71
71- 0
DIY Auto Service: Ignition Systems Operation Diagnosis & Repair
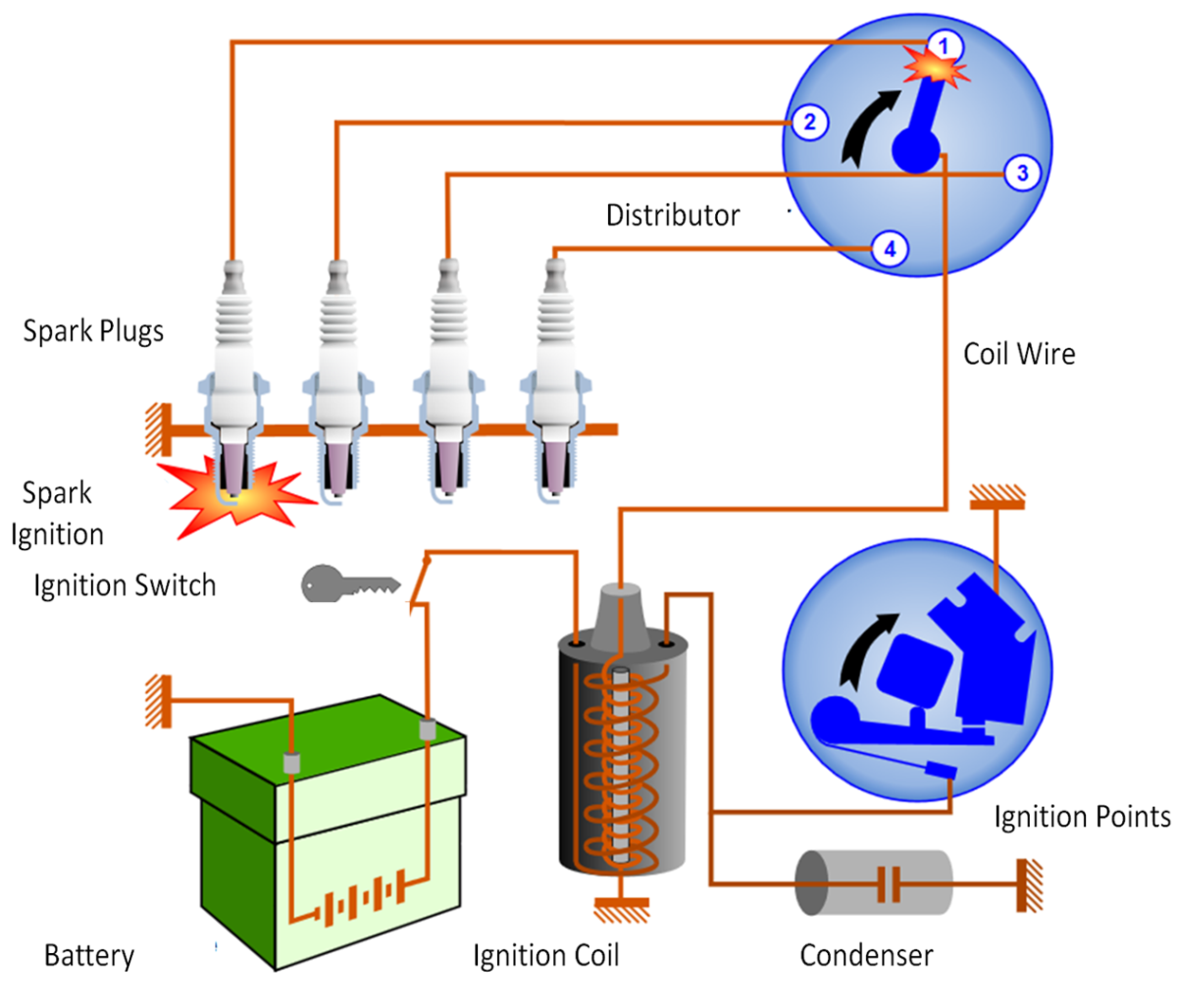
The ignition system consists of ignition coils, spark plug wires, spark plugs, pick-up coils, sensors, and control modules. Problems may cause misfires or no starts.
