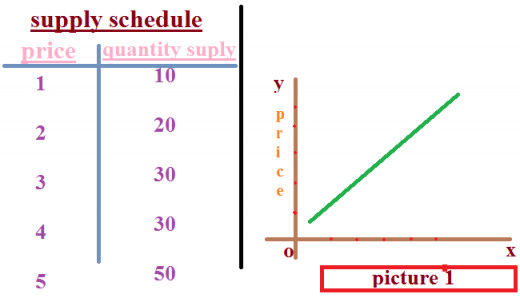
Supply in Economics: A Brief Note on Supply and Related Things

Production and distribution are the major two functions of every economy. Because demand or wants or needs arising in every economy from the part of individuals, firms, government etc. To satisfy those demand supply must be there. The only the economic system can be attain equilibrium condition. Any way supply is very important concept in economics. This article dealing with the meaning and definition of supply, factors which influence supply of a commodity, supply function and supply curve, market supply, elasticity of supply etc. Each one of the concept related to supply are briefly described in the coming section.
Meaning of supply: - simply supply refers to the ability of producers to sell their output at different prices.
Supply for a commodity: - supply of a commodity refers to the different quantities of commodity which the producers are ready to sell at different prices in a given period of time.
Factors determining supply for a commodity
Producers are supplying different commodities, for which they influence many factors. Some of them are briefly listed below.
A - Prices of the commodities
Price is the most important factor which influences the supply level of any commodity. When prices are high the producers will have a tendency to supply more. Because, higher price will increase the earnings and profit of the producer. So, prices and supply are directly related.
B – Prices of other related commodities
In the market there are substitute goods are available. So, the supply also influences the prices of other related commodities.
C – Cost of factors of production
Cost of production is another important factor which influences the quantity of supply of commodities. Since heavy cost of production will decline the profit of the producer he may has a tendency to supply less.
D – The state of technology
Production of commodities via using developed technology will reduce the cost of production and help the producer to increase profit. So using of best developed technologies will enable the producer to supply more.
E - Price expectation
If the producer expects high prices for making more profit, it also affect the quantity of supply.
There are many other factors which influence the supply of a commodity like whether condition, seasonal variation, number of sellers etc.
Supply function and supply curve
Simply supply function can be said to be the quantity of supply of a commodity that the producers supply. Here we assume that all determinants of supply are fixed only the price is varying. So supply becomes the function of its market price.
See picture I to understand supply curve.
Law of supply
The law of supply stating that there is an direct relationship between price and quantity supply. So, the producers are willingness to supply more at higher price level and supply less at lower price.
Market supply
Market supply refers to the sum total of individual supply. For instance, suppose there are three sellers in a market namely A, B and C. they are supplying of a particular commodity of 1000 units, 2000 units and 2500 units respectively. So the market supply will be equal to the sum of three individual supply, that is 1000 + 2000 + 2500 = 5500.
Increase in supply and decrease in supply or shifts in supply
Shifts in supply occur when the supply is changed due to the change in the determinants of supply, but price is fixed.
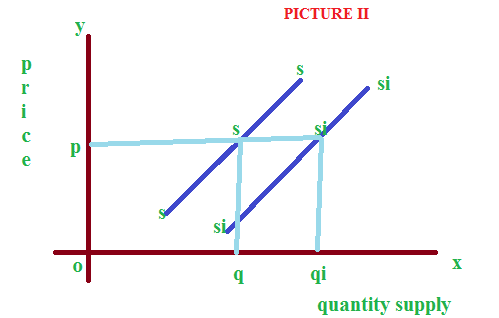
Increase in supply
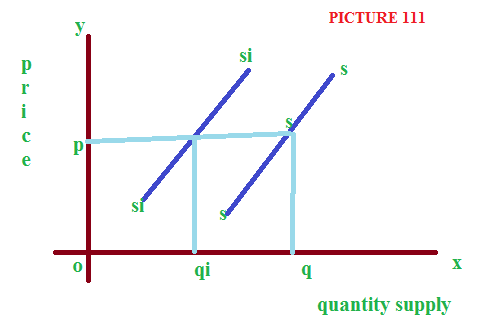
When the supply curve shifted from left to right, it shows increase in supply. See the picture II. Where the supply curve is shifted from SS to SiSi.
Decrease in supply
When supply curve shifted leftward, it showing an decrease in supply. It is represented in the picture III. Where the supply curve shifted from SS to SiSi.
Expansion and contraction in supply.
Expansion ad contraction of supply refers to the change in quantity of supply in the same supply curve. Here all the determinants of supply supply is fixed only the price is varying.
