MCQs on Eye, Ear and Taste
Picture of Eye

The eyes
Vision is the most important of the five senses by which we gather information about the surroundings. Any difficulty with the vision, we get a lot worried and fearful. How do we see the things in our surroundings with the help of eyes? The eyes gather light from the surroundings and it allows for the brain to determine the colour, shape and movement of these objects with the help of specialised structures.
The eye has got three tissue layers; the cornea/sclera, the uvea and the innermost layer of retina. The retina has got specialised cells like rods and cones that convert the light energy of different wave lengths into nerve impulses and they are transmitted to brain through the optic nerve.
The eye works like a camera. There is a lens in the eye which together with cornea, helps to focus the light rays on the retina
Aqueous humor
Aqueous humor is a clear watery fluid produced by the ciliary body and collected in the anterior cavity of the eye. The main function of aqueous humor is to provide nourishment for cornea and lens. The aqueous humor is drained by the canal of Schlemm. If there is any block in the drainage, it may give rise to a rise in the intraocular pressure and may result in Glaucoma.
Far vision and Near vision
During far vision, the muscles of the ciliary body are relaxed. During near vision, the muscles of the ciliary body contract resulting in reduced tension on the suspensory ligaments attached to the lens. By this, the lens becomes more round in shape increasing the refractive power.
Fill in the blanks
1.Cones absorb photons from a .......... of wavelengths for ......... vision
2.Rods absorb photons from a ............of wavelengths for ........... vision
Answers:
1. narrow range , color
