Nature's perfect storage device – DNA!
Computer users generate enormous amount of data on daily basis that has to be accessed at the time of need. Scientists are hoping to revolutionize current method for digital storage by imitating far better data storage system found in nature - DNA.

DNA is incredibly durable and fantastically dense whose one speck can store millions of digital images impeccably preserving them. Which implies that the space expected to store today's computerized information could recoil from the measure of a distribution center to the tip of a test tube possibly turning data storage contrivances obsolete, transforming technology as we are aware of it.
We are using synthetic DNA for data storage and so the images videos etc. can be stored in the form of zeros and ones. Due to its density, one can store a ton of information in a small volume. To give an idea of the whole accessible internet, which is estimated to be seven Exabyte, it would fit in the size of a shoe box. Plus it is durable and in the right conditions DNA can last for thousands of years compared to other source technologies that last a year or a decade.
— Luis Ceze, Professor at University of WashingtonHow does it work?
DNA is made up of various sequences of four types of molecules:
- Adenine (A)
- Cytosine (C)
- Guanine (G)
- Thymine (T)
The first step in the process is to turn the data into sequences of those four molecules along with the markers that identify where data belongs in the original sequence. The sequences are then synthesized into actual DNA. When the DNA is received, many files come together in a single pool. A number of checks are made and then a process, called Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is used to select only the sequences of the files to be read. The PCR process multiplies only the sequences of those files. The sequences are then read and turned back into data in the last step.
A couple groups of computer scientists around the globe have been exploring different ways regarding approaches to store information into DNA. Also, they worked with bio-specialists to combine information and assemble it obstruct by piece. The researchers took the zeros and ones form of data needed to be encoded, and changed over it into base 4, to coordinate those four building pieces of DNA. They then included ID tags that allowed them to access any byte within a large pool of data. They encoded four large files, and they were able to access them almost perfectly.
Last year, Microsoft’s Research Lab stored hundreds of kilobytes of data in DNA and fully recovered it. This year, they are working with hundreds of megabytes of data, which means a thousand times more DNA. Microsoft Research has additionally collaborated with the University of Washington and has demonstrated that it is able to recuperate data built out of 1.5 billion nucleotides.
The growth that has been experienced in Microsoft’s global data centers is truly astounding. It was a challenge to form a foundation for the future and DNA storage gave that new foundation.
Barrier
It takes a lot of money and time to synthesize and sequence the DNA. But bio-engineers are bringing those barriers down every single day because they have incentive to do so.
Interesting Facts
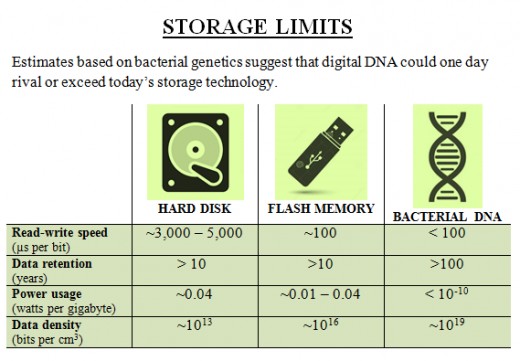
- 150 smartphones, which mean a total of approx. 10,000 gigabytes, can easily be fitted on the tip of a pin if the storage medium is DNA.
- The theoretical limit of data storage in DNA is an Exabyte of data per cubic millimeter (Exabyte/mm3).
- The data stored in DNA can survive for up to 500 years, even in harsh environments.
- The world produces about 25 billion gigabytes of data, EVERYDAY.
3 Reasons Why DNA Is a Great Storage Medium
- It’s really small and dense and can store a large amount of data in a very small space.
- It lasts for a long time as scientists have already retrieved DNA from very old fossils.
- DNA is our genetic material and the world will always be interested in reading DNA. Unlike floppy disk that 10 years from now nobody will be able to look at it.
The growth that has been experienced in Microsoft’s global data centers is truly astounding. It was a challenge to form a foundation for the future and DNA storage gave that new foundation.
Will DNA be the future of data storage?
© 2016 Mehreen Zakaria Lala