- HubPages»
- Education and Science»
- Teaching»
- Lesson Plans
The 1930s and The Great Depression Hands-on American History Elementary Lesson Plan

This is the 34th lesson in a series of 35 hands-on lessons covering U.S. American History. This lesson focuses on the 1930s: the Great Depression and the New Deal. I used this plan while teaching a 45 minute history class for children in Kindergarten, 1st, & 2nd grades. Each lesson includes a biography report, history notebook page, history song, our favorite children's books, YouTube video, a history joke, & a variety of hands-on activities to make each lesson engaging & memorable. Use these fun lessons with your classroom, homeschool, after-school program, or co-op!
Depression Cake

1. If you are not limited by time, make Depression Cake. If you do make this cake in class, you'll need to skip the first two picture studies and the building activity. If you choose to not make this in class, you can make it at home and bring in the prepared cake for the students to taste.
Allow the children to measure, add, and stir the ingredients. Make sure everyone gets a turn. If you have more than 16 students, divide the group into 2 and have each group make a cake. (You can send home the extra slices.)
Depression Cake
- 1 1/2 cup flour
- 1/3 cup unsweetened cocoa powder
- 1 cup sugar
- 1 teaspoon baking soda
- 1/2 teaspoon salt
- 1 teaspoon white vinegar
- 1 teaspoon vanilla extract
- 1/3 cup vegetable oil (or your oil of choice)
- 1 cup water
Instructions
- Preheat oven to 350°F. Grease a 13x9 pan with non-stick cooking spray. (They didn't have this back then. They would have used lard/fat/Crisco.)
- Combine the flour, cocoa powder, sugar, baking soda, and salt.
- Add the vinegar, vanilla, oil, and water and combine thoroughly.
- Bake for 30-35 minutes or until a toothpick inserted comes out clean.
- Cool completely.
(The recipe is from https://kitchenfunwithmy3sons.com/chocolate-depression-cake/.)
You will need:
- Ingredients for the above cake, non-stick cooking spray, mixing bowl & spoon, measuring cups & spoons, 9x13 casserole dish
2. Mention the following:
- Who has made a cake before? What did you notice was missing from this cake? (eggs, milk, butter)
- The Depression Cake recipe was probably developed during World War I when families needed to conserve food at home so that soldiers could get food when they were away at war.
- It again became popular in the 1930s when many families didn't have much money following the Stock Market Crash of 1929 and the Great Depression, which we'll talk about today in class. This cake doesn't include expensive ingredients like milk, sugar, butter, or eggs, which was helpful when families didn't have much but still wanted an extra treat.
Student Biography Presentation: Eleanor Roosevelt
3. Student Biography Presentation on Eleanor Roosevelt
Review & Presidents Song
4. Review questions: On what island were immigrants processed after they arrived in New York? (Ellis Island) Name one of the tycoons who fueled our nation's Industrial Age by developing American resources such as railroads, oil, steel. (Andrew Carnegie, John D. Rockefeller, Cornelius Vanderbilt, etc.) What is one important event or action Theodore Roosevelt is known for? (Setting aside Yosemite Valley as a National Park, ending the big businesses, the Panama Canal, etc.) Name one of the countries that was part of the Central Powers during World War I. (Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Ottoman Empire/Turkey) Name one of the countries that was part of the Allies during World War I. (France, Great Britain, and Russia, United States) Who was the President of the United States during World War I? (Woodrow Wilson) World War I used trench warfare. What are trenches? (Long holes/ditches dug into the ground to protect the soldiers from getting shot at) Who lost during World War I? (Central Powers including Germany) Who won World War I? (Allies including America) In 1920, the 19th Amendment was added to the U.S. Constitution; what did it say? (Women could vote in national elections) What was another name for the 1920s? (Roaring Twenties or Jazz Age) What's something you learned last week about movies, music, or dancing in the 1920s? (Answers can vary.) What type of car did Henry Ford invent that was very popular in the 1920s? (Model T) Why could so many people afford a Model T car? (They could purchase it on credit, and it was made relatively inexpensively using mass production on an assembly line.)
5. Sing through the entire President's Song 2 times while either showing the video or flipping through pictures of the Presidents. (We add in "Trump, Biden, Trump" at the end of the song.)
You will need:
- Screen to show the below video or a book showing Presidents or point to their pictures on a President place mat
America's Changing Landscape & Industrialization

6. Study Charles Sheeler's painting American Landscape, 1930.
- In the 1920s lots of people started moving from rural farms to cities to work in industries like this one. People were able to make more money. They could now buy more and spend more. Businesses like this one started getting built around the East coast of America.
- Ask questions such as these from Picturing America: Find the only person in the painting. (A tiny figure on the railroad track) Find the ladder. Find the silos. What lines look like they were drawn with a ruler? Which lines aren't geometric? How do the buildings compare with the person?
- How does this compare to the painting we studied by Albert Bierstadt of Yosemite Valley? (Sheeler is trying to show how "the forces of human culture, propelled by industrialism, have overtaken the forces of nature..."
- How does this painting make you feel? Today this scene might upset us because we might see pollution or the destruction of nature, but at the time it "would have stood for the triumph of American ingenuity."
- Does this look more like a painting or a photograph? Sheeler was originally a photographer and wanted to make his painting look like a photograph. He tried to make sure none of his brushstrokes showed.
You will need:
- a copy of Charles Sheeler's painting American Landscape, 1930
Buildings & Skyscrapers
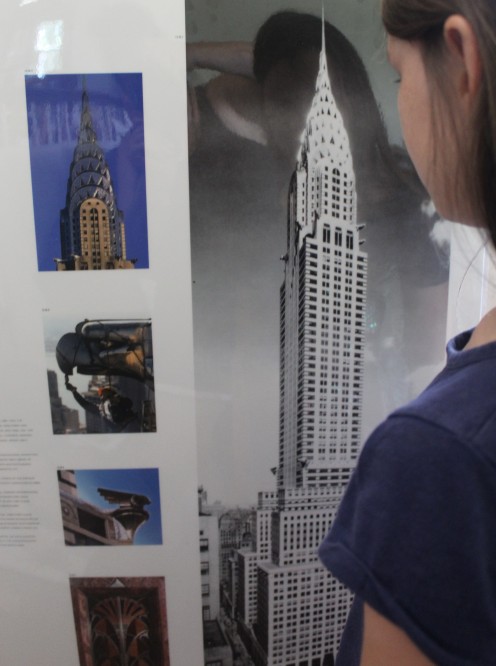

