The Universe is Absurd: What's at the end of space? Is the Universe infinite?
So what's the issue? Why is there a paradox?
Have you ever asked yourself the question: what is on the other side of the end of space? It is a question that worries even the brightest minds. At the surface, the issue is wholly paradoxical. This apparent paradox can be summarized as follows: If space ends, what is on the other side of it? If space never ends, how can we reconcile the concept of infinity? It's a catch-22 at its finest.

Here's an explanation of each side
The thought of space ending, or the Universe being finite, always makes the individual try to explain what could be beyond that threshold. After all, there has to be something. If there is some sort of cosmic border, there needs to be something on the other side of that border. It is a product of humans' undying need to question. This is the reason we have come so far in our pursuit of reality. I applaud these individuals' curiosity and would like to explain a few possible loopholes to ease their cognitive strain. First, i'll touch on the other side of the paradox.
The next obvious case is that the Universe is infinite. When compared to the border problem, an infinite Universe seems easier to reconcile at first. You can simply claim that it is infinite, and because this resolves the issues with a finite Universe, people assume it must be correct. The problem is, we can no better conceptualize infinity than we could a border with nothing beyond it. Just because a theory resolves some issues doesn't make it correct, and doesn't mean it doesn't have issues of its own. After all, what could cause something to be infinite? Wouldn't that force have to be more than infinite? What does infinite even look like? Why is my brain on fire?
So... you said something about a loophole?
Yes, I did, but first let's talk about what it means to be flat in a cosmic sense. Don't worry, I'm going somewhere with this. The type of Universe we live in depends on whether it is flat, positively curved, negatively curved, and either finite, or infinite. I will go over the concept of flatness first, and then attempt to tackle infinity.
Alright, let's talk about "flatness," whatever that means
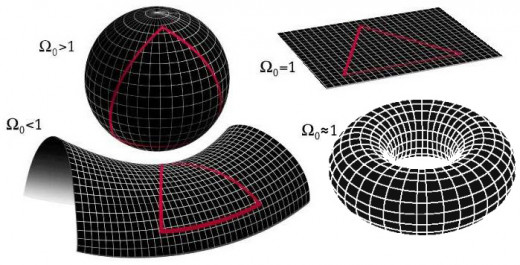
What I mean when I say "flat" is that space follows Euclidean geometry. Parallel lines stay parallel, and right angles stay perpendicular into infinity. This idea of flatness or higher dimensional curvature can be true in three dimensions. The problem is, it is just exceedingly hard to visualize, since we typically have access to a maximum of three dimensions. We need an extra one to see the curvature.
Contrarily, we can easily evaluate if a two dimensional surface is curved because we can see into the dimension in which it is curved. Think of a ball. A ball has a two dimensional surface which experiences a positive curvature, allowing something to travel around it and end up in the same place it started. This has super cool implications for our Universe problem but unfortunately, not everything is positively curved. In contrast, flat or zero curvature would be like a piece of paper where things move in a manner consistent with Euclidean (normal) geometry. For the Universe problem, this is worrisome since paper has edges, or borders, which we do not like.
Now we're going to learn about infinity, right?
Yeah, we are getting to that. We actually do think is that the Universe is "flat," but we don't know if the Universe is infinite or finite. Although I say we think the Universe is flat, that's just what the data is saying so far. There is a discrepancy toward positive curvature, but it's within the margin of error. It could simply be that the Total Universe is so large that our comparatively small Observable Universe seems flat, kind of like how we used to think the Earth was flat because our sample was too small.
The reason I bring up flatness again is because it has distinct implications for the possibility of an infinite or finite Universe. In order to shed more light on this interconnection, and hopefully bring our understanding closer to reality, I will now explain four different cases that explore the possibilities of curvature and infinity in our Universe. There exist more, but I find these to be the most likely.

Case #1: A flat, infinite Universe
If we have a flat Universe, which we think we do, the most intuitive conclusion would be that it extends into infinity. If you traveled in one direction, you would never get to the end, no matter how fast you could travel, and you would never return to where you started. This would truly be an infinite, flat Universe, and some physicists like this scenario best.
The reason I have a problem with this theory is that it implies an infinite amount of matter and energy. This is an issue since we think all of the energy/mass in the Universe came from the Big Bang. Since the Big Bang occupied/produced a finite amount of space at its origin, it seems unlikely it would be able to reach infinity in a finite amount of time. This is all the time we have so far, it is finite, 14.7 billion years.
