How to Plan Knowledge Management in Organisation?
Knowledge Management
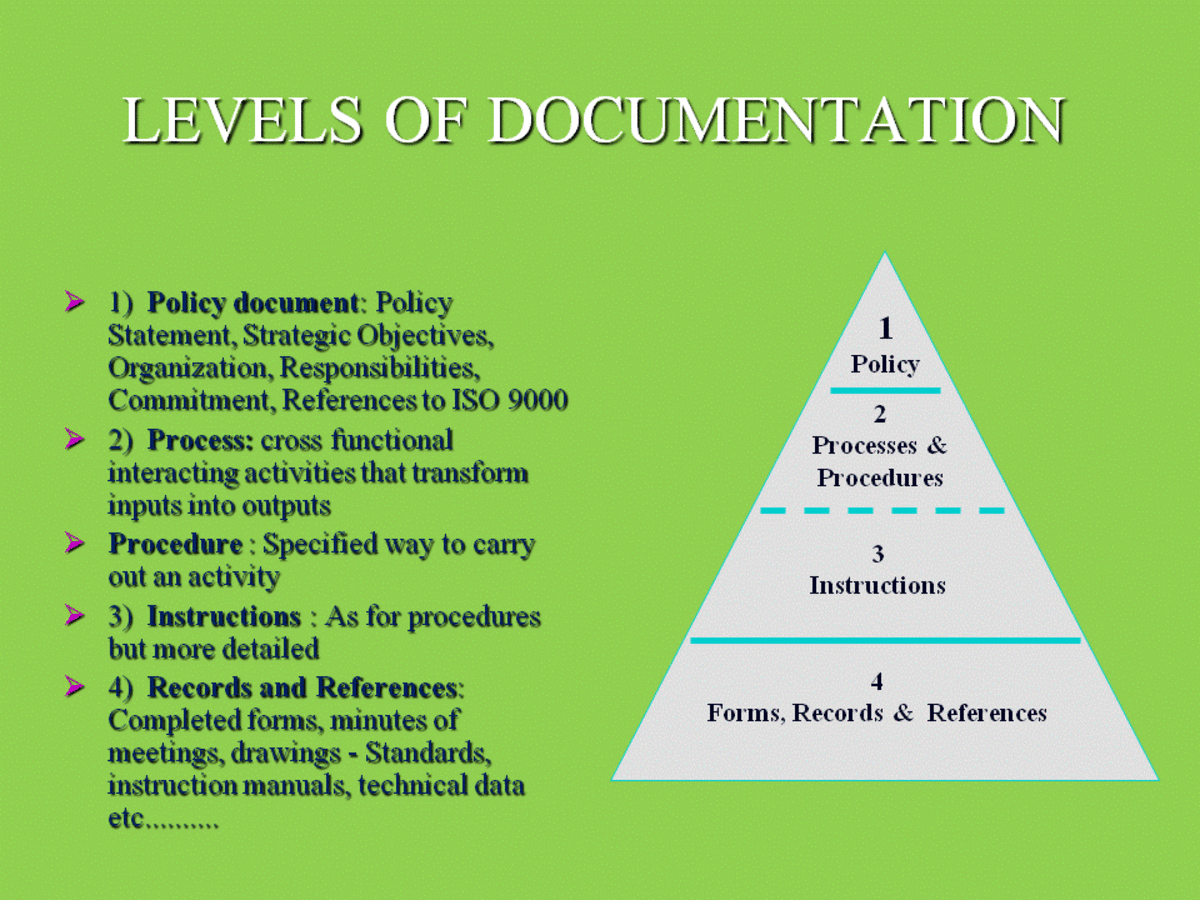
Documentation Core of Knowledge Management
Introduction:
As the amount of documents continues to grow within the organization, challenges with its creation, management, and distribution continue to grow as well. As we’ve moved into the digital age, our organization is facing several challenges with document creation, management, and distribution—for both paper-based documents as well as digital documentations
What do we need?
ë Organizational rules for the DMS.
ë Unified Data Storage (physically – virtually).
ë Efficient document retrieving process.
ë Security for information assets.
