Deficiency Diseases
Now-a-days People are leading busy life. Most of them are engaged with their jobs and are unable to fulfill the needs of their children. Though, Due to lack of time, they are fulfiling their children apatite by giving the junk food but that food will not compensate the nutritious food as they require. So that most children are facing the problem of Malnutrition. The Poverty also leads to Malnutrition.
Eating of food that does not have one or more nutrients in required amount is known as malnutrition.
Reasons for Malnutrition:
- Willful starvation
- Poor health of the individual due to infections and diseases.
- Lack of awareness of nutritious food
- Socio-economic factors like poverty, partiality for boys & girls
- Poor quality of housing, sanitation, habitat etc.
Effects of Malnutrition:
If one or two nutrients are missing in the intake food the compensation is done by using the reserves of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats to generate energy. At the same time, excretion of required nutrients is reduced. Long term effects of malnutrition are different in adults and children.
Adults:
During long term malnutrition, the body uses the reserves of carbohydrates, proteins and fats etc. Later the person looses weight, becomes week, lazy In this stage, the body effects by bacterial and viral infections.
Children:
Malnutrition in children is of 3 types:
1. Calorie malnutrition:
In this type, the children are given insufficient amounts of energy providing nutrients such as carbohydrates and fats. This is also called energy malnutrition.
2. Protein malnutrition:
In this type, the children are given less amount of protein in their diet or they are fed -on proteins that have lesser amounts of essential amino acids.
3. Protein - Calorie malnutrition:
In this type, children are given poor quality food in which energy giving substances and proteins are less.
Diseases of Malnutrition in Children:
Kwashiorkor:
It is an african word means displaced child. In this disease the child is given high amounts of carbohydrates and very low amounts of protein. Therefore the protein deficiency in the diet results in Kwashiorkor disease.
Effects of Kwashiorkor:
- Growth is slowed down
- Body parts become swollen due to accumulation of water in the intercellular spaces.
- Development of muscles will be poor
- Legs become swollen
- Face becomes fluffy like moon shaped
- Child suffers with loss of apetite, diarrhea
- Hair become thin and lifeless in appearance
- Skin becomes dry and loose
- Child becomes lethargic and looses interest in playing learning and other activities.

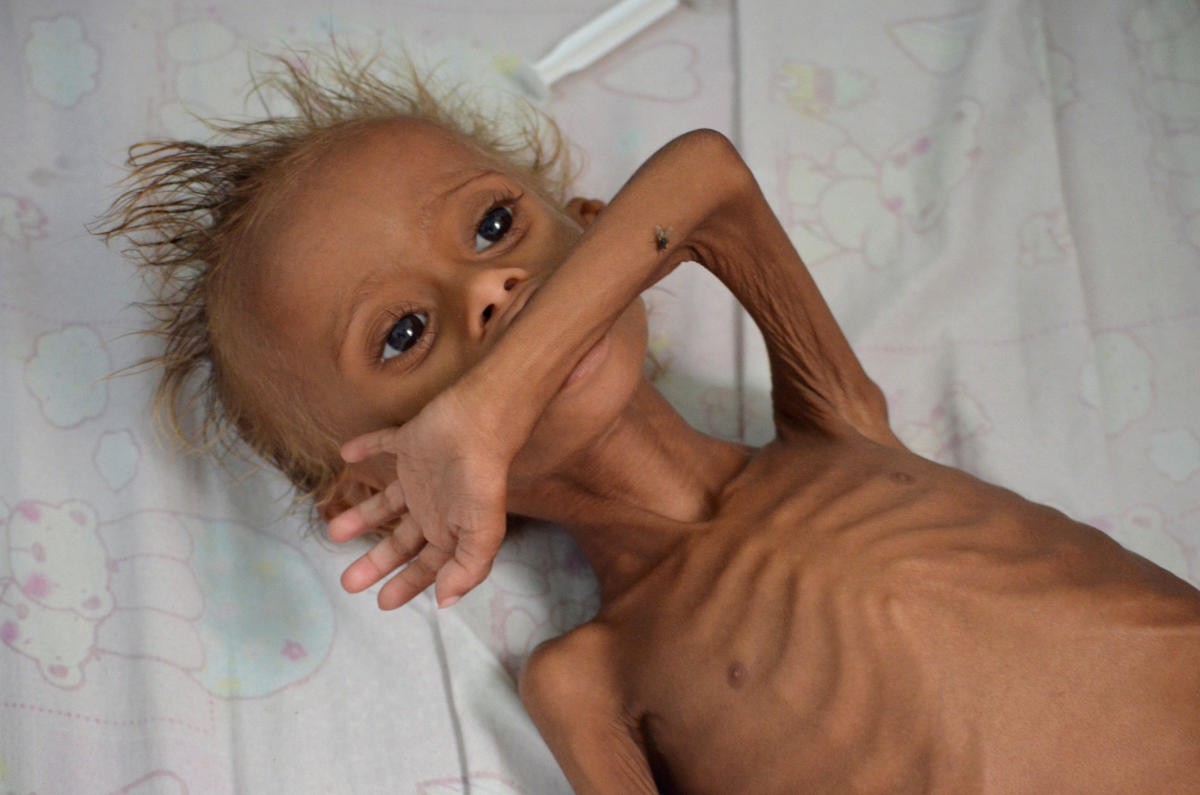
Marasmus:
This disease is due to the deficiency of both proteins and calories (protein-calorie malnutrition).
Effects of Marasmus:
- Body growth will be reduced
- Child becomes lean and under aged
- It results in weight less
- The limbs will be thin and the ribs are prominent in the child.
- The limbs will be thin and the ribs prominent in th child.
- Under developed muscles are seen and there is no fat under the skin
- Skin becomes dry and loose folds of skin are found
- Child suffers with infections and diarrhoea

