All You need to Know about Accountants and their Work (for Business and Enterprises)
The Accounting Profession.
Accountants are no longer just‘ bean counters’ engaged in the narrow definition of balancing the books of account of a business entity but are now regarded as financial management technocrats?
There are two classes of accountants. One class is employed within the organization their role being to assist in the management of the day to day affairs of the businesses and the other class is employed as auditors whose role is to check and ascertain the formers' work according to the needs of business owners. The training however is the same for both accountant and the auditor and involves all aspects of management. Since management is a very wide field, the modern accountant has therefore to specialize in the various management aspects but mainly finance, taxation, costing payroll and auditing.
The Accountant who specializes in finance understands aspects of treasury management. They should be able to manage cash, stock, debtors and creditors, and the interaction of these aspects as they form the working capital of any enterprise. Effective working capital management results in the success of an enterprise. The proper recording and security of the liquid assets of the organization is also an important function of such an accountant.
The Accountant who specializes in costing ensures that the value of goods and services is correctly recorded .They will ascertain that the methods used do not give misleading figures and are consistently applied. The guiding principle, in all cases is the selection of the most appropriate method of determining the correct value. Incorrect or misleading interpretation could lead in wrong pricing policies and hence affect the success of the business enterprise.
The Accountant who specializes in payroll management will ensure that the correct salaries and wages are paid to employees. They will compute the correct overtime, and ensure that absenteeism and leave allowances are in agreement with the employment terms of each employee. They will also withhold the necessary taxes and ensure that they are remitted to the government. They should therefore be familiar with employment and trade union laws.
The Accountant who specializes in taxation matters is expected to be familiar with the taxation matters of an enterprise, to ensure that the correct taxes are paid and the various statutory requirements adhered to.
The nature of the accountants work therefore, will involve the recording, the classification, and the tabulation of the particular aspect. The classification ensures that the information is properly presented to the management of the organization. The recording, classification and tabulation can be done with the aid of accounting software, but the Accountant has to make the decision involving how the items are to be recorded and classified, and ascertain that the tabulation gives the desired results.
These functions involve different levels of skills. The term Accountant, therefore, is a general term, that requires the definition and clarification as to whether it a junior or senior one. The hierarchy determines the significance of the function. That is why there are professional bodies which set the standards of accounting qualifications .They also determine the roles of the Accountant and Auditors in the management of organizations.
Hire Accountants Cheaply at Online Market Places
- Elance | Outsource to freelance professionals, experts, and consultants - Get work done on Elance
Outsource to expert programmers, designers, writers, translators, marketers, researchers, accountants and admin contractors with tested skills.
