MCQs on the Structure and Functions of a Cell
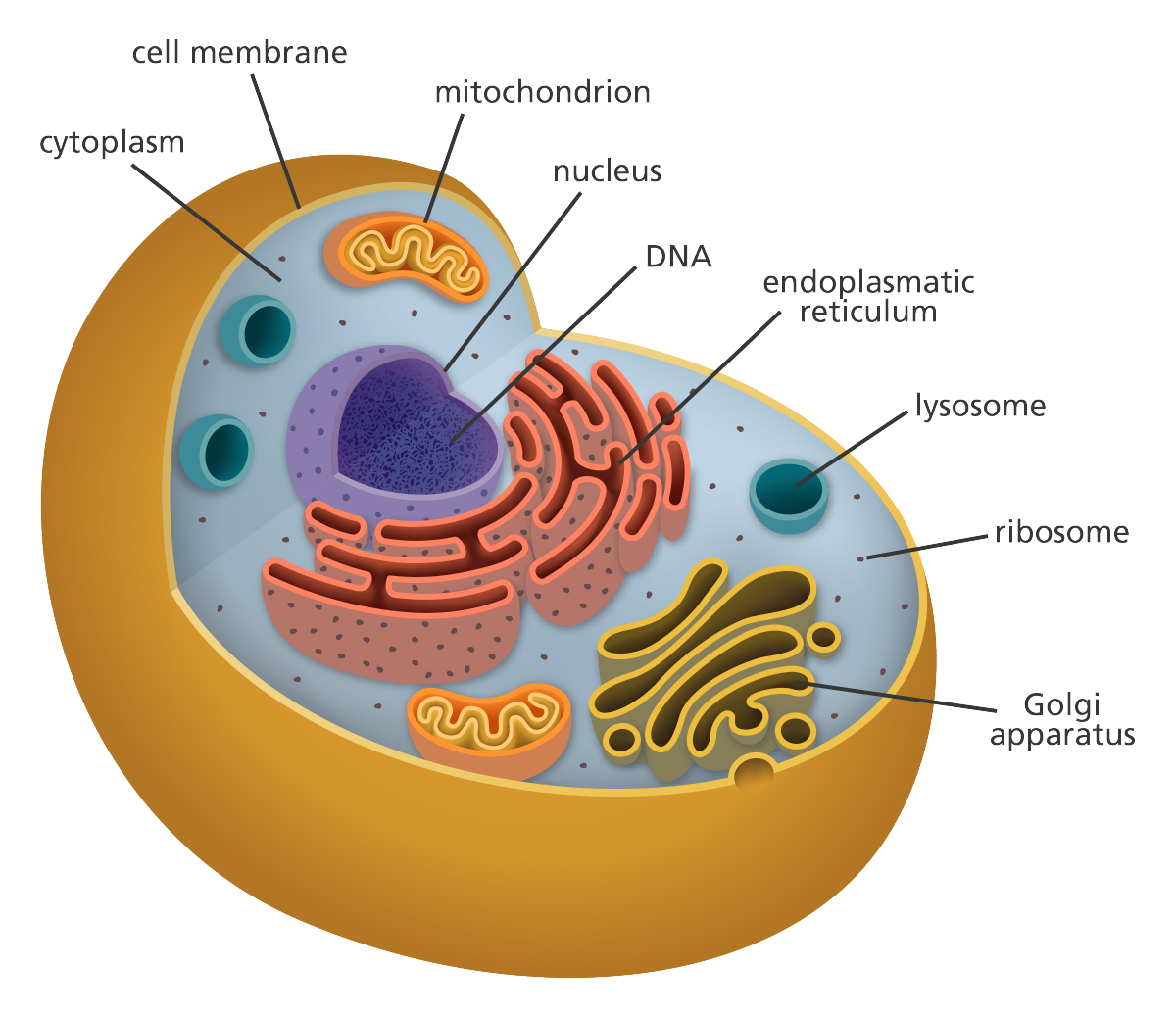
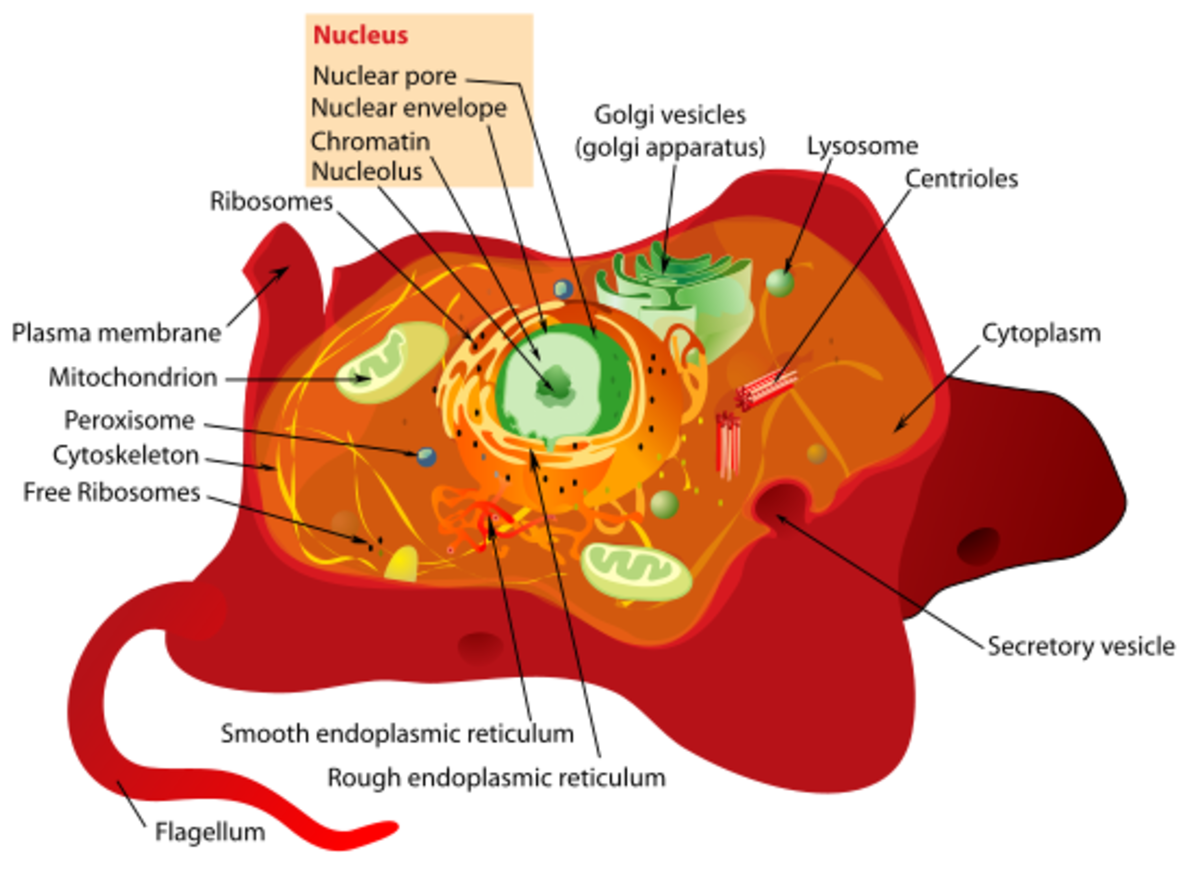
Cell

1. Each section of the chromosomal DNA that carries the information necessary for the synthesis of a single polypeptide is
Chromosome
DNA
Gene
Genome
2. The component of the cell composed of the cytosol and organelles
Cytoplasm
Nucleus
Nucleolus
Mitochondria
3. A highly coiled, condensed form of chromatin formed in the cell nucleus during meiosis and mitosis
Chromosome
DNA
Gene
Genome
4. The sum of all the chromosomal genes of a cell
Chromosome
DNA
Gene
Genome
5. A double helical molecule, consisting of two strands of four different nucleotides containing genetic information
Chromosome
DNA
Gene
Genome
Other MCQ Hubs
- Multiple Choice Questions on Electrolyte Disturbances
Electrolyte disturbance is something we need to manage everyday in the critical care units. Knowledge about management of fluid and electrolyte disturbances can be lifesaving. - Multiple Choice Questions on the Functions of Cell Organelles
Multiple choice questions for premedical competitive exams - Multiple Choice Questions on the Anatomy of Kidneys
Here is an article to learn about the basic anatomy of kidneys. There are also a few multiple choice questions on kidney anatomy. Useful for premedical entrance preparation. - MCQs on Brain: Cerebral Cortex and Subcortical Structures
Review questions (multiple choice) to prepare for medical entrance exams - Multiple Choice Questions on the Anatomy of Heart
Multiple choice questions on the Anatomy of the heart include few questions on the Anatomy of the heart at the high school level. It is useful for premedical entrance examination as well. - Multiple Choice Questions on Upper Limb Anatomy: Clavicle & Scapula