- 0
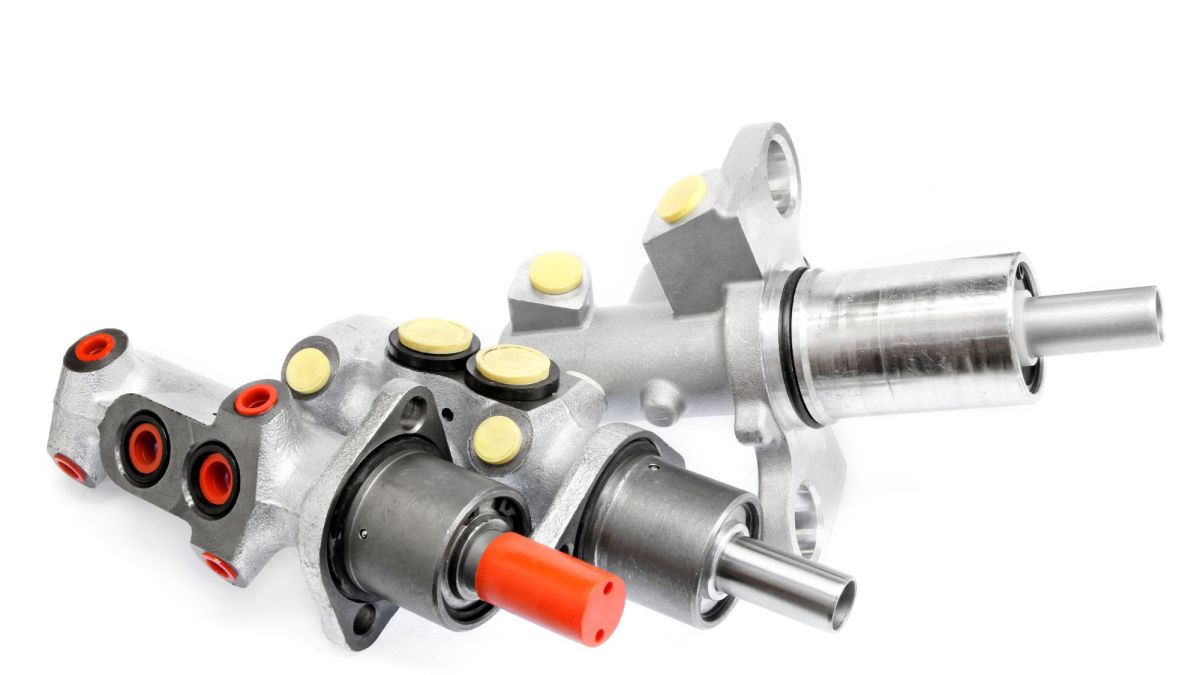
Diagnosis of a Car's Hydraulic Brake System, Including the Master Cylinder
Problems in brake systems could be caused by hydraulic or mechanical issues. Find out if you need to replace the master cylinder and find out how that is done.
- 0
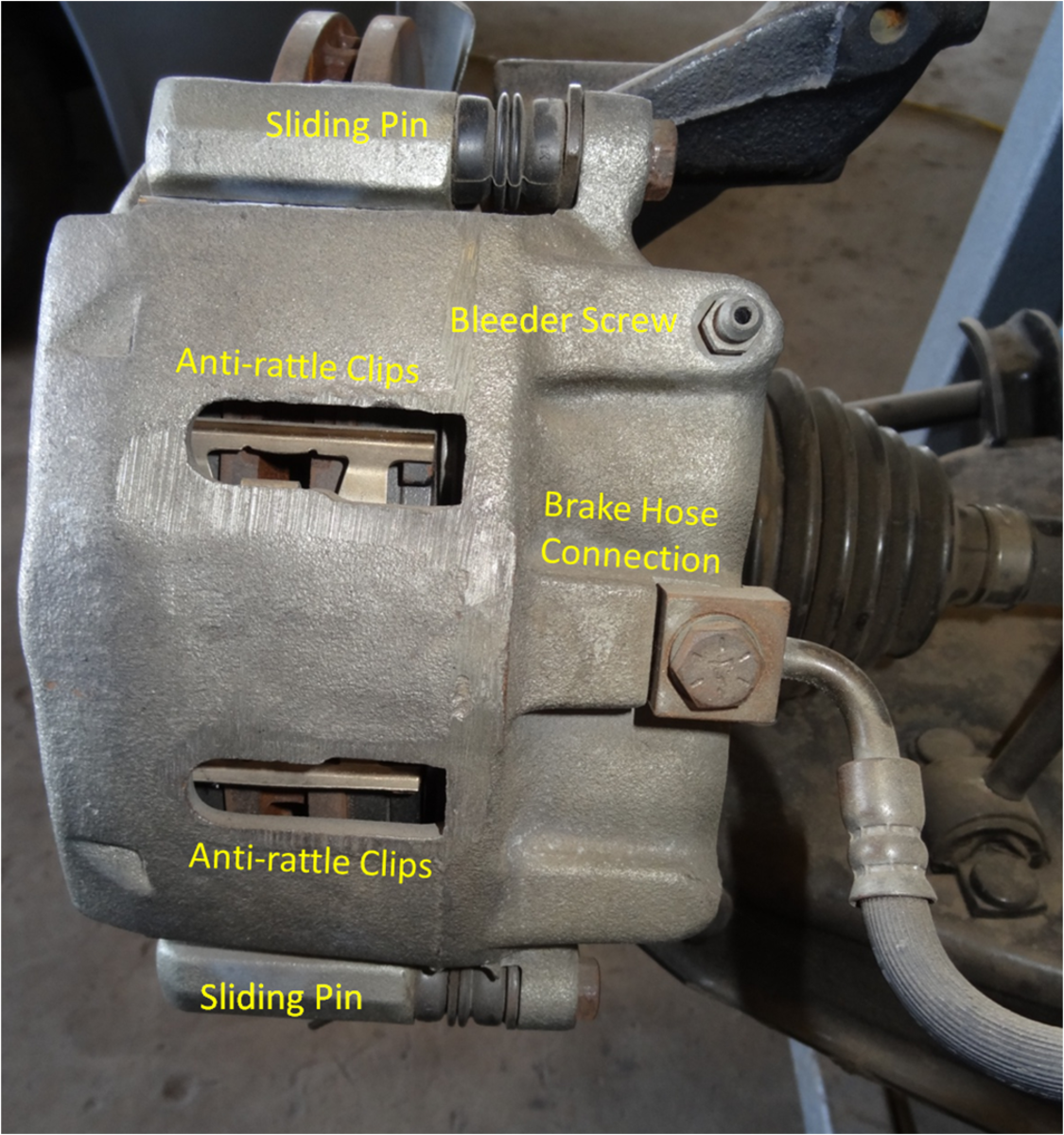
Performing a Disc Brake Job
Learn how to service disc brakes here, including how to inspect the rotor and how to remove and re-install rotors and calipers.