Accountants as Treasury Managers
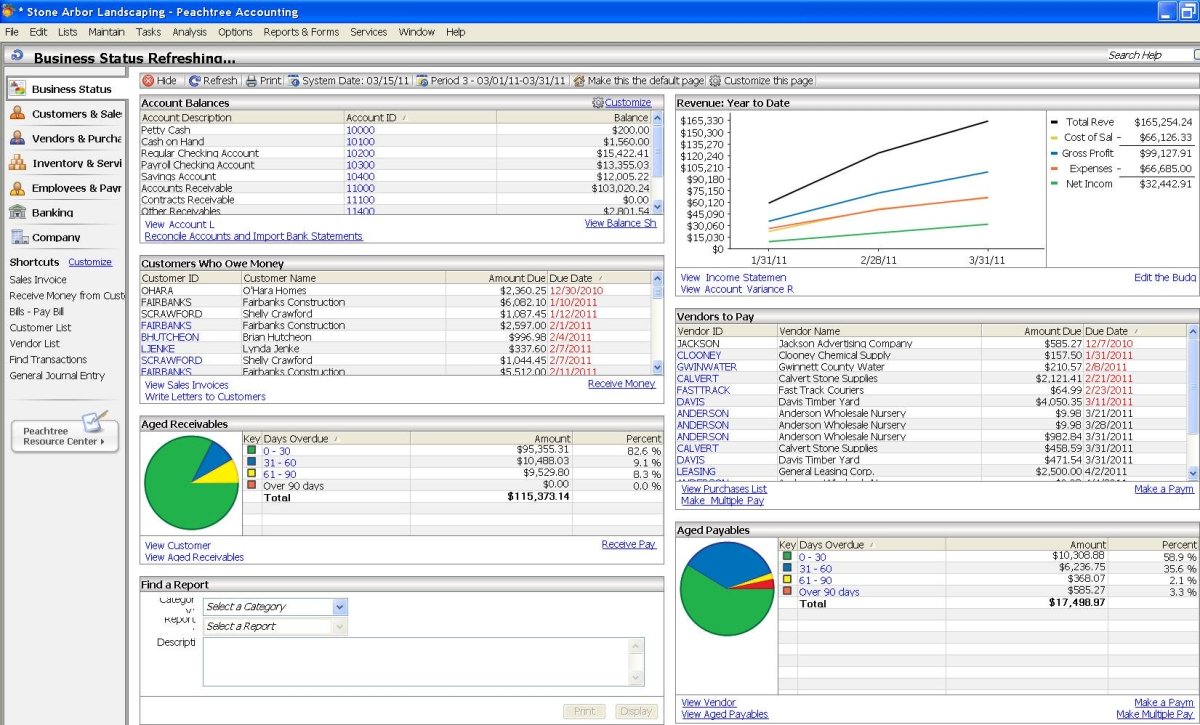
Accountants are employed as custodians of the liquid assets of a business enterprise. They are not just mere keepers of records of the cash, debtors, stock, and creditors, but as managers whose role is to control and plan the use of these assets.
Businesses have to ensure that they make the best use of the assets that are available. This is applicable whether the business is a trading, manufacturing or a service entity. As long as there is cash flowing in and out of the enterprise, the management of that flow is critical to the success or failure of the entity.
The Accountant therefore, must be involved in determination of how much cash is held in the bank. Any idle cash means that the entity is not maximizing the use of the asset. The Accountant will determine the cash requirements of the organization in advance to ensure that it is available when required and at the same time unnecessary amounts are not held.
Cash be held by debtors, or tied up in stocks when it is required to pay for goods and services.
The Accountant's role will be to ensure that funds are collected and deposited from debtors in good time. Thus, they will be involved in setting the trading terms of an organization. It will be the work of the Accountant to evaluate the creditworthiness of debtors to minimize bad debts.
Accountants will also determine that the best credit terms are available to an entity by negotiating purchases from suppliers of goods and services. Failure to settle the financial obligations of the entity in good time may result to the withdrawal of services or credit terms by suppliers of goods and services. Prompt settlement of debts can also enhance the reputation of the business and improve its creditworthiness.
Shortages of cash should be predicted in good time so that bank overdrafts and loans are negotiated in good time. The interest charged for such overdrafts and loans can also affect the overall success of a business. The Accountant should plan to have such facilities with financial institutions at the right time and at the necessary levels. If there is excess cash, it should be invested to earn interest for the firm.
For effective and efficient utilization of the funds of the firm, Accountants should be involved in drawing up the expenditure requirements in advance. Thus, they need to draw up cash flow projections to determine the inflows and outflows of funds.
These functions of planning and controlling the levels of usage mean that the Accountant is not merely a record keeper but a manager of funds. Accurate predictions of the needs and sources of funds will ensure that the operations are not hampered by luck of funds. The Accountant therefore will need to understand the functions of the operating units and departments so as to cater for their financial needs. This will require an adequate communication system between the Accountants and the operating units of any enterprise.
Cost Accountants
The accounting system is the major quantitative information system in every organization. It provides information for use in planning and control of routine operations. It also provides information to managers to enable then to make plans and policies of a non-routine nature. External users like governments, shareholders and lenders rely on accounting information to make various decisions regarding the business enterprise. Financial Accounting provides historical, custodial, and stewardship information, but cost accounting is relied upon to provide planning and controlling information. The Cost Accountant has therefore come to be regarded as a management accountant.
