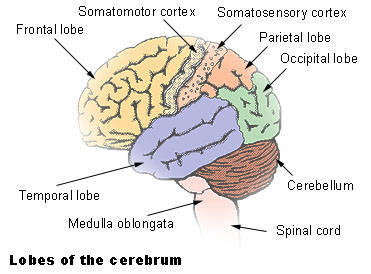
Anatomy, names and function of cerebral cortex areas
Introduction
Human cerebral cortex is the outermost layer the brain. It is the most important area of human brain. Even with current technology very little is known regarding the human cerebral cortex. However several cortical areas are found to be unique in their function. These clealy identified areas are discussed in this hub. Most of other areas may have variety of complex functions that are not unique or specific.
Primary motor area - frontal lobe
This is situated in precentral area of the brain. It is situated just in front of the large central groove called central sulcus. Precentral area of the brain can be devided into posterior or anterior. Primary motor area is situated in the posterior potion of precentral gyrus. In addition it extends over to the superior border into the paracentral lobule.
Function
Carryout the individual movements of different parts of the body. For this it receives numerous afferent fibers from premotor area, sensory cortex and thalamus, basal ganglia, and cerebellum. It is the final station that convert the motor design into action (execution of movements).
Cortical areas
My other Hubs
- Common clinical symptoms and signs of damage in cerebral cortical lesions
- What is Reticular system of the brain?
- How memory works - What are memory stores and how to improve our memory
Our Memory is stored in three different stores. They are sensory, short term and long term. - Best insomnia drugs
Common drugs that are prescribed for insomnia are Lormetazepam Loramet),Oxazepam (Serax ), Zaleplon (Sonata ),Zopiclone (Imovane),Melatonin, Ramelteon. However, natural methods produces more natural sleep. - The Side Effects of Antihistamines
Antihistamines are type of medications that inhibit the histamine action. They are given for medical conditions such as allergies and common cold. Most common side effect is drowsiness. - Best dofollow social media sites that allows you to earn money
best dofollow social media sites that can earn money are tumblr and redgage. - Common side effects of Elavil (Amitriptyline)
- Use, actions and side effects of Fluoxetine (Prozac, Fludac)
- How sudden migraine attacks are treated with drugs
- Hallucinations and Delusions that are needed for diagnosis of Schizophrenia
Hallucinations and Delusions of schizophrenia are unique. Presence of them for more than one month is needed to diagnose schizophrenia.
Premotor area
Premotor area is wider superiorly than below and narrows down to be confined to the anterior part of the precentral gyrus. It is situated anterior to the somatomotor cortex.
This area receives various inputs from sensory cortex, thalamus and the basal ganglia.
Function is store programs of motor activity. In addition it is involved with the basal ganglia to control coarse postural movements.
Frontal eye field
Area that is extended from the facial area of the precentral gyrus into the middle frontal gyrus. It connects to extra ocular muscles through superior colliculus.
Frontal eye field is considered to control voluntary scanning movements of the eye that is independent of visual stimuli.
Motor speech area of broca
Brings about formation of words by its connections with the adjacent primary motor areas. It make sure muscles of larynx, mouth, tongue, soft palate and respiratory muscles are appropriately stimulated.
It is located in inferior frontal gyrus.
Prefrontal cortex
Prefrontal cortex is an extensive area situated in the most anterior part (frontal) of the brain. It has large connections with other cortical areas including thalamus, hypothalamus and the corpus striatum. In addition frontopontine fibres connects cerebellum through pontine nuclei. Commissural fibers of corpus callosum unite both prefrotal corteces.
Functions
1. Form the individuals personality
2. Regulator of the persons depth of feeling
3. Determine the initiative and judgment of an individual.
In fact, prefrontal cortex seems to make us human. READ MORE
Primary sensory area - Parietal lobe
This occupies the post central gyrus on the lateral surface of the cerebral hemisphere and the posterior part of the Paracentral lobule on the medial side. It receives sensory projection fibers from VPL and VPM nucleus of thalamus. Pharynx, larynx and perineum sensations go to both sides of the cortex. Other areas are represented by the opposite side.