- 0
DIY Auto Service: How Hydraulic Brake Systems Work
Hydraulic brake systems use the principles of hydraulics to amplify the driver's foot power to slow the vehicle. They use Department of Transportation (DOT) rated brake fluid.
- 10
DIY Auto Service: Cooling System Repair and Diagnosis by Symptom
To diagnose a cooling system you have to understand the basic cooling system components. The cooling system takes heat from one location, moves it to the radiator and gives the heat off to the air.
- 111
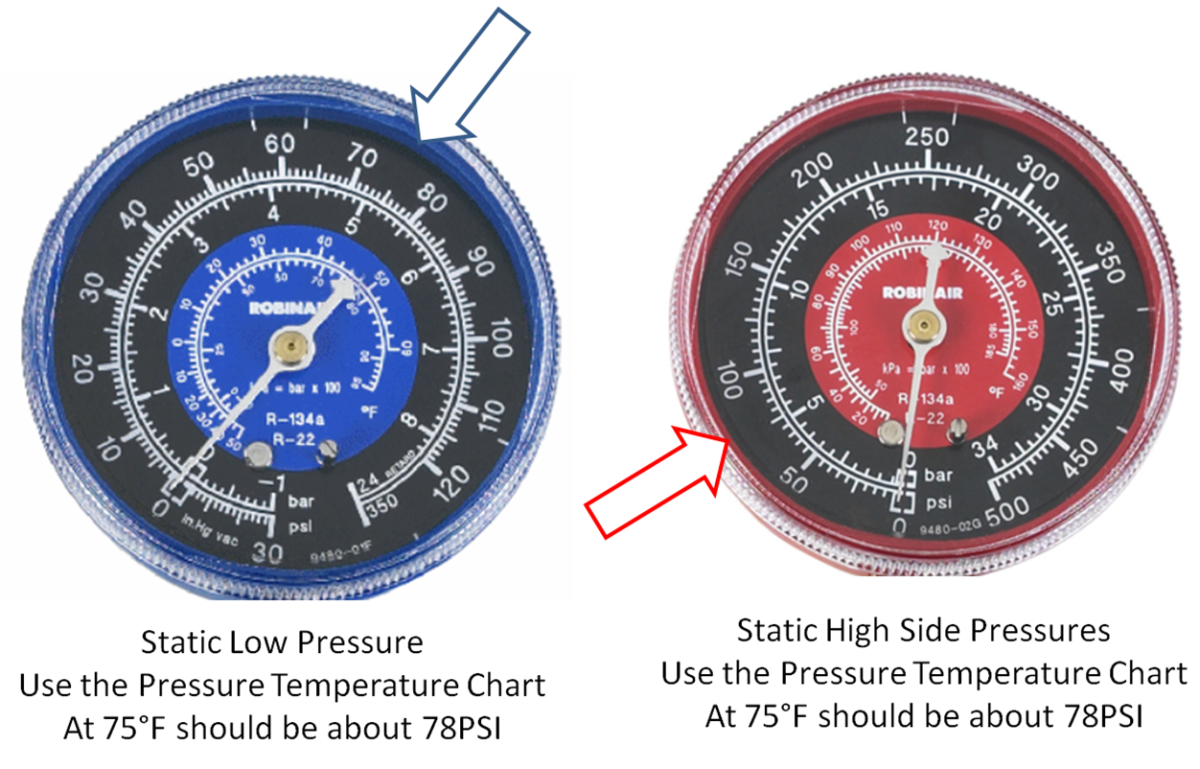
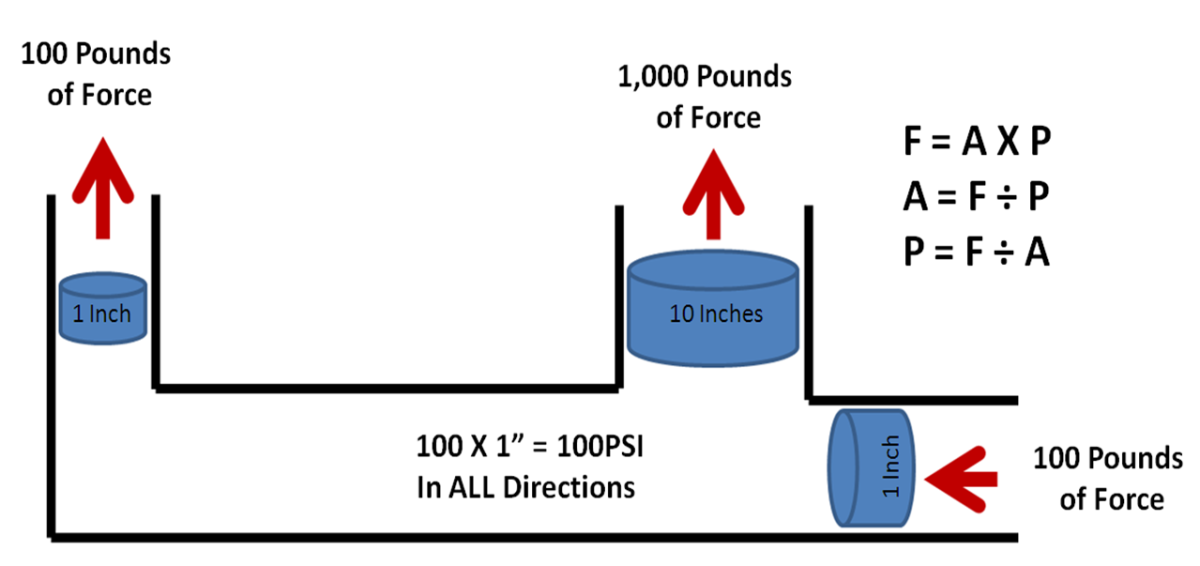
Troubleshooting Car AC Systems (Pressure Readings and More)
One way to diagnose problems with refrigerant levels in a car's AC system is to hook up gauges to the high and low lines, measure the pressure, and note the temperature. Keep in mind that the AC system sometimes has problems that have nothing to do with refrigerant.
