Hearing - How Do We Hear Sound Waves?
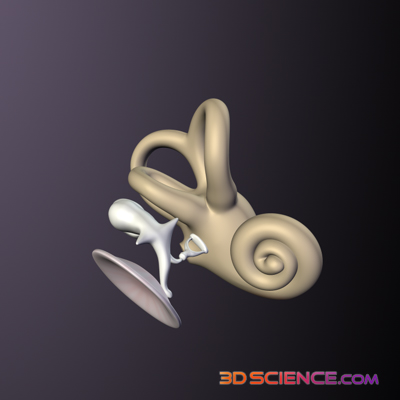
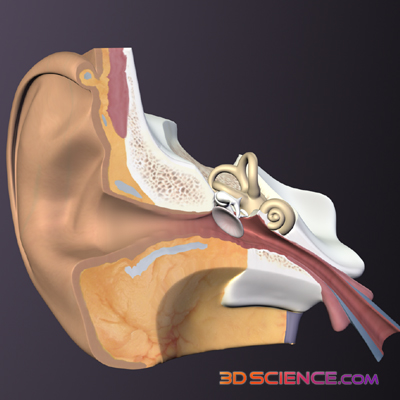

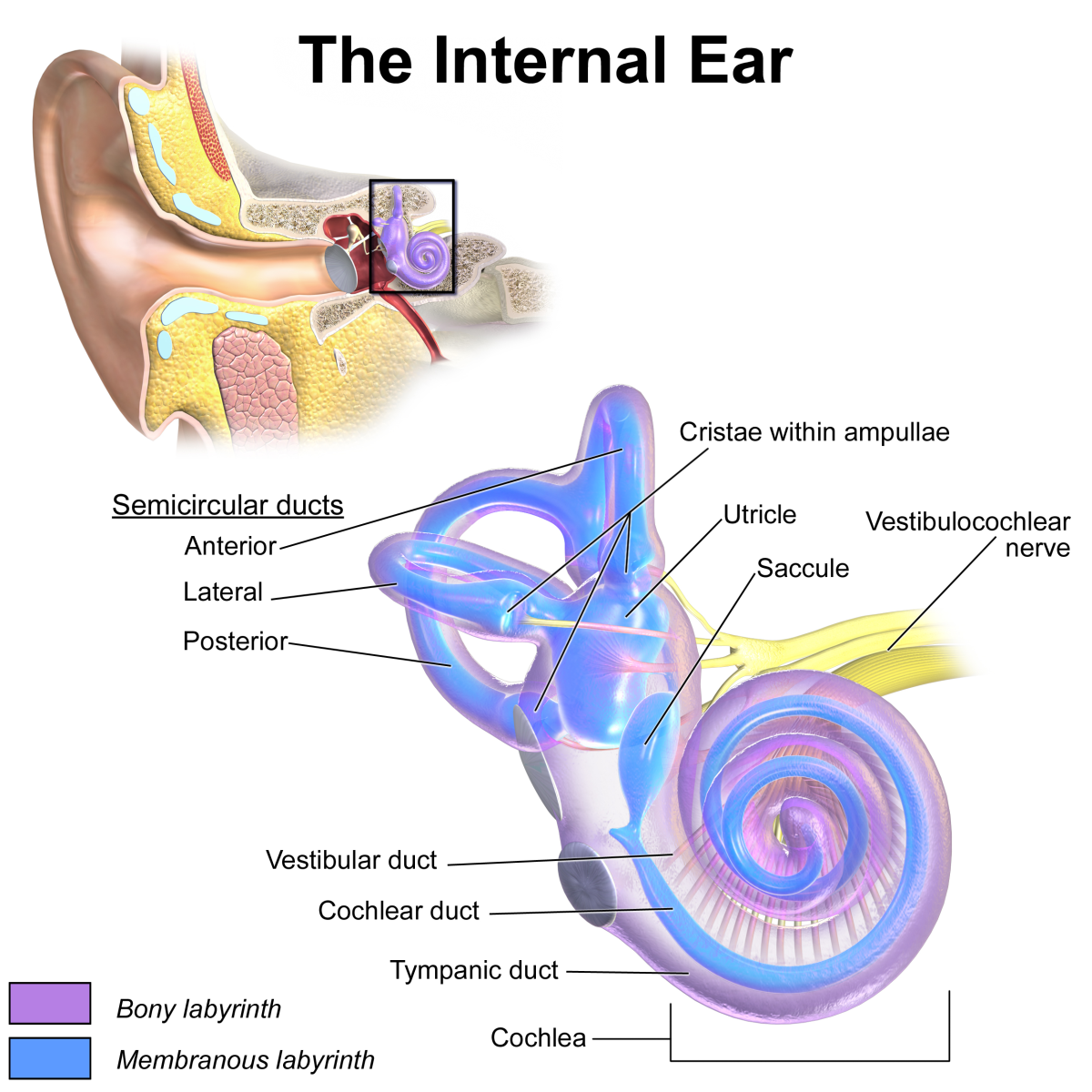
The organs of hearing or audition are your ears. These, along with the cochlear nerves and brain, allow us to hear.