You cannot turn something from a finite thing to an infinite thing without adding an infinite amount of that thing, which would take an infinite amount of time. If we leaned that the Universe was infinite, which would probably be impossible to observe anyway, it would invalidate the Big Bang Theory or any theory with a finite origin. We are confident in our theory of the origin since it has been validated by Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation. Still, we've been surprised before.
Case #2: A flat, finite Universe
Another theory is that the Universe is flat, but finite. This would be like the piece of paper I mentioned earlier. Since the Universe is constantly exponentially expanding, it will likely reach infinity eventually, but it will take an infinite amount of time to do so. I like this theory because it respects time as a currently finite thing.
What I do not like is that this theory implies there is an edge of space. Nobody I have talked to likes the idea of borders in space. If we were able to travel fast enough to get to that edge, we have no way of conceptualizing what might happen. Seriously, what is on the other side of that border?
Personally, this is enough to want to reject the theory, but we should be careful not to let our own potential misunderstanding invalidate an otherwise worthy theory. After all, relative to us, this proposed edge of the Universe is moving much faster than the speed of light, and can therefore never be reached. In this sense, even this version of the Universe would be effectively limitless.
Case #3: A spatially flat, finite, borderless Universe
There is a workaround that keeps the Universe spatially flat, and finite, all without the existence of an edge, or border. This all sounds great, but the theory does have one drawback, it is increasingly convoluted. Here's how it goes: the Universe is spatially flat, and finite, but shaped like a torus (think of a doughnut) or an analogous shape.
You would be able to travel infinitely in one direction, but would eventually be in the same place you left off, like travelling around the globe. This would be kind of like a repeating, sidescrolling video game where you start seeing the same terrain and generated NPCs if you play long enough. Note that space would feel infinite, perpendicular lines would not cross each other, and the Universe would have no borders, but the amount of mass and spacetime would be finite.
This resolves our issues with infinite mass/space via finite time, and borders, but does so with a significant increase in complexity, which has been shown to be a bad sign for theoretical physics. It also implies multiple paths to the same points with varying distances. This means that someone travelling through the hole of the doughnut would get back to point A faster than someone travelling around the edge, which seems illogical, but we are currently testing for evidence of this. Don't worry, no astronauts will be harmed as a direct result of this testing, since we won't be attempting to actually send them beyond the speed of light. Not yet, at least.
Case #4: A positively curved, finite Universe
The final theory I will present is one that violates popular opinion and, as far as we know, the current data set. It is also the theory I most qualitatively enjoy. This is a Universe with positively curved space, analogous to the two dimensional surface of a sphere. It would mean that we could travel infinitely in any direction and reach the same place we left off, ignoring the cosmic speed limit. It also means that spacetime and mass would be finite, but feel essentially infinite. Using this theory, we rid ourselves of any inconsistencies with different paths being varied distances to the same points, like the doughnut example stated above.
The main problem with this theory is that the current data seems to suggest that our Universe is flat. It also implies that, on a large enough scale, our Universe is non-Euclidean, though we would never notice this in practical application since we live in a comparably microscopic realm of the Total Universe. Currently, the data is very close to a flat Universe, but has a very small tendency toward a positively curved one. This discrepancy is within the margin of error, which means we cannot reasonably admit it into evidence for the purposes of this discussion. It does, however, raise an eyebrow on my particular set of eyes.
I like to think of a possible reconciliation where our sample is just too small. After all, there has only been a relatively small amount time for us to collect this data set. This idea is analogous to when people thought the earth was flat simply because the area immediately surrounding them looked flat. Our observable Universe could be a significantly small enough portion of the Total Universe for it to appear flat right now. We may be wrong. We do not know. We may never know.
A Final Note: All of these theories are valid, and all have their respective downfalls. The truth is, we may never know how the Universe really works, but the journey sure is fun. If you have an idea for a configuration of the Universe that you think gets closer to reality than any that I have put forth in this article, please let me know about it in the comments. If you have come across a technical discrepancy in my analysis, please do your best to explain it below. I will review any reasonable criticism and I will publish a resolution following a diligent vetting process. Thanks for reading!









