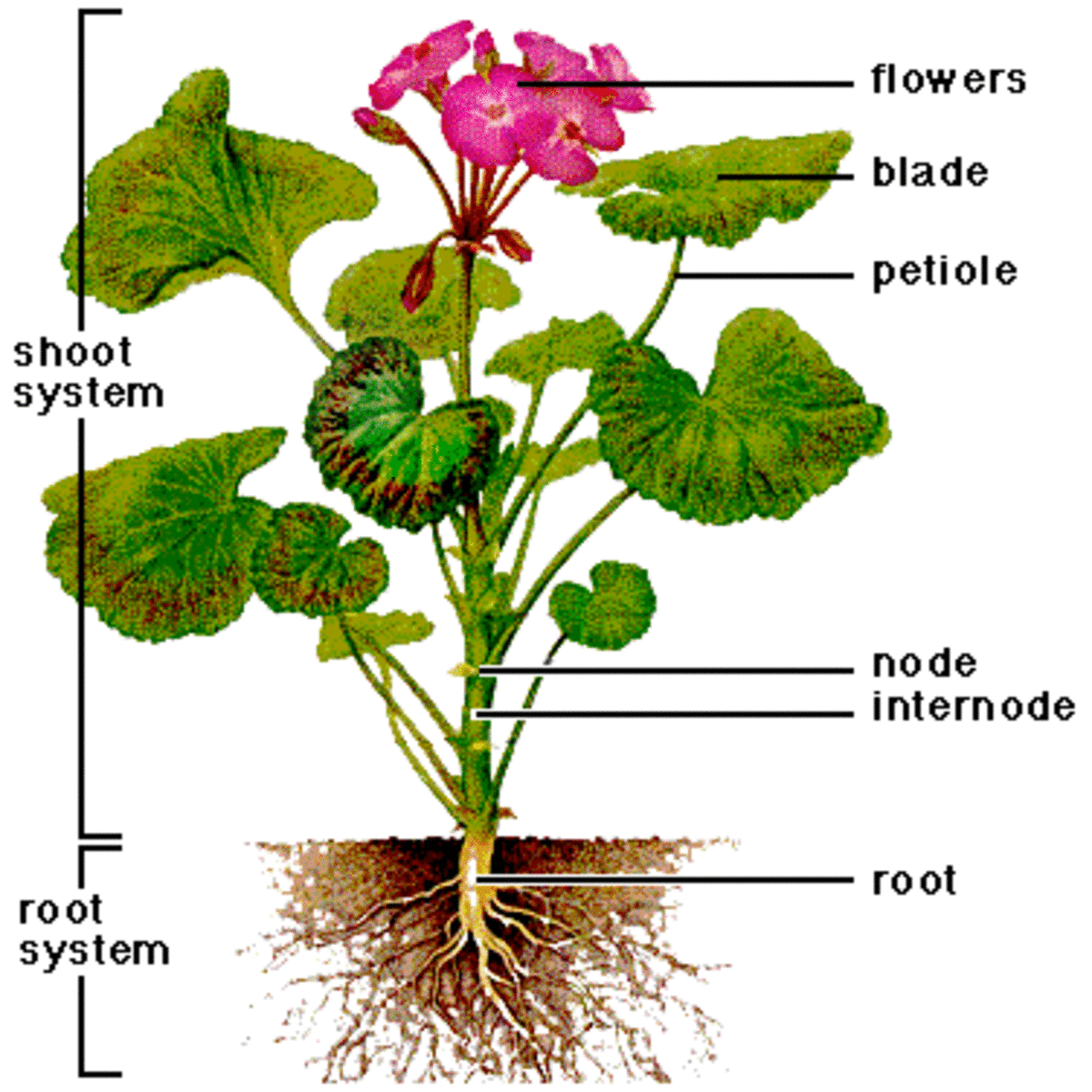
Reproduction in plants
Reproduction in plants
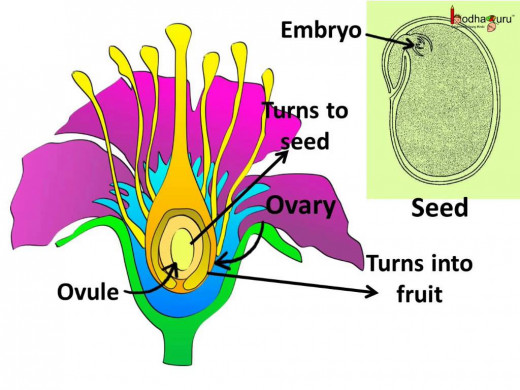
Reproduction in plants
Plants are very useful to us. Life cannot exist without plants. That's why we should grow more and more plants. But how do plants grow ? Let us read how new plants grow.