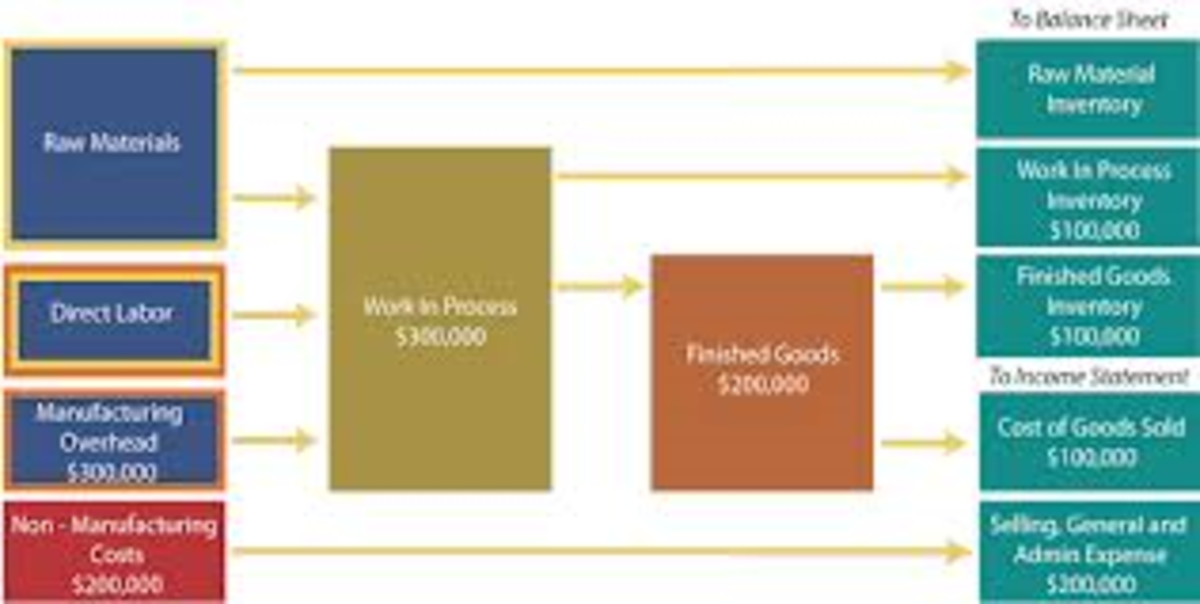
The information provided by cost accounting is used in stock valuation in the determination of the income of business enterprises. This is a specialized form of accounting information. Different methods like job costing, processing costing are used in the determination of the product value.
Operations of enterprises are also planned by using budgets drawn by cost accountants. Budgets set targets which the operating units have to achieve within specified periods of time. Cost accountants provide the information to evaluate the efficiency of the operating units. Pre determined performance targets are used to ensure that the overall objectives of a firm are achieved.
Cost accountants therefore have to understand production systems in order to measure the performance of production departments. This requires that they have the skills to collect production statistics and tabulate them and make comparisons with the set production budgets.
Where an organization may want to introduce a new method of production, it will rely on the cost accountant to determine the effect of the new system, and to compare it with the existing one, to determine the suitability of adapting the new method. Comparative schedules between the new and the old system are drawn and used by decision makers in the firm.
Sales and manufacturing budgets are drawn by cost accountants, with the information provided by the sales and production departments. Comparisons of actual performance and budgeted figures assist organizations in arriving at the set targets.
The requirements in materials, cash and labor have to be 'costed' by cost accountants, to ascertain that the desired results are achieved. Efficient utilization of these production factors is constantly assessed to ensure the desired result is achieved. Deviations and shortfalls can be identified and corrective action taken in time.
Cost accounting information is also used to reward and admonish managers in the performance of their duties. This information allows management to compare group as well as individual performances, determine causes of variations and make corrective actions where necessary.
Cost Accountants are therefore critical in the provision of data for decision – making within the firm. Modern systems of data accumulation and translation like accounting software programs are devised by cost accountants to provide for timely and specific information within organizations. Cost accounting is a challenging task that overlaps many phases like engineering, behavioral sciences, economics, law, statistics and mathematics. It entails complex issues in terms of time, labor and money. The contribution to the success or failure of an enterprise can be determined by use of the information provided by cost accountants.
Tax Accountant
A Tax Accountant is a specialist in taxation law and practice. Taxation authorities normally indicate that one need not be a tax expert to file their tax returns, but there is always the risk making errors by not consulting an accountant; with the resultant penalties and other legal implications. Taxation laws in most jurisdictions are complex and the lay person may spend a lot of time trying to figure out the amount of tax that they should fairly pay. Tax Accountants are involved in the planning of the tax regime that a person or an organization wants to adapt. They ensure that the tax that is paid is computed correctly, and that any tax reliefs that may exist in the law are enjoyed. Proper planning can reduce the amount of tax without breaking the law. A properly qualified accountant undergoes rigorous training in taxation laws before they are allowed to practice. This is critical because failure to advise clients can result in costly tax regimes.