- 1
Servicing an Auto AC System and Replacing Components
Learn how to recover coolant from an AC system and recharge it, plus what's involved in replacing AC components: compressors, condensers, evaporators, accumulators, and more.
- 2
TXV vs. Orifice-Tube Car AC Systems: Operation and Diagnostics
AC systems remove heat and moisture from a car's passenger compartment using refrigerants such as R-134a in a closed system. AC systems in passenger cars use either a thermal expansion valve (TXV) or an orifice tube.
- 0
DIY Auto Service: Cooling System Operation and Testing
Cooling systems are one of the most important systems on the vehicle including; water pumps, thermostats radiators and hoses. Antifreeze testing and maintenance can extend the life of the vehicle.
- 0
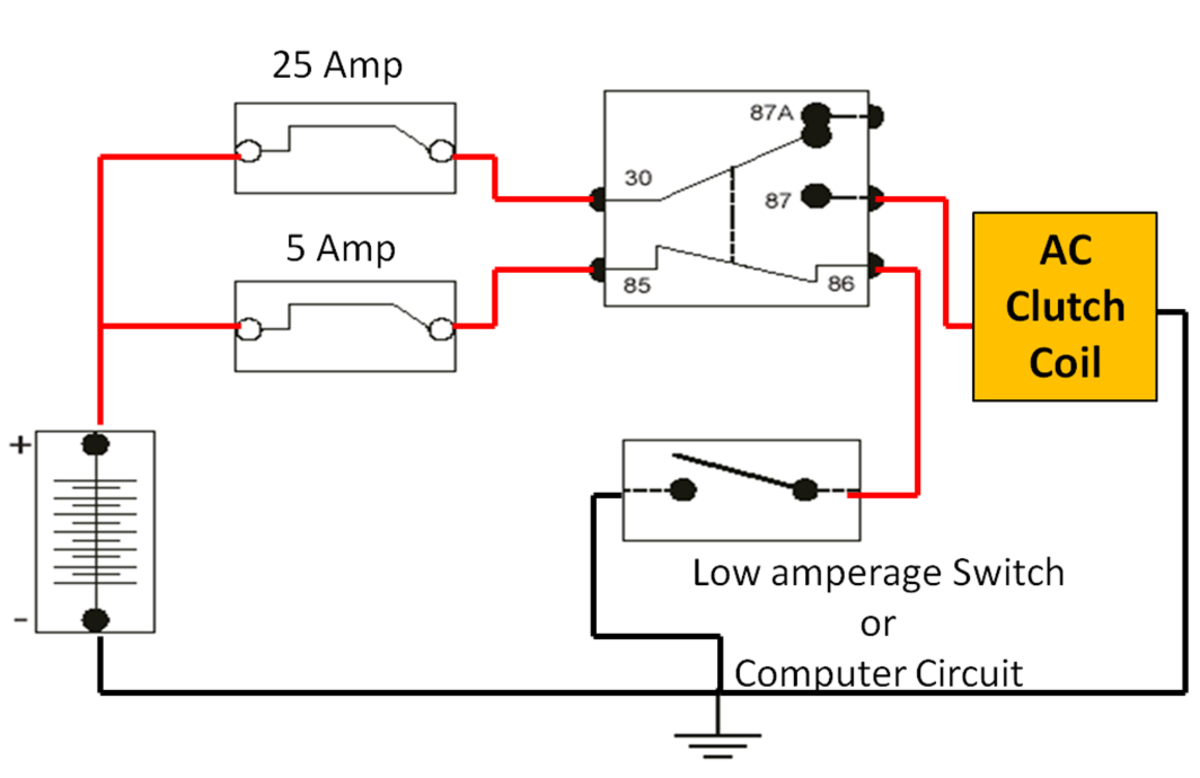
DIY Auto Service: Electrical Switches and Relay Diagnosis and Testing
Electrical switches and relays can control the power or ground to an electrical device. The switches can also be used to be input into a computer system. SPST, DPDT, and SPDT are types of switches.
