Big Bang Theory
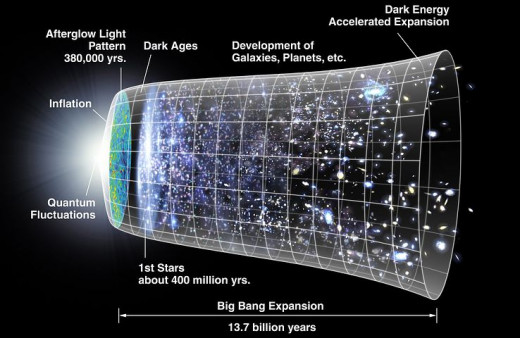
Big Bang Theory
A theory of the creation of the universe. According to this theory, the universe was created by the explosion of a huge object about 1.3 billion years ago. From this time the age of the present universe is captured.
The first Big Bang theory was published in 1926 by the Belgian physicist Georges Lemaître. According to this theory, about 1.5 billion years ago, all the objects in the universe gravitated into a super atom. George Lemiter named this atom the primæval-atom. This atom later exploded, creating the universe. This doctrine was supported and explained by Edwin Powell Hubble in 1929. However, George Gamo established this theory through a detailed explanation.
Hubble's observations show that galaxies in space are gradually moving away from each other at a certain speed. According to him, galaxies were originally formed as a result of the Big Bang, and the behavior of moving away from them supported the Big Bang. The radiation that was supposed to be generated by the explosion in this way could not be proved at first. As a result, there is a conflict among scientists. In 1974, two scientists, Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson, proved the existence of radiation. As a result, the idea of the Big Bang became more well-established. This theory is still considered to be true of the creation of the universe. Recent research suggests that the Big Bang occurred about 13.697 ± 0.036 billion years ago. It is now roughly said that this event took place 1370 crore years ago.
Note that no space and time existed at this time. Due to the dense insertion of matter inside this super atom of infinite density, its temperature stood at 1017 Kelvin. Scientists have divided the events that took place in the first 1 second after the Big Bang into several inter-epochs over time. The parts are - 0 to 10-43 seconds: The time from 0 seconds to 10-43 seconds of the Big Bang is called Planck epoch. At this time all the forces of nature were unified. Scientists have named this ball as super force. During this time the universe expanded to only 10-35 meters. Note that this distance is called 1 plank length. At this time the temperature was 1032 Kelvin.
10-43 to 10-38 seconds: The astronomer named this period the Grand Unification Epoch. The amount of energy generated during this time was 1015 giga volts. The temperature was 1026 Kelvin. During this time, strong nuclear forces, weak nuclear forces, and electromagnetic forces combined with very large balls combined to form an electronuclear force. And the gravitational force debuted as a separate force. The effect of this ball was that the universe reached its maximum contraction level. At that time, in terms of density, the object per cubic centimeter in the universe was 57 10 + 93 grams.
It is thought that two boson particles এক্স the X and Y bosons তৈরি were formed inside the primordial ultra-atomic particle during this time. These two particles decayed to form two quark particles (up and down) and two particles of the force particle lepton. At the same time their antiparticles were made. When both particles were destroyed by the collision of the original particle with the antiparticle, only the quark and lepton particles remained.
10-36 to 10-32 seconds: The period after the Big Bang is called the inflationary epoch. During this period the temperature drops to 1026 to 1022 Kelvin. During this time the universe continues to expand rapidly.
10-32 to 10-12 seconds: This time after the Big Bang is called the Electroweak epoch. Because at this time a weak nuclear force and an electromagnetic force came together, this force was created. As a result, strong nuclear forces were introduced as individual forces. During this time heated quark-gluon particles were formed. In addition, three particles of the boson class were formed. These are- W and Z boson particles and Higgs boson particles.
10-12 to 10-7 seconds: This period after the Big Bang is called the Quark epoch. During this time the electromagnetic force also separates the weak nuclear force and manifests itself as two separate forces. As a result, the first four natural forces are able to influence the material world individually at this time. Huge quantities of quarks, electrons and neutrinos were created during this time. But at this time the temperature was 1012 Kelvin. And the amount of power was 100 megavolts. At these high temperatures it was impossible to make hadrons from quark particles. Leptons and counter-particles were formed without quarks. However, in the collision of the original particle and the antiparticle, both particles were wiped out. This collision caused Mason and baryon particles to form from quark particles. 10-7 to 1 second: This period after the Big Bang is called the Hadron epoch. During this time the temperature dropped from 1012 Kelvin to 1010 Kelvin. During this time a lot of Hadron particles were created from quark particles. In the beginning Hadron and anti-Hadron particles were formed and destroyed by collisions with each other. But due to the rapid drop in temperature, this process was stopped.
1 second to 10 seconds: This period after the Big Bang is called the Lepton epoch. Originally, the temperature dropped from 1010 Kelvin to 109 Kelvin within 1 second to 10 seconds. During this time there are collisions inside the lepton and every lepton. After this collision, a few leptons remain, but the rest of the particles turn into photon particles.
10 seconds to 1000 seconds: This period after the Big Bang is called the Nucleosynthesis epoch. During this time the temperature dropped from 109 Kelvin to 106 Kelvin. The original atomic nuclei were formed by the synthesis of the original proton and neutron. During this time hydrogen as well as helium nuclei were formed. And about 24 percent of the universe's mass was filled by this nucleus.