Reproduction is a process in pants and living beings by which they produce young ones of their own kind.
There are three methods of reproduction in plants:
- From seeds.
- From spores.
- Vegetative propagation (from body parts)
Reproduction in plants
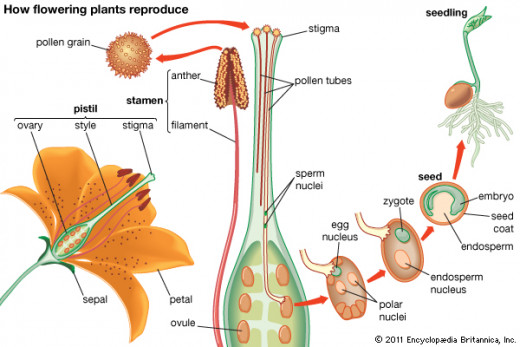
Reproduction in plants from seeds
Flowers are the reproductive organ of a plant. Flowers grow into fruits. Fruits contain seeds. Seeds germinate to grow into plants. All seeds do not grow into a plant. Some seeds are eaten by animals; some seeds are destroyed by rain or wind; some seeds do not get right soil or enough air and water.
Parts of seeds
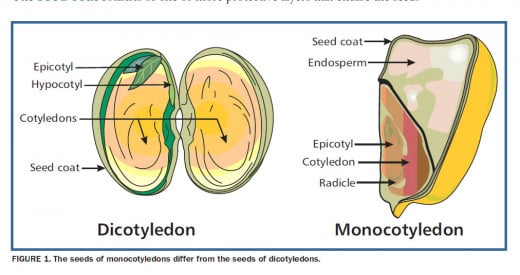
Parts of a seed
A seed has two main parts:
1.Seed coat:
It is the outer protective covering which protects the baby plant inside the seed. It has a tiny hole through which the seed gets water.
2. Seed leaves or cotyledons:
They contain food for a growing baby plant.
Germination
The development of a seed into a seedling (baby plant) is called germination. When the seeds get proper air, water and warmth (sunlight), they germinate to form a new plant.
Germination is one of the most important process in the cycle of reproduction in plants.
Germination

Stages of germination
Seed absorbs water from the soil. As a result, the seed coat becomes soft. It breaks up and baby root comes out. It develops and goes deep into the soil. Baby shoot develops and grows towards the sunlight. Gradually, the shoot grows and tiny leaves appear on it. When the leaves grow, they start preparing their own food. The new plant produces flowers which grow into fruits. Fruits contain seeds. Under suitable condition of air, water and warmth, these seeds germinate and grow into new plants. In this way the cycle of reproduction in plants continues.
Dispersal of seeds
The scattering of seeds to different places away from the mother plant is called dispersal of seeds. Agents like air, water, animals, birds, human beings and explosion help in dispersal of seeds.
Dispersal helps the seeds to reach the suitable place where they get enough air, water and warmth needed for their germination. It prevents the overcrowding of seeds near the mother plant. Thus helps in reproduction of plants.