- 1
DIY Auto Service: Permanent Magnet and Hall Effect Sensor Diagnosis and Testing
VSS, WSS, CKT and CMP speed and position sensors are used by the ECM or other computers to keep track of the position and speed of the crankshaft/camshaft, and the speed of the vehicle and its wheels.
- 7
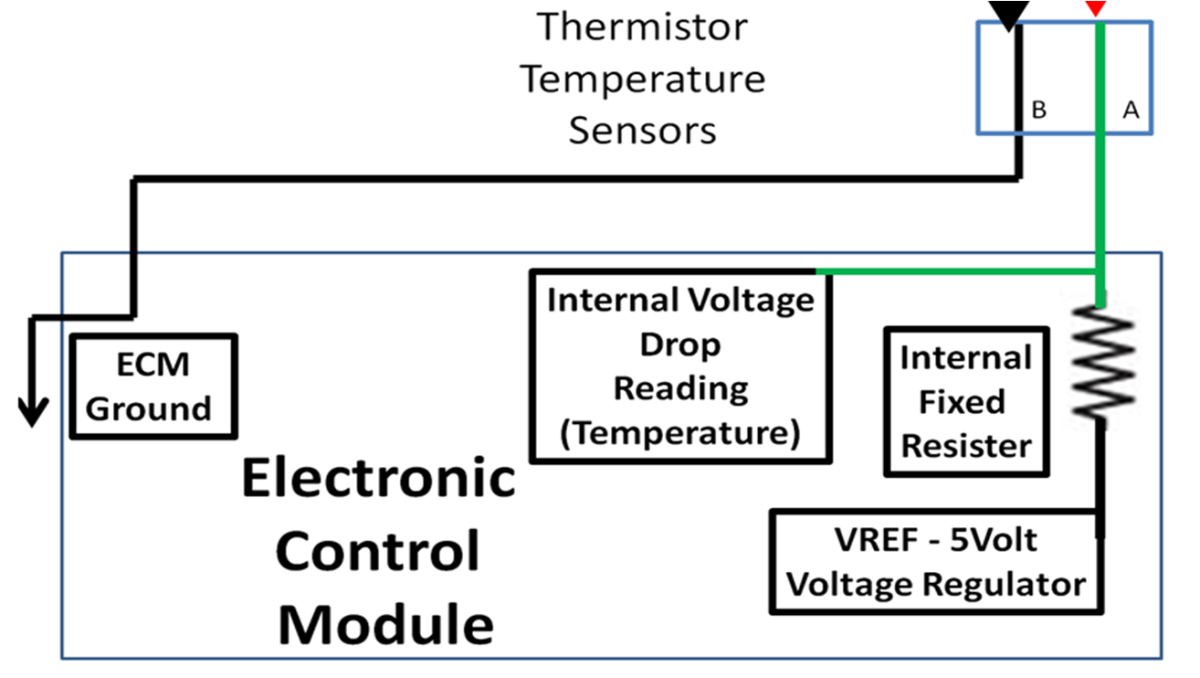
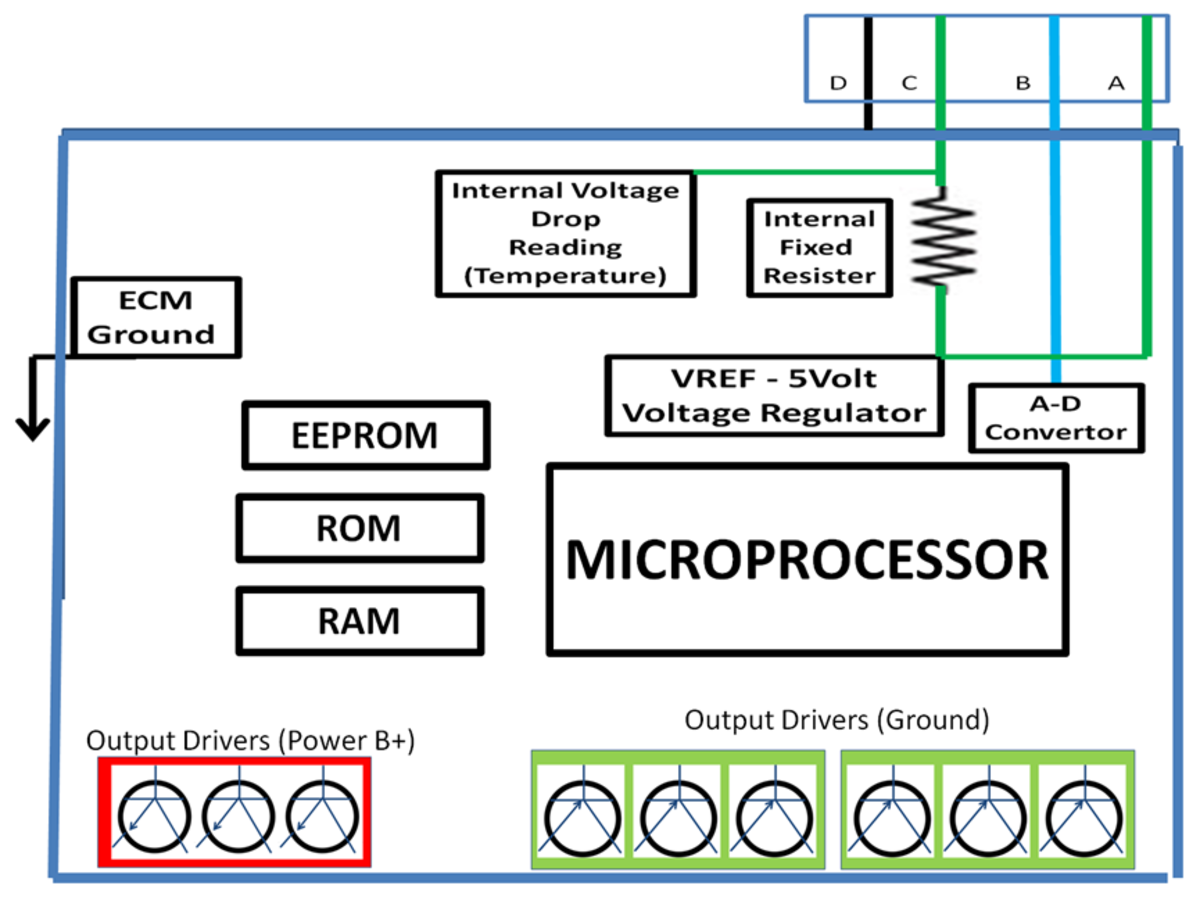
DIY Auto Service: ECM PCM Computer Sensor Diagnosis and Testing
A malfunctioning sensor can cause performance problems, turn on the "Check Engine Light," and fail an emission test. Testing a sensor is usually done with a DVOM. Test the ECT, TPS, and pressure sensors.
- 2
DIY Auto Service: ECM PCM Automotive Computer System Operation