From 1000 seconds to 36o, 000 years: The process of creating massive photons began after the Big Bang. This process intensifies from 10 seconds. From this time on, the universe was filled with photons. That is why this period after the Big Bang is called the photon epoch.
Basically, due to the collision of different types of primitive particles and their antiparticles and the combination of different types of electrons, protons and neutrons, a huge amount of photons overwhelmed the primitive universe. But there was no free movement of photons through ionized particles. As a result, the photons were trapped in a chaotic state. Although a large number of photons were formed in this state, the space looked like opaque matter with a large collection of different kinds of particles. By the end of the intervening period, the temperature had dropped from 108 Kelvin to 4,000 Kelvin. This opened the way for new additions between the cosmic particles.
1375 BC BC: This period after the Big Bang is called Recombination. It started 3.60 million years later. Temperatures in this intercontinental period were roughly around 4,000 Kelvin. During this time the first protons and neutrons combine to form ionized hydrogen and helium atoms. These ionized atoms then start attracting electrons and eventually hydrogen, helium and lithium atoms are formed. By the end of the Middle Ages, about 75 percent of the universe was hydrogen. There was also very little lithium except for the rest of the helium. Molecular clouds were initiated through this process.
In the meantime, a molecular cloud had spread in space. All these clouds also had photon particles. However, no stars were born at this time, so the space was in darkness. For this reason, astronomers have named it the Dark Age. This period is considered as the last half of the reunion period. At the beginning of this period the temperature of the universe was 4000 Kelvin. Since the formation of molecular clouds, its temperature has been declining. And at the end of the Dark Ages, the temperature of the universe dropped to 60 Kelvin.
At that time there were huge molecular clouds all over the space. The explosion caused these molecular clouds to move away from the center of space. This cloud was light somewhere, dense somewhere. In the gaseous state, this cloud formed a vortex somewhere. From this molecular cloud various kinds of stars, nebulae, galaxies etc. were formed. Towards the end of this period some stars were formed. For example, the age of the star BD + 17 ° 3248 is estimated to be around 1360 crore BC. In fact, this star was formed about 3.60 trillion to 150 million years after the Big Bang. HD 140283 was born about 3.60 trillion to 150 million years after the Big Bang. SMSS J031300.36-670839.3 1370 crore BC.
Ancient galaxies were in their infancy during this period. Inside it is our galaxy called the galaxy. It originated in 1360 crore BC.
1385 crore to 1300 crore BC:
Some of the constellations created during the Dark Ages showed light in space, but not in the form of the 'sky-filled suns' of the time. The stars that astronomers have been able to discover so far are: SMSS J031300.36-670839.3 (13.2 billion BC) HE 1523-0901 (13.2 billion BC) Sneden's Star (1.3 billion BC) SDSS J102915 + 172927 (1.3 billion BC) HE0107-5240 (1.3 billion BC)
At this time, space was enriched by ionized particles coming out of the stars. It is noteworthy that the universe was filled with ionized atoms before the formation of the atomic cloud. After creating stars from molecular clouds again, ionized atoms began to form again. This marked the beginning of a new cosmic chapter. Astronomers call this age the Reionization Ages. This process continued for about 1 billion years. As a result, the space environment changed. At the beginning of this period, the temperature of the space was 60 Kelvin. And at the end of 1 billion years, its temperature dropped to 19 Kelvin.
The process of star formation continued during this period as well. As a result, ionized atoms were added to the original molecules of the atomic cloud and the atomic clouds were evolving in a new form. These clouds contained tiny molecules. Astronomers have named it Cosmic dust. It contained a variety of interstellar materials, including ionized gas, hydrogen, and helium molecules. Such as- carbon, complex bio-molecules, formaldehyde, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons etc. The nebula was made by combining these. The process of creating the galaxy was still going on at this time.
GN-z11 is considered to be the oldest of all the galaxies that astronomers have found so far. This galaxy was formed in 1340 million BC. Below is a list of some of these ancient galaxies
GN-z11: 1340 million BC. Galaxy EGS8p7: 1320 million BC.
1300 crore to 1000 crore years ago:
The galaxy was formed extensively during this period. This is why it is called the galaxy-formation period. Note that during this period the temperature of the universe dropped from 19 Kelvin to 4 Kelvin. The star BPS CS31082-0001, named Cayrel's Star (1250 BC)
1000 billion to 470 million BC: As mentioned earlier, a galaxy called the galaxy was formed around 1360 billion BC. About 25,000 light-years away from the center of this galaxy, a massive space cloud formed about 500 million years ago in the Orion Arm. 460 million years ago, a supernova exploded near this cloud. Because of the explosion, the cloud shrinks and forms a stellar center. This center creates stellar embryos in a rotating state. The Sun was born about 460 million years ago from that stellar embryo. At this time, the new sun's mass of matter, surrounded by the sun. As a result, the sun was trapped in a cosmic ring. Over time, the mass of this ring collapses into smaller celestial spheres, which begin to orbit the sun. In this way, the planets and satellites of the solar system were created in a series of events. At present, the common solar system of the organization consists of a star called the Sun and a celestial body with a gravitational force revolving around it.
© 2020 Ashik Azadi








