GOOGLE PANDA UPDATE | 2014

Google Panda Update
Google Panda Update for 2014: Panda Algorithm Explained and Analyzed. Discover what content Panda attacks and how to improve your search rankings on Google.
____________________________
Google Panda first hit the headlines in 2011 and has been a major news story in the world of search engine optimization (SEO) ever since. Each Google Panda update since the original release sends webmasters to online forums to discuss changes in search results rankings.
Google Panda refers to a series of updates in the Google algorithms which affect webpage ranking on search engine results pages. The first roll-out of Panda was on February 24, 2011. It began like an oceanic earthquake that rose to tsunami proportions, and continued to shake websites in the aftershocks as subsequent Google Panda updates and/or data refreshes were implemented almost every month until March 15, 2013.
An update is an actual change to the algorithm; a refresh applies the algorithm to data received and stored when Google crawls the Web.
At Search Marketing Expo, June 12, 2013, Google's Matt Cutts stated that Panda is still doing a data refresh about once a month, but the refresh is now rolled out over a ten-day period and has a smaller effect than the previous updates. He said they are
"relatively small compared to the normal index flux."
Google Panda
When Panda first rolled out, the change in Google's formulas for producing search results affected over 20% of websites, according to webmasters' estimates. In simple terms, many websites that were ranking within the first 10 search results for specific keywords have been pushed down to number 200 or 300 on the search results hierarchy.
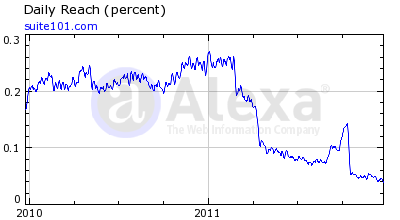
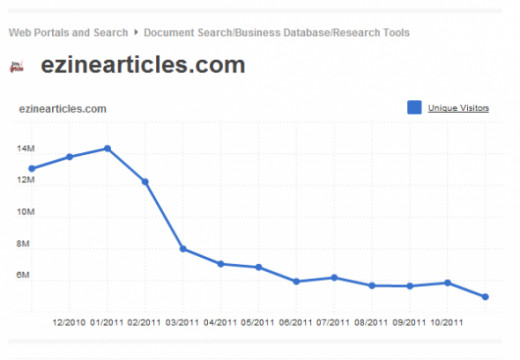
The abrupt changes in traffic to websites sent from Google searches has devastated many website owners, some of whom have watched their incomes drop by as much as 75% since Panda began. Suite101.com, a popular article site, reported traffic from Google was down by 94%, one week after Panda began. Other article sites such as EzineArticles.com, DemandMedia.com, eHow.com, and business.com also suffered severely from the implementation of Panda.
Yahoo's AssociatedContent.com was wounded so badly that it deleted over 75,000 webpages, deleted the URL, and reinvented itself as Voices.Yahoo.com.
Search engine optimizers originally called the Google changes 'Farmer', because so-called content farm sites were particularly hard hit. In its defense, Google software engineer Amit Singhal issued this formal statement on the Google blog in May, 2011:
"The Panda algorithm change has improved rankings for a large number of high-quality websites."


What is Google Panda?
Google Panda Defined:
"Google Panda: It's about Shallow Content and Duplicate Ideas."
– Writer Fox™
At Google, Navneet Panda is a software engineer who was instrumental in developing the Google algorithm change. The word, Panda, was used in-house at Google as a code name, of sorts, for the algorithm project – and then the name was leaked to the website industry.
The short-take is that Panda was developed to identify shallow content in a way that had not been possible before.
Google Panda Mauls EzineArticles.com

Google Panda Targets
Shallow Content.
Panda Updates
Panda updates and data refreshes all target shallow content. Website Content Writing is the critical element in success or failure under Panda.
Everyone has experienced the frustration of landing on webpages after a Google search that are full of non-information-text, text that rambles on and on and really says nothing. These pages are the primary target of Panda.
Not long ago, the SEO community was scrambling over duplicate content issues. The Google Panda updates may be described as dealing with duplicate idea issues.
Panda SEO involves removing shallow content from your website. Google Panda determines shallow content by identifying:
1. lack of complete or comprehensive information
2. writing that is devoid of expertise and/or enthusiasm
3. articles too short to be meaningful for the specific search query
4. only one-sided viewpoints
5. webpages full of language and/or factual errors and without editing
6. ordinary information
7. low quality compared to print publications.