They will advise on what are allowable deductions, and ensure that special circumstances are clearly described to the tax authorities to minimize anomalies. They also ensure that the tax payer takes full advantage of all allowable deductions in computing taxable income.
Tax law in most jurisdictions except the socialist economies provides for chargeable and non-chargeable income. A Tax Accountant will provide advice on issues that may not be clear cut. By virtue of their training they are also aware of what they tax authorities will readily allow and disallow. This will minimize the amount of time spent in filing the correct tax returns.
Taxation laws have provisions for penalties for non-disclosure of taxable income. At times, the disclosure need not be full but adequate. Disclosing too much may not be good for an organization and disclosing too little can be misconstrued as non-disclosure and attract serious penalties to the tax payer.
There are allowable formats of presenting the tax due within a time period. Tax Accountants will be familiar with formats that have no ambiguity and thus reduce the number of questions that may be raised by tax authorities. There are also penalties for not presenting the tax returns in time. The Tax Accountant will be familiar with the times when returns ought to be made. They will also be familiar with any special circumstances that may be provided by the law.
Where the tax laws may not be clear because of the unique circumstances of a taxpayer, a Tax Accountant should be able to ensure that the ambiguity in the law is not used to the disadvantage of the tax payer. In some circumstances, certain decisions may give rise to potential tax in the future. It is the role of the Tax Accountant, to ensure that such issues are pointed out to the tax authorities.
Due to the experience of dealing with different tax matters, a good tax accountant should be able to reason with the 'Taxman', and even refer to case law where it may not be apparent. Thus act like an advocate for the taxpayer, without resulting to exorbitant legal fees that may be charged by lawyers.
The Payroll Accountant
Wherever services are rendered by employees it is necessary to ensure that the amount paid is computed accurately. The computation of such services as wages and salaries are the functions of a payroll accountant. In addition to the usual training in accounts, the payroll accountant will need to be familiar with labor and trade unions laws for effective performance of his duties.
Terms of employment determine the mode of payment of wages and salaries. The terms could be weekly, monthly or any other periods that may be agreed between the employee and employer. Payments could also be on piece rate where, employee is paid on completion of certain jobs. The method of computation could be determined within the terms of employment, for example the computation of overtime, and leave allowances. These terms are specified within the letters of appointment, or union agreements which must be done by the payroll accountant. Accurate interpretation is necessary so that labor disputes and staff dissatisfaction is avoided. It is therefore necessary for the accountant to be able to interpret employment terms correctly, so that he can pay the amount specified. Erroneous computation can lead to losses to the organization, cause labor disputes and even costly time consuming lawsuits.
Where wages and salaries have to be recovered from third parties, the payroll accountant must ensure that the total cost incurred is recovered or charged .There are also government regulations that must be followed in the determination of the amounts paid to employees. This could be in form of payroll taxes, and other statutory deductions.
Employees could also be eligible to different rates of pay and allowances based on their performance, for example production bonuses and acting allowances. These therefore are not regular, but depend on predetermined outcomes or results. It is the role of the payroll accountant to ascertain that the special conditions pertaining to such payments are incorporated in the payroll.
After computation of wages and salaries, the method of payment could also be determined for example payment in cash from cash in hand, by cheque or direct remittance to the employees’ bank account. Timely remittances of employee’s wages and salaries will minimize work interruptions where employees have to disrupt their duties to sort out their wages and salaries issues.
Strict compliance with labor and taxation laws will also ensure that there are no penalties for wrongful computation and late payment of employee deductions. Where new employees are hired, the payroll accountant will need to ascertain that, such employees are promptly incorporated in the payroll of the organization and details of their employment obtained to comply with labor and trade unions laws.
Where employees are terminated, for various reasons, it is the payroll accountant who must compute their severance pay according to the terms set out in their letters of appointment or union regulations.
The payroll accountant is, therefore, a critical person in the proper operations of an entity. Thorough understanding of other subjects, in addition to accounting and finance is imperative. There is also the need to be up to date with the latest developments in human relations laws at all times.
All You need to Know about Accountants and their Work by Kimkay is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 3.0 United States License.
Based on a work at hubpages.com
.