Upper limb bones are the first one to be studied in anatomy classes. Upper limb has a total of 64 bones. Answering mcqs is one of the ways to study bones, their borders, surfaces and attachments
6. A small accessory DNA molecule used for DNA cloning
Lysosome
Mitochondrion
Plasmid
Ribosomes
7. The site of ATP production through the process of aerobic respiration
Lysosome
Mitochondrion
Plasmid
Ribosomes
8. Proteins are synthesised in
Lysosome
Mitochondrion
Plasmid
Ribosomes
9. Digestion centre of the cell is
Lysosome
Mitochondrion
Plasmid
Ribosomes
10. The process by which cytoplasm divides, each half taking with it one of the two nuclei to form a new cell
Cytokinesis
Exocytosis
Mitosis
Phagocytosis
11. A special form of endocytosis involving internalisation of particulate matter
Cytokinesis
Exocytosis
Mitosis
Phagocytosis
12. A process of cell division where each of the two daughter cells receives a complete set of chromosomes
Cytokinesis
Exocytosis
Mitosis
Phagocytosis
13. A process in which a secretory vesicle fuses with the plasma membrane and materials are expelled into the extra cellular fluid
Cytokinesis
Exocytosis
Mitosis
Phagocytosis
14. A specialised protein that binds to DNA and organises its structure in the nucleus
Chromosome
Histone
Hormone
Peroxisome
15. A small membrane bound bag that is involved in digestion and food waste in a cell
Chromosome
Histone
Hormone
Peroxisome
16. A chemical messenger that helps regulate the activity of other tissues and organs
Chromosome
Histone
Hormone
Peroxisome
17. Three base sequence in a polynucleotide of DNA or mRNA that specifies the location of a single amino acid in a polypeptide chain:
Codon
Exon
Intron
Polysomes
18. A structure composed of ribosomes attached to a single strand of mRNA and helps in peptide synthesis
Codon
Exon
Intron
Polysomes
19. Segment of eukaryotic gene that consists of DNA coding for a sequence of nucleotides in a specific molecule of messenger RNA
Codon
Exon
Intron
Polysomes
20. Noncoding region of a eukaryotic gene that is transcribed into RNA but removed by splicing during production of messenger RNA
Codon
Exon
Intron
Polysomes
21. One of the most common types of fatty acids found in phospholipids
Palmitic acid
Cholesterol
Glycophorin
Spectrin
22. The most abundantly found steroid located in cell membranes
Palmitic acid
Cholesterol
Glycophorin
Spectrin
23. An intrinsic glycoprotein in the red blood cell membrane
Palmitic acid
Cholesterol
Glycophorin
Spectrin
24. An extrinsic protein found only on the cytoplasmic side of the red blood cell membrane
Palmitic acid
Cholesterol
Glycophorin
Spectrin
25. Any compound that binds with a high degree of specificity to a receptor
Agonist
Antagonist
Exon
Ligand
26. A ligand that binds with high affinity to a receptor but evokes no response
Agonist
Antagonist
Exon
Ligand
27. A ligand capable of binding to a plasma membrane receptor and evoking response
Agonist
Antagonist
Exon
Ligand
Another Hub on Cells and Cell Organelles
Answers
- Gene
- Cytoplasm
- Chromosome
- Genome
- DNA
- Plasmid
- Mitochondrion
- Ribosomes
- Lysosome
- Cytokinesis
- Phagocytosis
- Mitosis
- Exocytosis
- Histone
- Peroxisome
- Hormone
- Codon
- Polysomes
- Exon
- Intron
- Palmitic acid
- Cholesterol
- Glycophorin
- Spectrin
- Ligand
- Antagonist
- Agonist