Computer systems operate and monitor almost every system on our vehicles today. Sensors and switches are used for inputs to the computer. Output devices are solenoids, relays, lights, and injectors.
- 3
DIY Auto Service: Automotive Lighting Diagnosis and Repair
Incandescent bulbs are being replaced by light emitting diodes or LED's for longer life and much lower amperage draw. The lights are prone to wiring issues that could affect their operation .
- 0
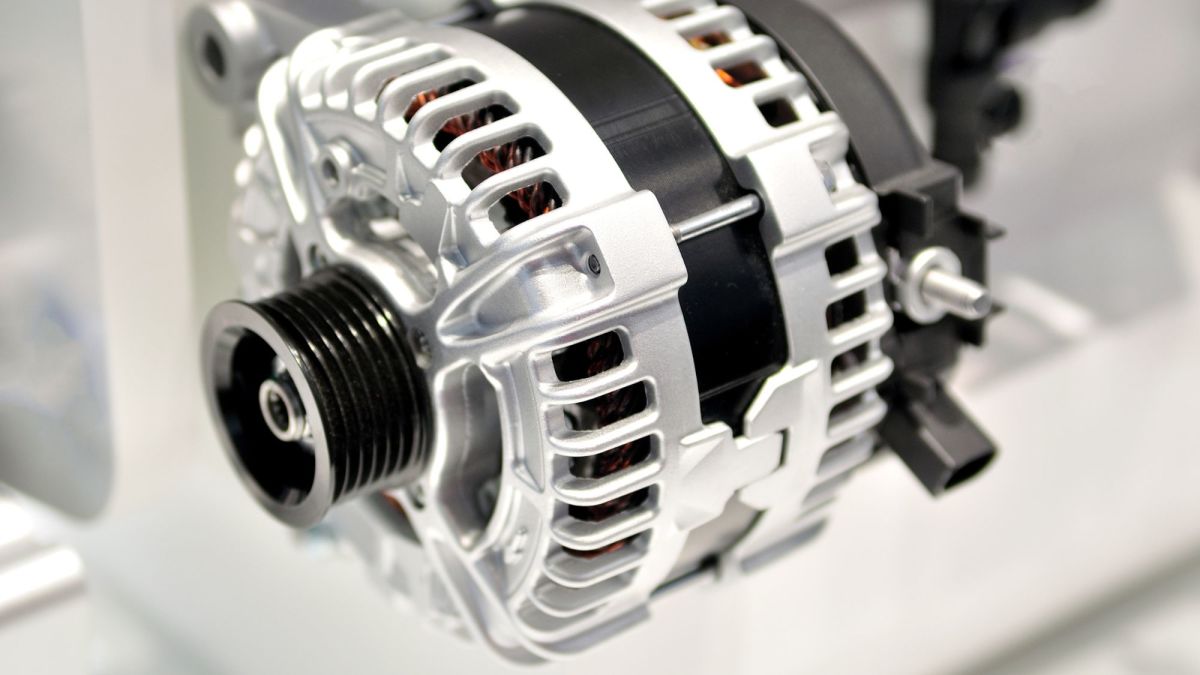
DIY Auto Service: Alternator Diagnosis and Repair
The alternator keeps the batteries charged and produces enough amperage to run the vehicle. Learn how to disassemble an alternator, test components, and more.
