Demand in Economics: A Brief Note on Demand and Related Concepts

Demand and supply are two very important concepts in both Micro and Macro Economics. Since demand is very much related to human behavior, the studying of the concept of demand and supply is also very important in an economy.
Demand meaning: Generally the meaning of the demand can be said the combinations of desire plus ability to pay plus willingness to pay. In simple form a want of a person become demand only when he can able to pay and he is ready to pay.
Demand for a commodity : the demand for a particular commodity can be said, “ the different quantities of a commodity which the consumer is able and willingness to pay or to buy at different prices in a given period of time.
Factors determining demand for a commodity
Demand is influenced by many factors. When a particular commodity is demanded the consumer may go through many factors before buying. Some of the factors that influence the demand are listing below.
A – Price of the commodity
Price is the most important factor that affects demand for a commodity. In normal goods (example; food items like rise, wheat) price and demand is negatively related. Which means when price increases the demand will decreases and when price decreases emend will rise.
B – Income of the consumer
Generally income and demand is positively related. That is when income raises the consumer having a tendency to consume more. It is applicable only in the normal goods. In the case of inferior goods like cheap cloths, even the income increased there may not be a tendency to consume or buy such cheap commodities.
C – Prices of related commodities
When a consumer wants to buy a commodity, he may inquire prices of related commodities. In economics commodities are classified in to two. That is, substitute goods and complementary goods.
Substitute goods are those goods which can able to satisfy a particular want. For example: tea and coffee are the perfect substitute goods.
Complementary goods are those types of goods, they are jointly demanded to satisfy a particular want. For example, car and petrol.
Any how the prices of related commodities will affect the demand for a commodity.
There are many other factors affect demand for a commodity, which includes factors like advertisement, taste and preference of consumers, educational level, weather condition, price expectation etc.
Demand function and demand curve
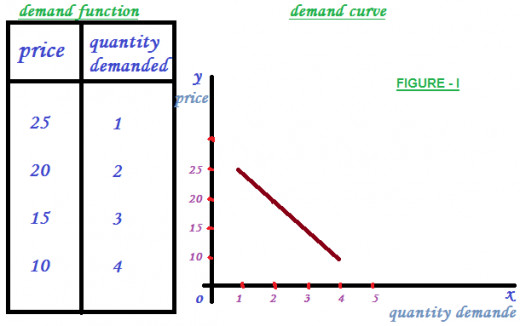
Demand function can be said to be, all the factors except price are unchanged or constant, and the consumer’s demand is the function of prices.
Symbolically, q= d (p). It can be read as, quantity (q) demanded is the function of price (p).
Demand curve : it can simply said that the graphical representation of demand function. See figure – I.
Law of demand: Law of demand can be defined as, all the factors are constant except price, and the demand for a commodity varies inversely with the price.
Market demand: Market demand refers to the sum total of individual demands in an economy or in a market. For a simple example, in a fruits market customers A, B and C are bought 1 kg, 3 kg and 2 kg of Apple respectively. So, the market demand is the total of the demand of consumer A, B and C, THAT IS 1+3+2 =6 Kg.
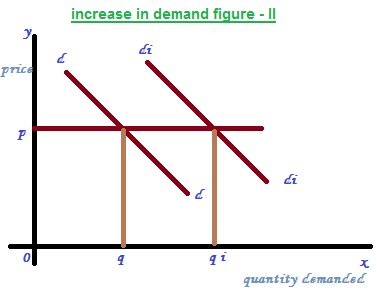
Increase in demand and decrease in demand or shifts in demand
It is a concept of change in demand due to change in all determinants of demand except price. In this case the demand curve will shift either rightward or leftward.
Increase in demand:
It means that the quantity of demand is increased due to changes in determinants of demand other than price. It can observe through a graph, when the demand curve is shifted rightward. See figure – II where the price is fixed at ‘P’ and the demand curve is shifted from DD to DiDi and the quantity demanded also increased from Q to Qi.
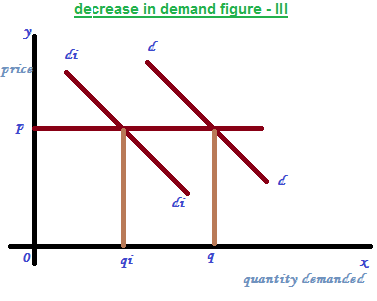
Decrease in demand:
It means quantity demanded is decreased due to the changes in the factors of determinants of demand other than price. It is represented in the figure – III. In the figure ‘P’ is constant and demand curve shifted from DD to DiDi and the quantity of demand is decreased from Q to Qi.