Free Website Magazine
Stay informed with a constant source of information for e-commerce, online marketing, search engine optimization and website design with a free subscription to Website Magazine.
Your subscription to this print magazine, including postage, is free for U.S. addresses. Not only that, when you subscribe a tree will be planted in your name by ReplaceATree.org.
Get your free subscription to Website Magazine


How to Survive Google Panda Updates
What can a website owner do to counteract penalties from Google Panda and to improve search rankings under Panda pressure?
1. provide in-depth information
2. choose passionate writers who are experts for the topic
3 create longer articles on a single webpage
4. include both sides of a story
5. carefully proofread, double-check facts, wisely edit, and NEVER, EVER publish spun content
6. produce interesting information showing insight and analysis
7. write content for a webpage as if it were for a magazine
Google Panda Devours Spun Content
Spun Content is the taking of original, creative text and rewriting it to appear as an original document. Spinning content can be done manually using a thesaurus to find alternative wording; but, in this day and age, it is most often done by software.
Some content writers in India – to the complete discredit of the magnificent producers of English language website content from India – are notorious for offering spinning content services for as little as $1.00 per 500-word article. To a human reader of such content, the software produces such ludicrous word substitutions as these terms for 'Long Island, New York':
extended Island, New York
lengthy Island, New York
Not only does spun content make no sense to a human reader, but it is almost always riddled with the grammar and syntax errors that Google's Panda algorithms target.
Here is an example of spun content on this topic, which was taken from Wikipedia.com, put through spin software, and posted on Squidoo.com as an original article:
"Google Panda is a change to the Google's seek results ranking algorithm that was first issued in February _ 2011_
a. The change directed to smaller the rank of 'low-quality sites', and return higher-quality sites near the peak of the search outcomes."

Panda Is About the Total Website
Google Panda Is about the website, not just the webpage.
Panda, more than at anytime in the past, analyzes an individual webpage for search results based upon the entire website on which the page appears. Don't confuse this with PageRank; Google PageRank is only about incoming links to a site or page.
The Panda update specifically demotes websites which:
1. have redundant information on several webpages
2. do not appear to be authorities on the topic
3. do not seem to be trusted by users
4. develop content and page titles only around keyword presumptions
5. are part of a network of sites
6. are riddled with ads (especially above-the-fold) that interfere with the content

Make Friends with Google Panda Updates in 2014
Webmasters can improve search rankings relative to Google Panda by:
1. consolidating similar articles into one comprehensive webpage
2. removing low quality pages
3. improving trust and authority status with branding
4. developing content primarily for users, while still using keywords
5. consolidating Web properties
6. re-positioning and limiting ads on webpages
The video below was released in September, 2013, by Matt Cutts, Google Head of Search Quality. In it, he explains how the Panda Updates will work in 2014 and what webmasters can do to improve their Panda evaluations.
Google Panda and User Feedback
Google Panda is also about user feedback.
User feedback is used in the Panda algorithm. Google is factoring the amount of attention a webpage receives from social bookmarking sites, tweets, and especially from the newly launched Google+ site.
Google also uses information from its feature that allows users to block sites from personal search results pages.
In short, webmasters who have avoided social media will need to enter social sites and become social media marketers.

Google Panda Updates in 2014
In 2012 – 2013, Panda Data Refreshes were coming at about 30-day intervals with the last refresh occurring March 15 - 18, 2013. Google's Matt Cutts announced on March 12, 2013, that Panda refreshes would no longer be rolled out manually, but would be on a continual basis, coordinating with the main Google algorithm.
What this means is that webmasters won't always know when they have been attacked by Panda.
The data refreshes will still be made about every 30 days in 2014, but they will stretch over a ten-day period so the effects will not be as noticeable to webmasters. Panda updates will continue as the main Google algorithm itself updates.
Webmasters still failing under Google Panda algorithms have increased their spend for pay-per-click advertising as they struggle to bring traffic to their sites. Whether or not searchers believe they are experiencing better quality search results is still debated.
As Google Panda has matured, one thing is certain: webmasters and Web content writers who ignore this Panda bear will be ignored by the Google search engine rankings.
Google announced in March, 2013, that a new change to Panda's younger brother, the Google Penguin Algorithm, "will be one of the most talked-about updates of the year." That update was rolled out on May 22nd and affected 2.3% of search queries in the English language.
The year 2014 will continue as a year of major Google ranking house-cleaning.

Everything You Need to Know about SEO
This is THE book for SEO reference. The first edition sold out and this, the second edition, was updated and published in March, 2012.
"This 500-page book is a comprehensive guide to search engine optimization strategies and tactics written by four SEO experts: Eric Enge, Stephan Spencer, Rand Fishkin, and Jessie Stricchiola." This great book has comprehensive information on Keyword Research and Keyword Strategy.
How To Overcome Google Panda
Related Content
SEO Resources
Learn more about search engine optimization from these articles.

Read a systematic approach to SEO in this comprehensive, free How-To Guide. SEO is explained with definitions, examples, videos and tips for high rankings on search engine results pages:
____________________________

Read about the Google Penguin algorithm and what to do if your site has been penalized:
____________________________

Learn how to write content for your website with search engine optimized copy in this guide to writing online copy:
____________________________

Find out about Google's duplicate content penalty and how to avoid receiving one:
____________________________

Learn how to optimize press releases for search engines.
____________________________

Read over 100 quotations about the World Wide Web, including quotes about SEO and quotes from the founders and employees of Google.com:
____________________________

Want to earn money working online? Join the Writer Fox Writers Den.
Connect with Writer Fox™ on Google+.

Share - don't copy.