ë Deal with mixes of old-fashion data.
ë Reliable IT solution
What we want to do?
DMS Rules:
Standard templates (structuring) for business documents
Allocating a location for Physical and Digital assets
Procedures to be followed for creating, sharing, retrieving and disposing documents
Procedures for reviewing and updating documents-
Document Lifecycle processing
Physical Data Storage, in addition Digital one.
Well defined and titled documentary categories
Filing system ports and management practices
Dynamic system for out-of-date documents
Capturing feature for documents
Retrieving process ..
Create a file location list.
Create records with well criteria (index)
Digital preview feature
preserving original data against series of actions for the modified copies made by users.
Security ..
Lockable store .
Insure security level for the users to access the SharePoint.
- Insure that content of document is encrypted
identifying the accessed point.
Making accessible only to who have the required encryption key.
- Insure metadata extension format ( images, texts, VCD and Audio)
- insure regular documents backup
Old fashion data..
Sorting topics accordingly.
Capturing (Images- Texts … etc..)
Locating and defining (a Historical) tree branches.
Setting Physical and digital document lifetime
Why we want to do it?
unify archiving standard and processes .
Improve business handling of physical and digital documents.
preserves data assets and reduce documents loss.
ensure efficiency and consistency for preserved and updated documents
facilitate searching processes.
- Paper and time reduction cost.
Save space for the store.
Why Record Management?
Record management is responsible for an efficient and systematic control of:
• Creation;
• Receipt;
• maintenance,
• use and disposition of records
• including the processes for :
• capturing and maintaining evidence of and information about business activities and transactions in the form of records.
Common approaches:
Highlighting on Physical & Digital record which are merged under the Record Management system (RMS), which has diverse solutions in order to be implemented such as:
v Document management system
v Content management system
R.M.S methodology
• location
• Where will documents be stored? Where will people need to go to access documents? Physical journeys to filing cabinets and file rooms are analogous to the onscreen navigation required to use a document management system.
• Filing
• How will documents be filed? What methods will be used to organize or index the documents to assist in later retrieval? Document management systems will typically use a database to store filing information.
• Retrieval
• How will documents be found? Typically, retrieval encompasses both browsing through documents and searching for specific information.
Security
• How will documents be kept secure? How will unauthorized personnel be prevented from reading, modifying or destroying documents?
• Disaster Recovery
• How can documents be recovered in case of destruction from fires, floods or natural disasters?
• Retention
• How can documents be preserved for future readability? Archiving is the removal from the active repository of documents and related metadata that have, by organizational definition, reached the end of their active lifespan, and are required to be stored, or archived, in a separate area. Usually archiving entails movement of documents, whether paper or electronic to a separate storage facility, be it an archival warehouse, or a near line or offline storage device.
• Distribution
• How can documents be available to the people that need them?
• Workflow
• If documents need to pass from one person to another, what are the rules for how their work should flow?
• Creation
• How are documents created? This question becomes important when multiple people need to collaborate, and the logistics of version control and authoring arise.
WHY DOCUMENT AND/OR CONTENT MANAGEMENT SYSTEM?
Simply, this is the formula :
Time +Cost +Resources = investment
What is Our objectives ?
ë Building up unified Data Storage.
ë Implementing an initial step toward MIS.
ë Investing well in infrastructure and return on investment.
ë Accomplishing the competitive advantage through improving and enhancing cost and productivity efficiency.
ë Control over un-managed data to enhance capturing, storing, distributing, , workflow and sharing documents.
ë Insuring a progressive future to implement a content-rich business application.
ë Create the awareness of management information system MIS for KGL investment employees perspectives.
ë The orientation toward Digital Asset Management ( Enterprise Content Management).
What is Document management system?
• Document imaging
Is used for entering, storage and managing electronic images of paper documents that have been previously scanned, faxed or e-mailed.