- 0
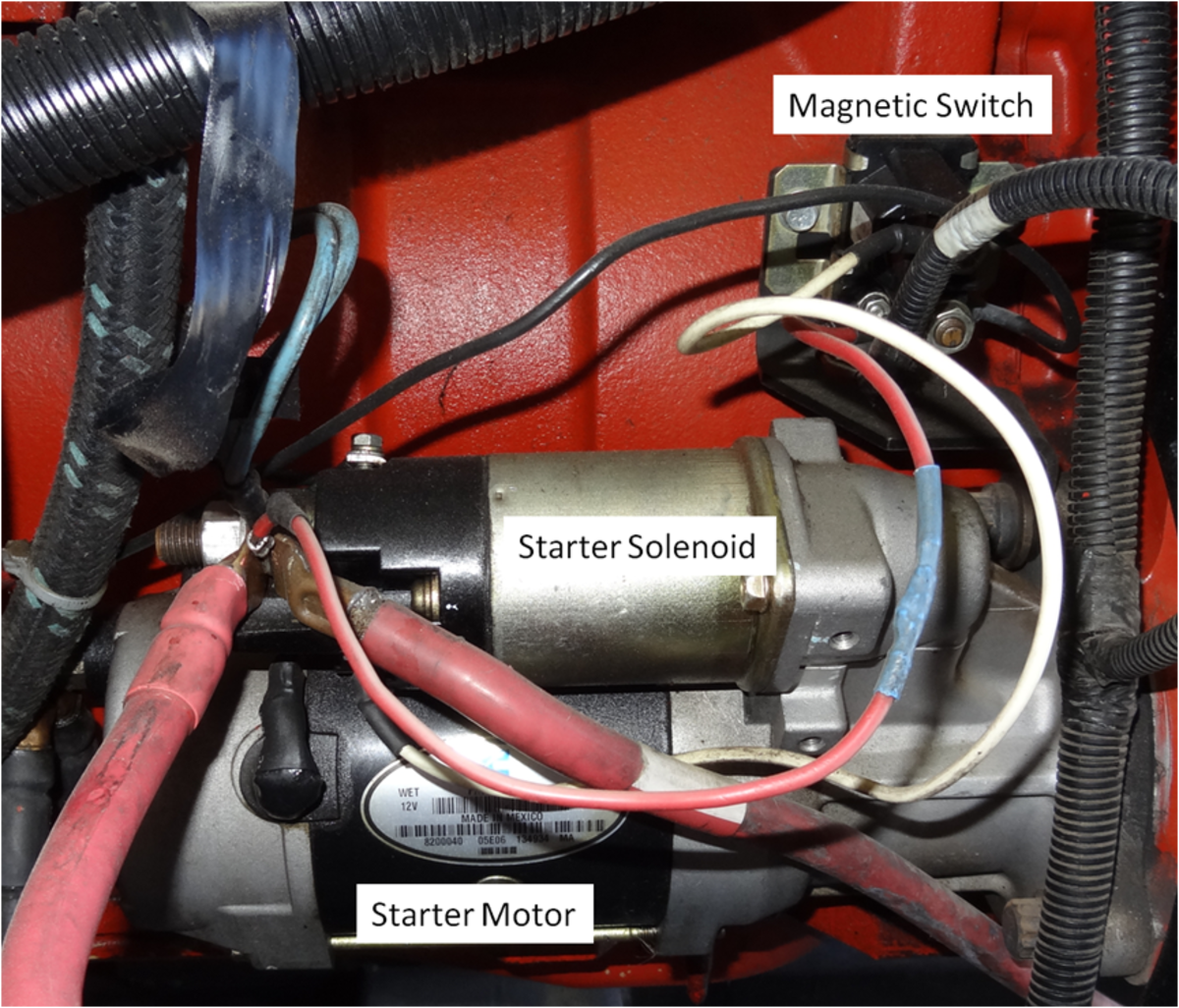
DIY Auto Service: Starter Diagnosis and Repair
The starter uses the battery and battery cables to provide the power to crank over the engine. The starting system can be tested to find a slow-crank or no-crank problem.
- 3
DIY Auto Service: Battery Diagnosis and Maintenance
Batteries are the heart of the electrical system of cars and trucks. Problems can affect the entire vehicle, so car battery testing and maintenance are important.