2. wide range , night
Picture of ear
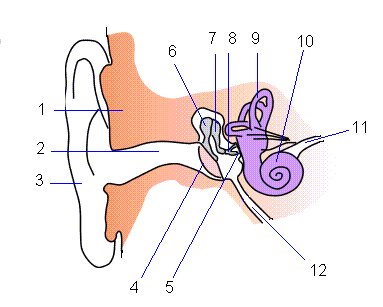
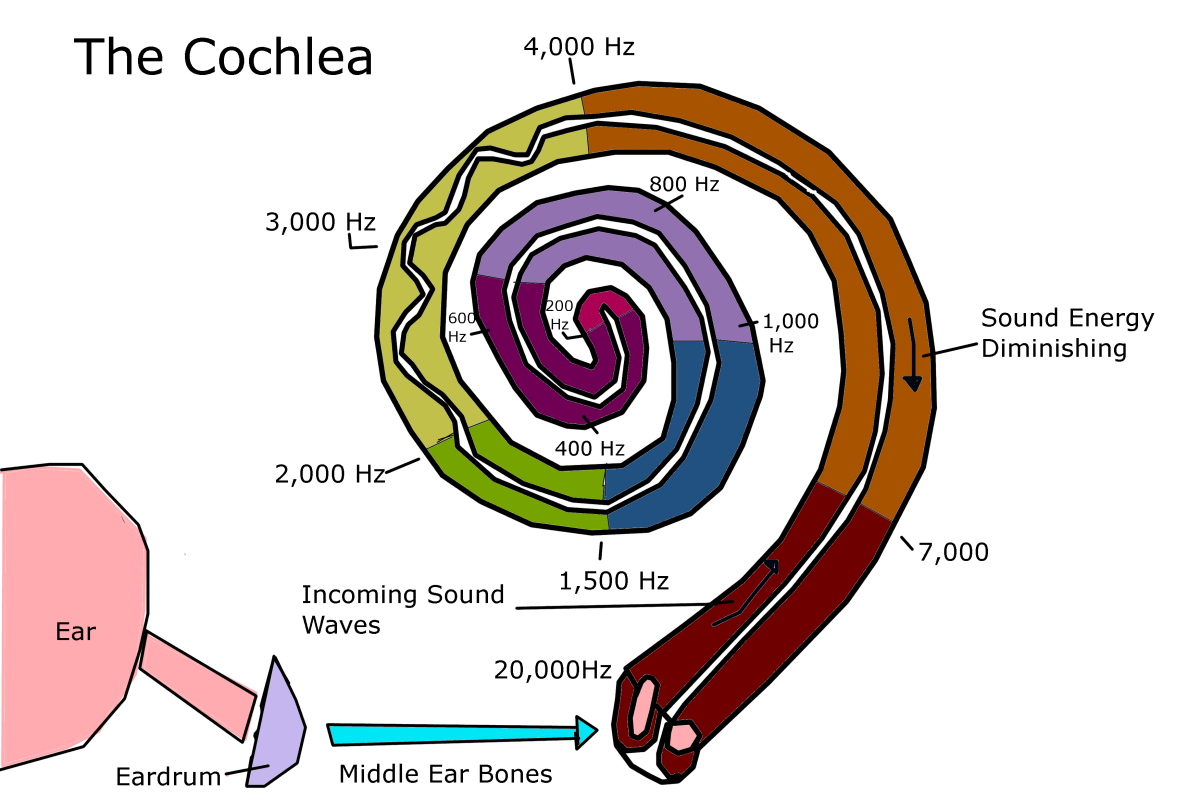
The ears help in hearing. It has got complex structures that convert sound into fluid vibrations and into nerve impulses that are carried on to the brain. In addition to helping with hearing, ear also helps to maintain the equilibrium of the body. The ear has three parts; the external, middle and inner parts.
External Ear
The external ear has got pinna (made up of cartilage and covered with skin) and the external auditory canal. The external auditory canal is a narrow canal ending with tympanic membrane or the eardrum. The tympanic membrane is a semi-transparent membrane stretching across the diameter of the ear canal and separating the middle ear from the external ear. The tympanic membrane or the ear drum starts vibrating when struck by the sound waves funnelling down the external auditory canal.
Middle Ear
The middle ear contains three small bones; malleus, incus and stapes, collectively known as auditory ossicles. Sound which is travelling down the ear canal causes the tympanic membrane and the attached auditory ossicles to vibrate. These vibrations are transferred to cochlea which is a part of the inner ear.
Inner Ear
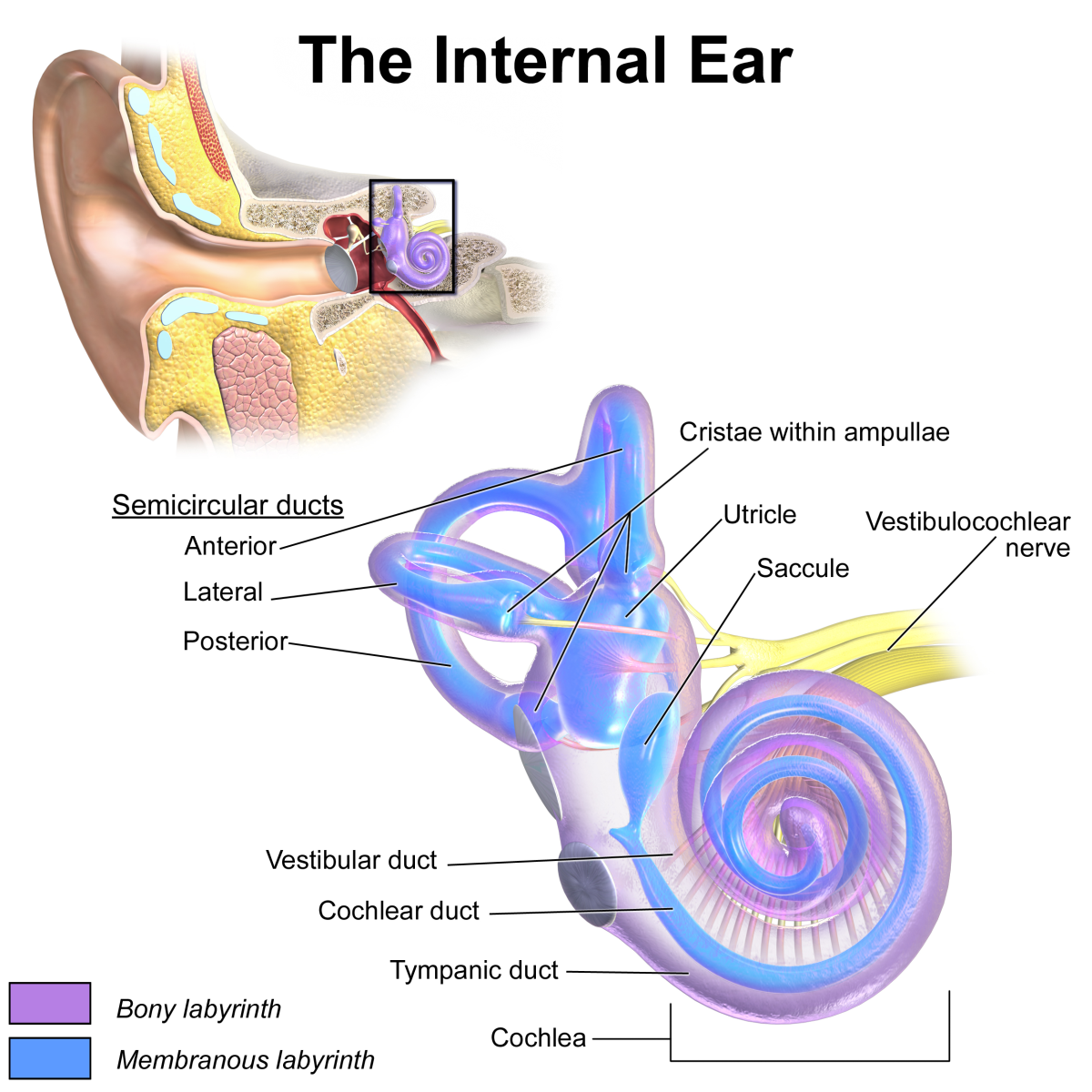
The inner ear consists of cochlea and the vestibular system. Cochlea is a snail shaped, fluid filled structure lying deep within the temporal bone. It has got hair cells, the receptors for sound. From the cochlea, these vibrations are transferred to the cranial nerve for the brain to process. The semi-circular canals which are also fluid filled attach to the cochlea. The sensory cells of the vestibular system are in the ampullae of semi-circular canals, the utricle and