Obesity:
Over - eating and excess of energy intake results in obesity. Due to overeating, excess energy is converted to fat and is stored in the cells of adipose tissue located below the skin, which results in increase of body weight and size, especially in circumference, obesity may also be due to genetic defects and is inheritable. Obesity is a health hazard. Obesity leads to diabetes, cardiovascular problems, renal and gall bladder problems' Only way to treat obesity under proper supervision, is to increase the energy expenditure and reduce the energy intake. To reduce the energy intake, obese people are advised to reduce eating of energy rich foods. They are advised to take more of balanced and fibre rich foods.

Vitamins
Vitamins are organic substances. They are micronutrients and are required in small quantities. They are not synthesized in the body and therefore they are the essential nutrients. Our body has no capacity to synthesise the vitamins but we have two sources to get vitamins.
They are
(1) Diet
(2) Bacteria present in the intestine synthesize the vitamins.
Vitamins are classified into two groups -
(1) Water soluble vitamins: Eg. vitamin 'B' Complex, Vit 'C'
(2) Fat Soluble Vitamins: Eg: A, D, E, K
Vitamin B Complex:
This is a group of vitamins. Vitamins in this group are
a) Thiamine, b) Riboflavin c) Niacin d) Pyridoxine e) Folic acid f) cyanocobalamine g) Pantothenic acid and h) Biotin
Thiamine:
It is a B Vitamin. This vitamin is necessary for the activity of some of the enzymes of carbohydrate metabolism. It is present in all the natural foods in cereals like wheat, rice, oil seeds like ground nut, milk, meat, fish, eggs, vegetables etc. Deficiency of Thiamine leads to a disease called Beri-Beri.In this disease the calf muscles become tendor, Vomitting, tremors, convolutions etc. may also occur. In some cases, difficulty in breathing and paralysis are also seen
Riboflavin: (B2 Vitamin):
It is essential for oxidation, reduction reactions in the cell and it participates in cellular respiration. Deficiency of Riboflavin results in Glossitis, mouth cracks at corners, watering of eyes, photo phobia and skin becomes scaly.
Niacin or Nicotinic acid (B3 Vitamin):
This is essential for the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins and fats. Kidney, liver, meat, poultry fish, legumes and groundnut are good sources for Niacin. Deficiency of Niacin results in a disease called Pellagra.
Pyridoxine: (B6 vitamin):
It plays an important role in the metabolism of amino acids. It is available in milk, liver, egg, yolk, fish etc. Deficiency of Pyridoxine results in hyper irritability, anaemia, nausea and vomitting.
Folic Acid:
Folic acid is required for the synthesis of nucleic acids -like RNA & DNA and for the development of blood cells in the bone marrow. It is present in liver, meat, eggs, milk, fruits, cereals and leafy vegetables. It deficiency leads to anaemia, diarrhoea and a decrease in the number of leucocytes.
Cyanocobalamine (B12 vitamin):
It acts an important role in the metabolism of nucleic acids and in protein synthesis. Bacteria present in the intestine synthesis this vitamin and supply to our body. Deficiency of this vitamin causes pernicious anaemia.
Pantothenic acid:
This vitamin is required for the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins and fats. Deficiency of pantothenic acid causes burning sensation of feet in human beings.
Vitamin C:
This is also known as Ascorbic acid. Vitamin 'C' Plays an important role in tissue oxidation reactions and is required for the formation of collagen, normal growth, tissue repair healing of wounds and fractures of bones. Collagen is required for the formation of blood vessels, connective tissue, cartilage and dentine of teeth. This vitamin is present in green leafy vegetables, tomatoes, citrus fruits etc. Deficiency of vitamin c results in a disease called scurvy.
Fat Soluble Vitamins
Vitamin 'A':-
The chemical name of vitamin A is called Retinol. Its functions in the body are varied and they are as follows.
- This is quite essential for normal vision
- This is also required in the production of pigments such as rhodopsin of rods and idopsin of cones These pigments are essential to have normal vision.
- This vitamin also helps for the growth of the body.
- This vitamin is also required for the growth of the skeletal system and protects it from infections.
- It is also helpful to resist infection of the skin and mucous membrane.
Deficiency of vit. A causes the following diseases:-
1. Night Blindness:-
The person having deficiency of A cannot see the objects in dim light and in nights. It is called night blindness.
2. Xeropthalmia or dry eyes:-
In this disease, the lachrymal glands in the eyes do not produce tears. The conjunctiva becomes dry.
3. Cornea soft:
The cornea becomes soft and bursts open. This leads to the loss of vision.
4. Skin becomes scaly and rough.
Vitamin D:-
This is called calciferol. It helps in the absorption of calcium and phosphorus by the intestine and their deposition in the bones. It helps the body to use calci um and phosphorus to form bones and teeth. The sunlight acts on the cholesterol present in the foods and converts into vitamin D in our body.
Vitamin E:-
This is also called Tocoferol or antisterility vitamin. It is essential for the normal functioning of sex organs. It prevents oxidation of vitamin A. In its absence, the life span of RBC's is reduced.
Vitamin K:-
This also called Phylloquinone. It is necessary for blood coagulation or for the normal clotting of blood. Its absence makes us loose more blood from wounds and injuries.