- 0
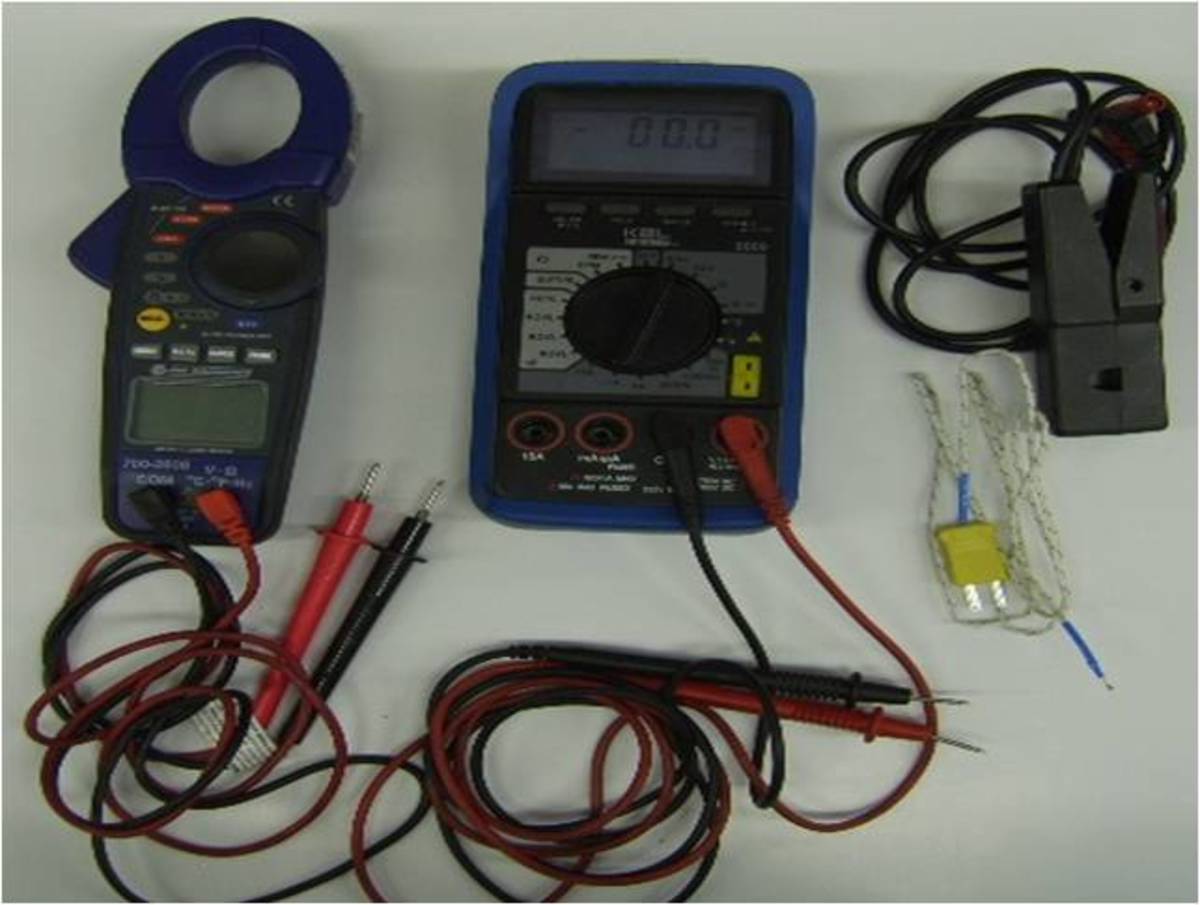
DIY Auto Service: Basic Digital Volt Ohm Meter (DVOM) Electrical and Electronics Testing
Using a DVOM is an important tool to diagnose vehicle components, including batteries, starters, alternators, computer sensors and actuators, injectors, lighting and accessories like ABS and AC systems.
- 1
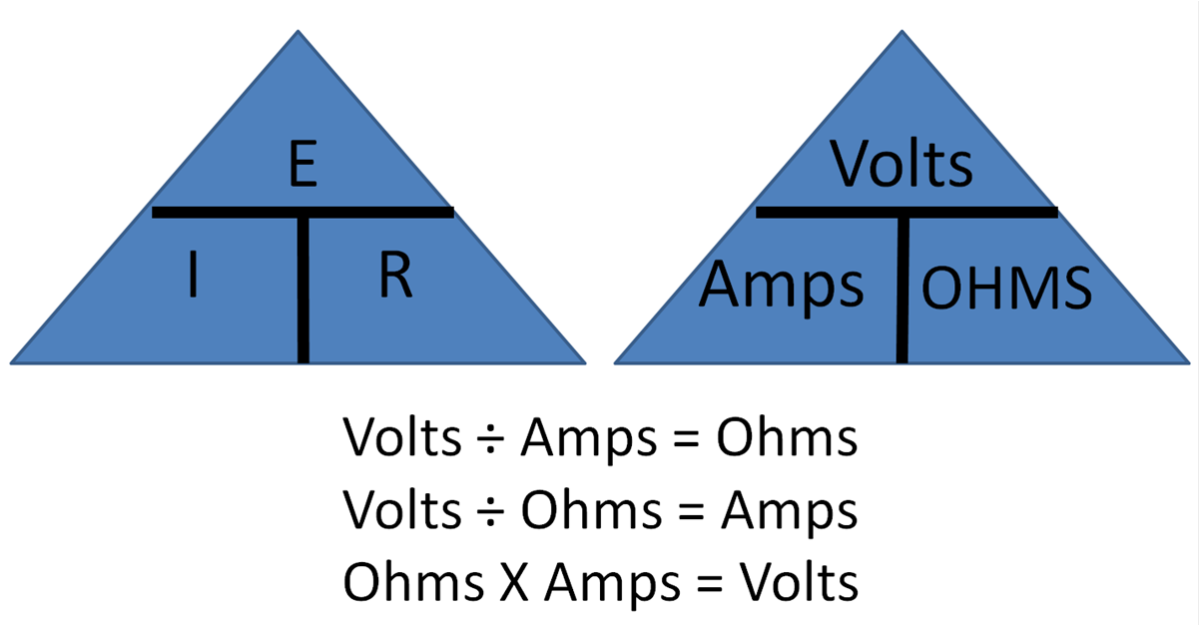
Using Ohm's Law in Basic Electrical and Electronics Testing in Vehicles
Basic electrical knowledge applies to so many vehical components: batteries, starters, alternators, lighting, sensors, actuators, AC systems, electric windows, and computer systems.