saccule. These structures play a pivotal role in maintaining balance and coordination by sending information to the brain through cranial nerve. The vestibulocochlear nerve carries impulses from the semi-circular canals for the sense of equilibrium and cochlea for the sense of hearing. The fluid from the middle ear is drained into the pharynx by the Eustachian tube.
Picture of tongue

Taste
The tongue is the organ of taste. It is a strong muscular organ of the mouth. The tongue is covered with numerous taste buds on the surfaces of its papillae (tiny papules giving the tongue its rough structure). There are special taste receptors on these taste buds which can identify the chemicals associated with these five tastes; sweet, sour, salt, bitter and umami – meaty taste. Taste buds are formed when the chemoreceptors called the gustatory receptors coalesce together with other cells.
Fill in the blanks
- A salty taste is transduced by entry of ........through passive ion channels
- The binding of sweet compounds elevate .........leading to closure of ............ channels
- Sour compounds produce ........which penetrates the cell membrane and causes the closure of ........... channels
Answers
1. sodium
2. cAMPlevels, potassium
3. H+ , potassium
- Multiple choice questions on the functions of cell o...
Multiple choice questions for premedical competitive exams - MCQs on muscle stretch reflexes; tendon stretching
MCQs on muscle stretch reflexes; tendon stretching; a guide for students - MCQs on Cerebral Cortex and Subcortical Structures
Review questions (multiple choice) to prepare for medical entrance exams - Multiple Choice Questions on Neurons
A compact article on information about neurons and multiple choice questions on neurons to prepare for competitive exams.