Sound waves enter the outer ear, which consists of the ear flap, made of cartilage and called the pinna, and the outer ear canal, which ends at the eardrum. The sound waves are reflected into the ear by the pinna, and travel along the ear canal. The middle ear commences with the eardrum, or tympanum. The sound waves hit the eardrum, causing it to vibrate. The wave information is transmitted through the air filled middle ear cavity, across three tiny bones called ossicles, the smallest bones in your body. These are individually called the malleus (hammer), incus (anvil) and stapes (stirrup). The vibration from the eardrum causes them to move, transmitting the wave information to a membrane at the entrance of the inner ear called the oval window. This process changes the wave vibrations from low pressure to high pressure so they can be detected by the fluid filled inner ear.The inner ear contains the cochlea, as well as non-hearing related structures. The movement of the oval window transmits the waves through the fluid of your inner ear into the fluid filled cochlea. Spiralling lengthwise through the cochlea is the organ of Corti, which is a membrane with thousands of sensory hair cells attached. Each hair cell contains a bundle of tiny sensory hairs which emerge from the cell. Lightly resting on top of these hairs is a second membrane. When the waves move the fluid in your cochlea, the first membrane vibrates, pushing the hairs against the second membrane. This changes the waves into nerve signals. These travel along the cochlear nerve to your brain.Having two ears allows us to perceive where a sound is coming from. This is because sound waves will reach the ear closest to the source of the sound sooner, allowing the brain to interpret the location of the sound.Hearing Test
Humans can usually hear sound at frequencies between 20 Hz and 20,000 Hz (20kHz). As we get older, our ability to hear the high end of the range progressively diminishes. Most teenagers can no longer hear 20kHz, and the high range for most people gets progressively lower as they age.
Below is a video which allows you to test your hearing range. Do not play this too loudly, as the higher frequencies can be uncomfortable.How to Choose a Hearing Aid : What a Hearing Aid Does
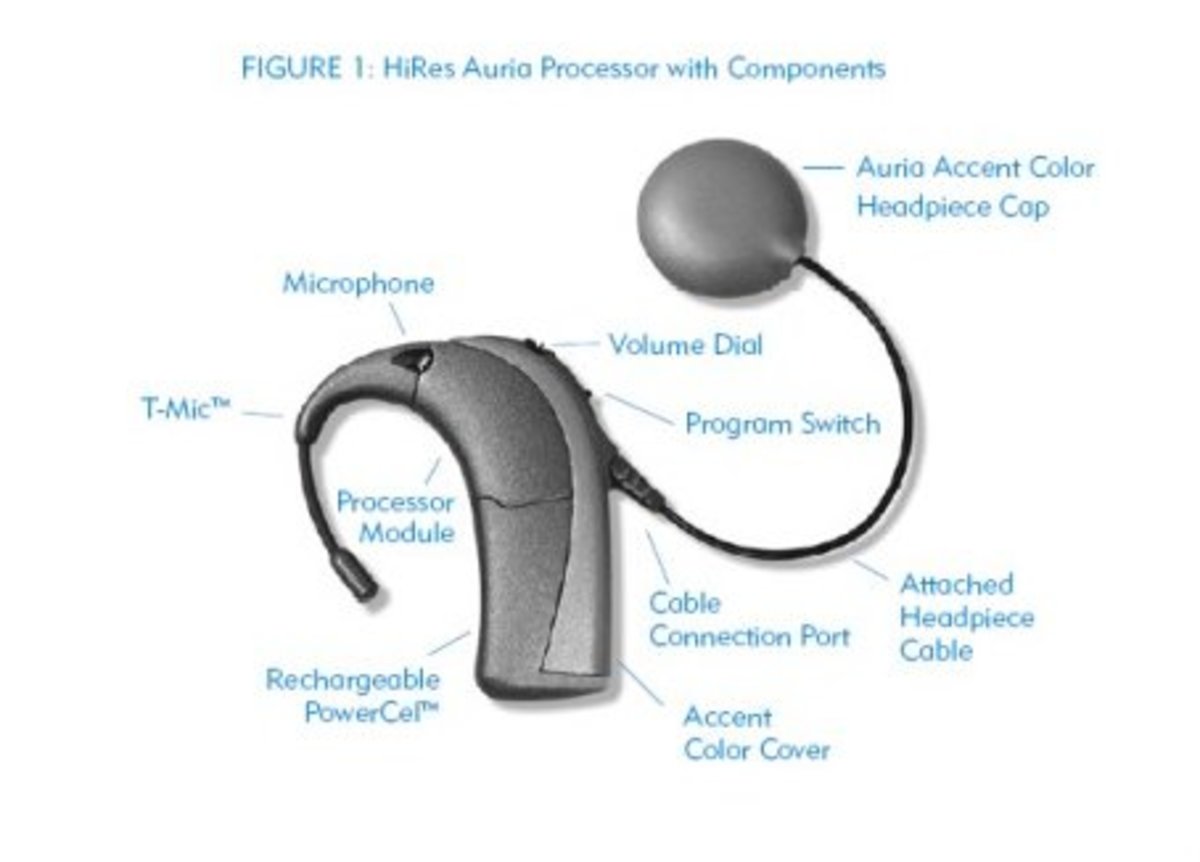
What Does The Cochlear Implant Do?
"Many people with hearing loss can use hearing aids to amplify sounds and help them hear. For some people with severe or profound sensori-neural deafness hearing aids do not help. These people may make use of the cochlear implant.
The cochlear implant replaces the function of the entire ear. It uses a microphone and directly stimulates any remaining hearing nerves using electricity to enable the brain to perceive sound."