.
To provide easy access to any word in MM, a distinct address is associated with each word location. Addresses are numbers that identify successive locations.
MM is also known as random-access memory (RAM). RAM is a memory in which any location can be reached in a short, fixed amount of time.
The time required to access one word is the memory access time. For RAMs, this time is fixed, independent of the location of the word being accessed. It typically ranges from 10 to 100 nanoseconds for most modern computers.
Main Memory Divisions
· Input Storage Area – this area accepts and stores the input data to be processed.
· Working Storage Space – holds the data being processed as well the intermediary results of such processes.
· Output Storage Area – maintains the final outputs or processed results of the operations.
· Program Storage Area – holds the programs or processed instructions given by the user. It stores the entire program that is being executed.
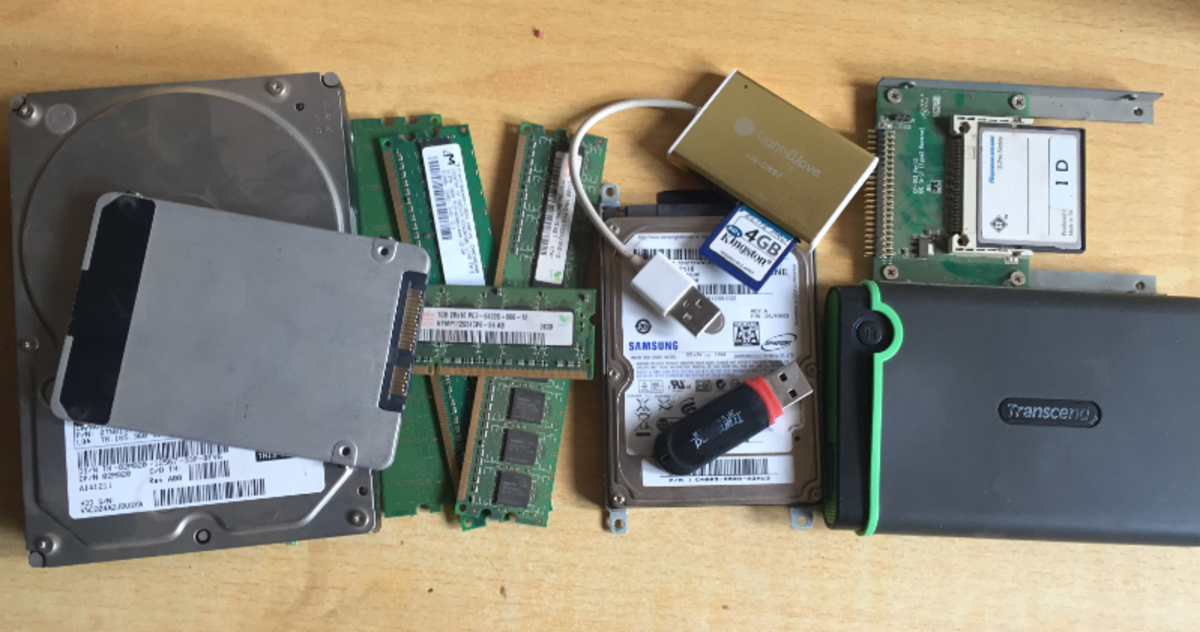
Memory Unit – Secondary Storage
Secondary Storage or Auxiliary Storage.
- This is used when large amounts of data have to be stored (on a more permanent basis), particularly if some of the data need not be accessed very frequently.
- This is a storage medium that will hold data and program/sets of instructions even if the computer system is switched off.
Picture, if you can, how many filing cabinet drawers would be required to hold the millions of files of, say the tax records kept by the Bureau of Internal Revenue (BIR). The record storage rooms would have to be enormous. Computers on the other hand permit storage on tape or disk in extremely compressed form. Storage capacity is unquestionably one of the most valuable assets of the computer. Take a simple diskette for example, it can hold the equivalent of 500 printed pages and an optical disk (CD-ROM) can hold approximately the equivalent of 400 books.
Examples: Magnetic Disks (diskette, hard disk), Drums, Tapes, CDROMS, DVD-ROMS Hard disk nowadays has a capacity ranging from 20 GB – 120 GB.
Processing Unit
- Also called the Central Processing Unit (CPU) or Central Processor.
- It contains a number of high-speed (10 times faster than MM) storage elements called registers that are used for temporary storage of frequently used operands. It is mandatory for data to be stored in a register before it can be processed.
- The CPU is composed of the Arithmetic-Logic Unit (ALU) and the Control Unit (CU).
The ALU is where all arithmetic and logic operations and manipulation of numbers take place. The CU is the nerve center of a computer. It controls the entire activity of the CPU. It controls and coordinates the order and execution of program instructions. It accesses instructions in sequence, interprets them and then directs their implementation.
Output Unit
It sends processed results to the outside world. Examples: Display screens, printers, plotters, modems, microfilms,synthesizers, high-tech blackboards, film recorders.
Basic Operation of a Computer
The operation of a computer can be summarized as follows:
1. The computer accepts information in the form of programs and data through an input unit and stores it in memory.
2. Information stored in the memory is fetched, under program control, into an arithmetic and logic unit, where it is processed.
3. Processd information leaves the computer through an output unit.
4. All activities inside the machine are directed by the control unit.