Inverted ‘U’ Hypothesis of Kuznet's: Development and Inequality

Introduction
In the field of development economics, many studies conducted by various economists focusing on the trend of different socioeconomic factors like economic growth, population growth, inequality, structural changes, employment etc. Professor Simon Kuznets was a renowned economist who propagated his famous theory titled ‘Kuznets’s inverted ‘U’ Hypothesis’. In this thesis, Kuznets tell us about the relationship between economic growth and distribution of income. He published his article relating to this titled “Economic Growth and Income Inequality” in American Economic Review in 1955. Professor Kuznets got Nobel Prize for this work in 1971.
The Idea of Kuznet’s Inverted ‘U’ Hypothesis
The theory studies the relationship between economic growth of a country and inequality in income distribution. The theory says that, in the early stages of economic development, inequality will be higher. Then, gradually the economic system itself will reduce inequality. Therefore, he says inequality will be higher in underdeveloped economies and lower in developed countries. This can be explained with the help of the following figure.
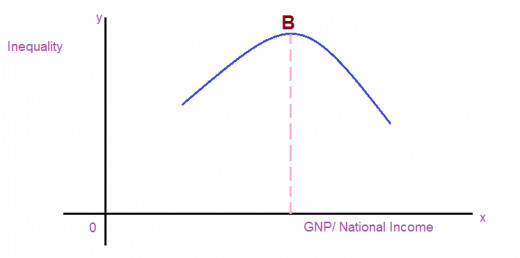
In the above figure, a change in national income/ per capita income is represented on the ‘x’ axis and the level of inequality on the ‘y’ axis.
Initially, the starting of growth will increase the tendency of inequality. When the economy grows, initially the richer sections of the society will get more benefits than the poor class. This expanding tendency of inequality will continue at a certain level. In the figure, ‘B’ is the point, where maximum inequality is concentrated. Then, when the economy continues for further development, the inequality will began to reduce. Therefore, at the maximum level of growth and development of an economy inequality will be lower.
Causes of Increase in Inequality in the Initial Stages of Development
In the first stage of growth of an economy, inequality in terms of income will be much higher. This happens because of many reasons. When a country enters in to the path of development, there will be structural changes. That means, as an impact of growth and development, the economy may focuses on industrial and service sectors. This will reduce the priority consideration of the agriculture. Along with the structural changes, there will be large urbanization. Because most of the industries are locating in the urban areas. So, in fact a huge portion of national income will flows in to the urban area due to the influence of higher industrial and service sectors. At the same time, major portion of the workers in the economy will depend the agricultural sector. However, the agricultural workers will earn only lower incomes. This is why in the initial stages of development the income inequality between rich and poor become higher.
Causes for the Decline in the Inequality in the Later Stages of Development
The theory says that, in the later stages of economic growth and development, the inequality will decline. This is because of many reasons. When the developmental process of a country goes ahead, naturally the profit of entrepreneurs will fall. So the higher level of development will reduce the per capita income of rich class in the economy. On the other side the demand for agricultural products will increase sharply because of the neglecting of agriculture. Then gradually the lower income earning group will earn more income. Further, when development began to experience, the educational system, health care etc will also improve. In fact inequality will decline in the long run.
The trend explained in the theory is that, the rate of inequality will decline in accordance with the development of the country. But in the initial stages of development, the inequality will increase steadily. This phenomenon in the theory is labeled as ‘trickle down effect’ by Hirschman and ‘spread effect’ by Gunner Myrdal.
Another trend associated with the developmental progress of a country is the relationship between per capita income and population growth. When a country achieved higher level of development, population growth rate will be lower and per capita income will be higher and more equitable.
Conclusion
The theory is not free from criticisms. The main challenge of the theory is that, it is not based on empirical analysis. At the same time, larger assumptions and speculation plays an important role in the idea. However, there are some experiences of such development in some countries like Costa Rica, South Korea, Sri Lanka etc.