Agents of dispersal
1. Wind
Seeds of madar, cotton and maple are light in weight. They have wings and hair which help them to move away to far-off places with wind.
2. Water
Coconuts are hollow from inside with a fibrous covering. This makes them float in water. The lotus has a spongy part which enables it to float on water.
3. Animals
Animals and human beings eat fruits and throw their seeds here and there. Some seeds stick to the bodies of animals as they have hooks, thorns or stiff hair. In this way, they reach far-off places with the help of animals, e.g., xanthium and cocklebur. Birds swallow some seeds and these seeds are passed out in their droppings.
4. Explosion
Fruits of peas, balsam and lady's finger burst open when dry. Theur seeds are thus thrown away with a great force.
Agents of dispersal
From spores
Plants like fern and mosses reproduce through spores. These are non-flowering plants. They do not have fruits and seeds. They produce spores which germinate under suitable conditions and grow into new plants.
Vegetative propagation
In some plants, reproduction does not take place from seeds, but new plants grow from body part like root, stem, leaves, etc. This type of reproduction in plants is called vegetative propagation.
Plants growing from roots

Plants growing from roots
Plants like sweet potato, beetroot, etc. develop from the root of the parent plant.
Plants growing from stems
Onion, potato and ginger are stems that grow underground. New plants grow from them. The stem of the onion is known as bulb. A potato has buds called 'eyes'. Any part of potato has 'eyes' on it can grow into a new plant.
Sometimes new plants grow from the stem cutting of the parent plant like rose, sugarcane and hibiscus.
Plants growing from leaves
Plants like bryophyllum reproduce through leaves of the parent plant.
Crops, fruits and vegetables
We eat different kinds of crops, fruits and vegetables. They all need different types of soil, temperature and water for their proper growth.
In India, farmers grow two types of crops:
1. Rabi crops :
Crops grown in winter are called rabi crops, e.g., wheat and gram.
2. Kharif crops :
Crops grown in summer are called kharif crops, e.g., rice, maize, jowar and bajra.
Different plants require different kinds of soil to grow.
CROPS
| SOIL
| STATE
|
|---|---|---|
1. Rice, jute
| Clayey soil
| West bengal, Orissa, Kerala
|
2. Wheat
| Loamy soil
| Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh
|
3. Cotton
| Black soil
| Maharashtra, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh
|
4. Jowar, bajra
| Sandy soil
| Uttar Pradesh, Rajasthan
|
5. Tea
| Mountain soil
| Assam, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka
|
Apart from crops, fruits and vegetables are also grown in India. Vegetables like brinjal, lady's finger and gourd are grown in summer. Vegetables like radish, cabbage and cauliflower are grown in winter.
Himachal Pradesh is known as the apple state in India. It is famous for its high quality apples.
Nagpur is famous for orange. Kerala is known as the land of coconuts.
Maharashtra is known for its alphonso mangoes.
Methods of getting healthy crops
- Soil should be prepared well.
- Healthy seeds should be used.
- Manure and fertilisers should be added.
- Soil should be irrigated at the proper time.
Protection of crops
- Fencing should be done to protect crops from grazing animals.
- Fungicides and weedicides should be used to protect crops from fungus and weeds.
- Insecticides and pesticides should be used to protect crops from insects and pests.
Storage of crops
The harvested crops should be stored in dry, waterproof and insect-proof containers.
Fruits and vegetables should be packed in cardboard boxes with insect killing medicines.
Remember
- The process of giving birth to young ones by living things of their own kind is called reproduction. When this process occurs in plants, it is called reproduction in plants.
- Seeds germinate to grow into a plant.
- The development of a seed into a seedling is called germination.
- The scattering of seeds to different places with the help of wind, water, animals, etc. is called dispersal of seeds.
- The development of a new plant from a stem or leaf is called vegetative propagation.
- Good quality seeds, manure and irrigarion help to get good crops.
- Harvested crops should be dried and stored in air-tight containers.