See the picture IV
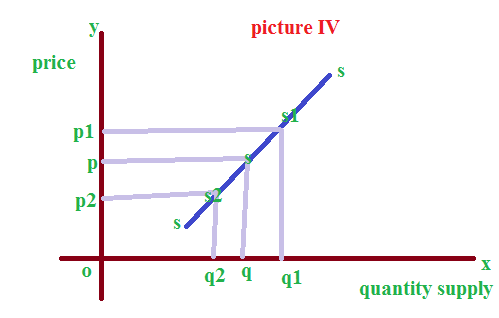
In the picture IV the initial supply is ‘Si’ and the price is ‘P’. when price increases from ‘p’ to ‘pi’ the supply also increases. It is called expansion in supply. On the opposite side the price reduced to ‘P2’ and supply also decreases to ‘S2’. So this is called contraction in supply.
Elasticity of supply
Elasticity of supply means the percentage of change in quantity supply due to changes in price. There are mainly five types of elasticities of supply. They are…
1 – Perfectly elastic supply
2 – Perfectly inelastic supply
3 – Elastic supply
4 – Inelastic supply
5 – Unitary elastic supply.
They are briefly described below one by one.
1 – Perfectly elastic supply
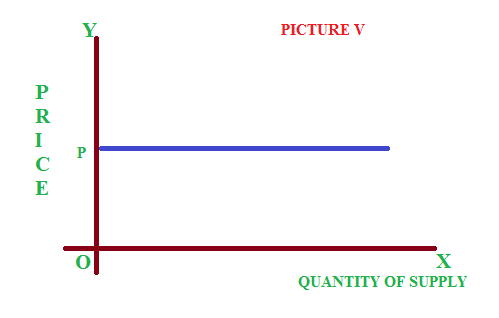
If the quantity of supply changes at an infinite rate due to a small change in price, it is said to be perfectly elastic supply. See picture V. where the curve will be parallel to horizontal axis.
2 – Perfectly inelastic supply
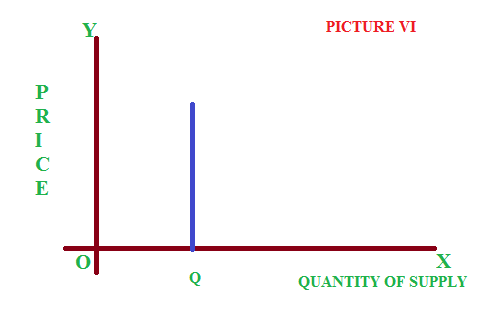
If a big changes in price will lead to a very small change in supply, it is said to be perfectly inelastic supply. See the picture VI, where the curve is parallel to vertical axis.
3 – Elastic supply
If a small changes in in the price will effected in a big changes in supply, it is said to be elastic supply. See picture VII, where the curve some what flatter to horizontal axis.
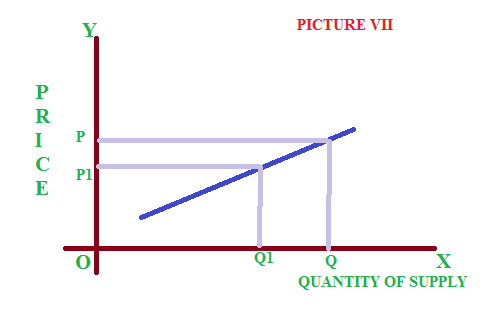
4 – Inelastic supply
If a big change in supply will resulted in only a small change in supply, it is said to be inelastic supply. See the picture VIII, where the curve is a steep one.
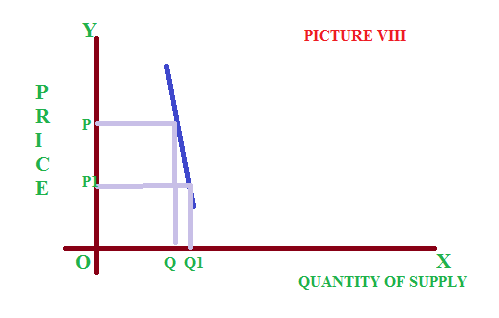
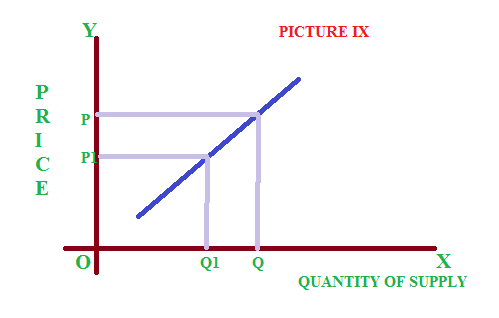
5 – Unitary elastic supply
If a given percentage of change in price will effected in the same percentage change in supply, it is said to be unitary elastic supply. See the picture IX. The shape of the curve is called rectangular hyperbola.