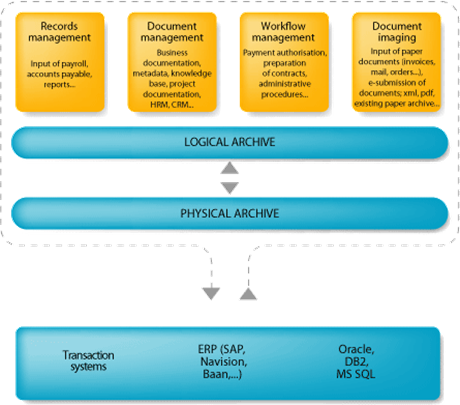
DMS: efficient business documentation operation comprises following elements:
DMS
• Document management
comprises technological solutions that enable:
• search
• access
• protection
• management of documents
Documents are entered into the system by scanning paper documents or import electronic documents created with applications for electronic tables editing or text editing, images, audio/video clips creation and editing, etc.
DMS
• Output management (COLD - Computer Output to Laser Disk / ERM – Enterprise Report Management)
Contains technological solutions for:
• electronic capture
• indexing
• permanent storing of formatted output data (printed pages) in electronic format
In this way, companies have electronic original documents provided in exactly the same format as those printed on paper and sent to the customer.
DMS
Automates the flow of documents and information in the work process whereby we can precisely define working methods with regard to employees and their tasks, their input and output values.
At the same time the automated process enables the company to create business policies and strategies for the management of workflow, control and communication in the completion of work tasks.
DMS
• Logical archive and physical archive
are used for document and information storage; a physical archive stores actual documents, while the logical archive stores their meta-data. The physical archive also ensures that these documents can be accessed and protected.
What is E. content management sys.?
Enterprise content management (ECM) provides a platform to house unstructured content and deliver it in the proper format to multiple enterprise applications. Unified ECM provides the full array of content management functionality, including:
- document and imaging management;
- Web content management;
- digital asset management;
- and records and retention management—on one platform.
Advantages
The unified approach yields much greater return on investment (ROI) in just a few years, especially if more than one application is used. Consolidating the overall architecture on a single code base, security model, and API eliminates “Band-Aid” integrations, leverages a common IT infrastructure, and minimizes application development and support costs, thus lowering costs; improving user experiences; and enabling simple upgrades, maintenance, and training.
What do we really need?
If we assess the document flow and stored at present, we can observe that it is still minor in comparing with future expectation for handling and retrieving documents.
In the other hand if we take in account the financial resources to implement the ECM, that will exhaust - at present - our financial resources because of the high price. So I think that implementing the e-DM system will be quite fear for our business interests. In coming future we can develop our archival system project to reach the ECM system.
The System


Knowledge Managment in Hub Pages
- About Knowledge Management
Knowledge Management is the science whose ultimate purpose is to come up with smart ways to collect, to gather, to explicit and to spread Knowledge among a community of people. Companies have started to... - Knowledge management
What is knowledge management? It is : .the acquisition, sharing and development of knowledge .the response to the increase in new technology .a strategy to flatter forms of organizational structure .replace... - HR Practices - Impact of Knowledge Management in HR ...
The best hr practices are always concentrated on knowledge management. In recent years, Knowledge Management has emerged as one of the prime concerns of human resource Management (HRM) system. ... - Knowledge Management - 8 Step Method
Knowledge Management (KM) is the term given to the process of capture, refinement, aggregation and sharing of data and information between employees, departments, subsidiaries and partner organizations to... - Business Ethics and Knowledge Management
Business managers and educators classify knowledge according to the answers they generate to the questions: What, Why, Where, When, and How. Knowledge management is the judicial application of these knowledge... - Benefits of Knowledge Management
To really understand the benefits of knowledge management it's important to understand exactly what knowledge management is. The term is just over ten years old, and refers to the ability to understand and... - Small Business Knowledge Management
Small businesses use knowledge management every day, perhaps without even realizing that they're following knowledge management processes that are much more formalized in many larger companies and... - KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT-A CASE STUDY OF WALLMART
Practice of Knowledge Management; Case Study of Wal-Mart Inc Wal-Mart is an American multinational corporation running a chain of large discount departmental stores and warehouse in several countries.... - Knowledge Management Process
Knowledge management is the concept of taking data and turning it into useful and applicable knowledge in a business environment. There is no one specific way that this done, and there's really no one...