Elasticity of demand
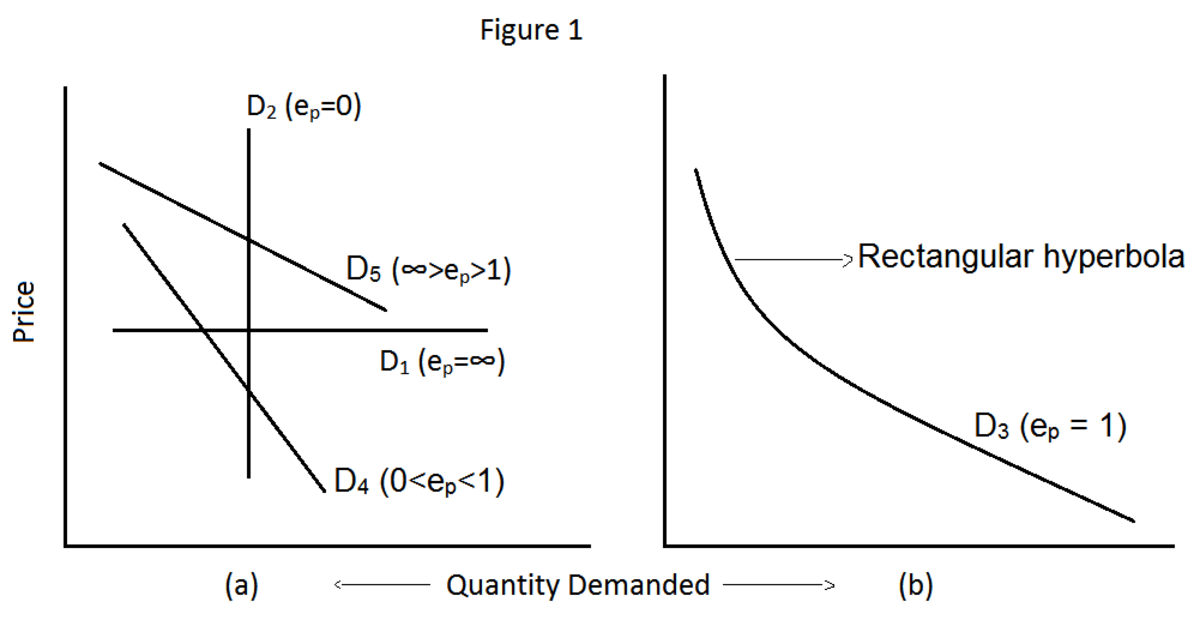
This is another concept related to demand. Here we assume that all the factors of determinants of demand is fixed and only the price is flexible or varying. So, elasticity of demand means the level of responsiveness due to changes in price. Any way mainly five types of elasticity of demands are there.
Types of elasticity of demand
There are different types of elasticity of demands. Mainly they are classified in to five types. Namely
1 – Perfectly elastic demand
2 – Perfectly inelastic demand
3 – Elastic demand
4 – Inelastic demand
5 – Unitary elastic demand
Each one of them is described separately as below.
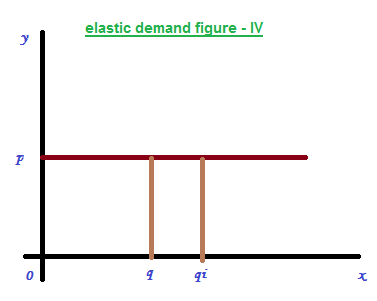
1 – Perfectly elastic demand
Perfectly elastic demand is a phenomenon in infinite change in quantity demanded due to a very small change in price. It is represented in the figure - IV. Here, since elasticity is more it can represent by a horizontal line parallel to ‘x’ axis as shows the diagram.
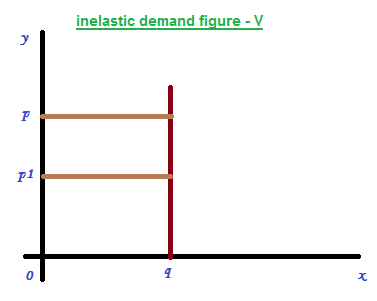
2 – Perfectly inelastic demand
Perfectly inelastic demand is showing just opposite of the perfectly elastic demand. Where any change in price will never effected in change in quantity demanded. It can showed in diagram –V by a vertical line parallel to ‘y’ axis.
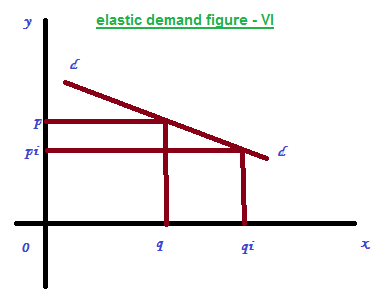
3 - Elastic demand
It can be defined as a small change in price lead to a big change in quantity demanded. That is the percentage change in the quantity demanded will exceeds the change in price. So the curve will be a flatter one as showed in the figure – VI.
4 – Inelastic demand
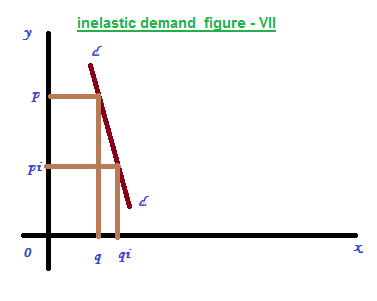
It is just opposite of elastic demand. It can be defined as a big change in price will lead to a small change in quantity demanded. The curve will be a steep one as represented in the figure – VII.
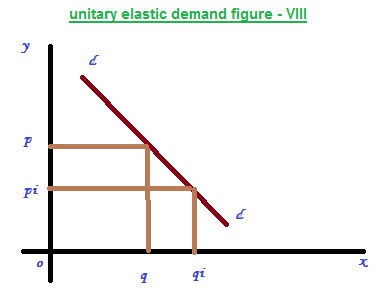
5 – unitary elastic demand
It can be defined as a given percentage change in price lead to same percentage change in quantity demanded. It can be represented in the figure – VIII. The shape of the curve is called rectangular hyperbola.