Sensory association area - Parietal lobe
Occupies the superior parietal lobule extending onto the medial surface of the hemisphere. It has many connections with the other sensory areas of the brain.
It receives and integrates various sensory modalities. It helps to recognize objects placed on the hand without visual stimuli.
Primary visual area
Primary visual area is situated in the posterior part of the calcarine sulcus. It is usually thinner than other parts of the cortex.
Visual cortex receives afferent fibers from the lateral geniculate body. Visual cortex also receives fibers from temporal half of the ipsilateral retina and nasal half of the contralateral retina. In addition superior quadrants of the retina (inferior visual field) pass to the superior wall of the calcarine sulcus. Inferior quadrants of the retina (superior visual field) are passed to the inferior wall of the calcarine sulcus.
Macula lutea, which is the central part of the visual cortex and it is accounts for one third of the visual cortex. Visual impulses from the peripheral parts of the retina terminate in concentric circles anterior to the occipital lobe. Visual cortex is receives raw visual stimuli from the retina.
Secondary visual area
This area surrounds the primary visual area on the medial and lateral surfaces of the hemisphere. Receives impulses from the area 17 (visual cortex) and other cortical areas as well as from the thalamus. Function is to relate past experiences to the impulses received from the primary visual area.
Occipital eye field
Is thought to be exists in the secondary visual area. Function is to move reflex move eyes. In contrast frontal eye field is responsible for voluntary eye movement.
Auditory areas - Temporal lobes
Primary auditory area
Primary auditory area is situated in the inferior wall of the lateral sulcus. Projection fibers to the auditory cortex arise primarily in the medial geniculate body and form the auditory radiation of the internal capsule. Anterior part is responsible for the reception of low frequency sounds. Posterior part is responsible for high frequency sounds. Unilateral lesion in primary auditory cortex results in partial deafness of the both ears. However the deafness is marked in contralateral ear. This is due the fact that medial geniculate body receives fibers mainly from the opposite organ of corti.
Secondary auditory area
This is situated posterior to the primary auditory area in the lateral sulcus and in the superior temporal gyrus. Secondary auditory area receives supply from both primary auditory area and from the thalamus. Its function is to interpret raw sounds received from the ears. In addition it is important for the association of auditory information with other sensory information.
Wernickes sensory speech area
This is located in the left dominant hemisphere. It is situated chiefly in the superior temporal gyrus. It extends into the parietal region around the posterior end of the lateral sulcus. This region of the cortex is connected with the broca’s area with nerve fibres called arcuate fasciculus. In addition it receives fibers from visual cortex, auditory cortex. Wernickes area allows the understanding of written and spoken language and permits a person to read a sentence, understand and speak it out loud. This is a very important cortical area where somatic, visual and auditory association areas come together.
- Mental Health Information
Blog maintained by me - Candid B cream and its uses and side effects
Candid B is a local skin application that consists of Clotrimazole and betamethasone. Clotrimazole is an anti-fungal medication. Betamethasone is a steroid. Candid B is prepared by mixing above two ingredients. - Flunarin uses and side effects
Flunarin is a medication used for Migraine prevention. Most common side effects are drowsiness and weight gain. - Use and side effects of Jonac
Jonac is a medication used for painful conditions. It is a Diclofenac sodium brand that is commonly available as gel and tablet form. - Use and side effects of Giloba
Giloba is a trade name of a Ginkgo biloba preparation. Its uses include improving blood circulation, improve stamina and to prevent the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. Side effects of Giloba are possible increased risk of bleeding, gastrointestin - Use and side effects of Enhancin
Enhancin is an antibiotic medication. It is used for various types of infections. Main side effects are gastrointestinal upset and allergic reactions.