7. Show a picture of the Chrysler Building, 1926-1930, designed and built by William Van Alen. (Alternatively, show the Empire State Building.)
- In the late 1920s, there was a race to create a new type of building called a skyscraper because it was so tall. People who design buildings are called architects. Not only were architects trying to build tall buildings, they were also trying to create beautiful works of art.
- Use questions such as these from Picturing America: Find the triangles, squares, rectangles, and semi-circles on the Chrysler Building. (These shapes were important to the art style called Art Deco, which was popular in the 1920s.) How does this building look like a car/automobile?
- This building was built for Walter P Chrysler, one of the wealthiest men in the car/automobile industries. Who's someone else we learned about last week that ran a car company that made Model T cars? (Henry Ford)
- The building is supposed to remind you of a car. The building has stainless steel to make you think of polished chrome on a car. Some parts (frieze) look like hubcaps.
- [Show a picture of the Empire State Building.] When it was finished, the Chrysler Building was the tallest building in New York City. A year later (in 1931) the Empire State Building beat its height by 202 feet.
- Even worse, the architect who designed and built the Chrysler Building, William Van Alen, never received full payment for his work because of something called the Great Depression.
- We'll talk about the Great Depression in a moment. First, let's have a building contest like they did in New York at that time.
You will need:
- a picture of the Chrysler Building & Empire State Building
Building Contest
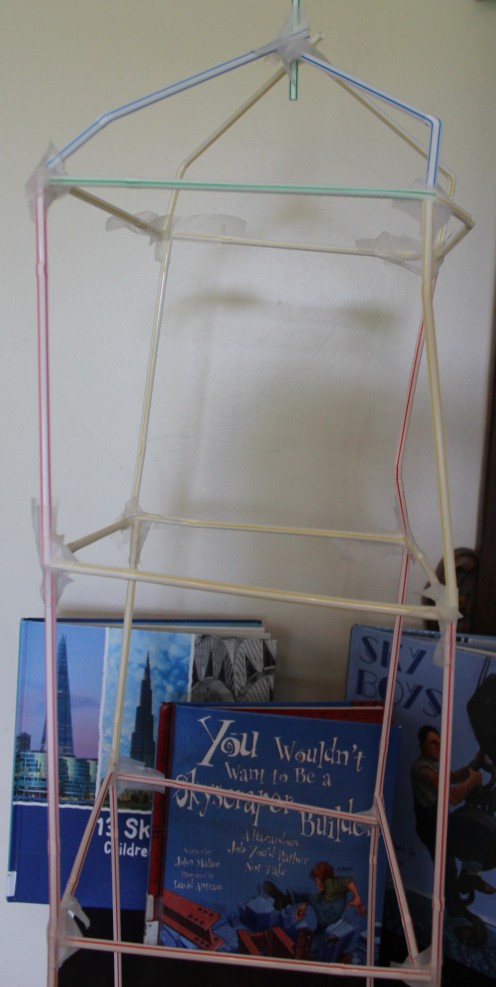

8. Building the tallest skyscraper race:
- Divide the children into groups of 5-7.
- Give them each a box of bendable straws and scotch tape.
- Have each group try to build the tallest "building" in 5 minutes.
- After 5 minutes are up, allow students to admire each group's design.
- Name the winner of the highest skyscraper contest. Their building can be named the "Empire State Building." The second highest building can be named "the Chrysler Building."
You will need per group of 5-7 children:
- a box of bendable straws & scotch tape
The Stock Market Crash and the Great Depression

9. Quickly describe the Stock Market Crash of 1929 and what caused the Great Depression by saying something such as:
- [Show some fake money such as prints of the Reichsmark (pictured above).] Something sad happened with money in 1929. Who has money? Who has a savings account at a bank like First Federal? My children do. When they get birthday money, they put it in a savings account at First Federal. First Federal then takes the birthday money that Sophia put in there along with the money I put in there and the money that other people put in there.
- What do you think would happen to our money if First Federal closes for good and shuts its banks forever? Do you think we'd get our money bank? Today, yes, we'd get our money bank (up to $250,000) if our bank is FDIC insured. That means if First Federal has to close, the government would pay everyone back their money. That wasn't always the way it was, though.
- In the 1920s people were spending a lot of money to get nice things like a Model T car, helpful tractors for farms, nice dresses to wear to go out and dance the Charleston, nice suits to wear to the movie theater, etc. Sometimes they bought things on credit, meaning they didn't have all the money right then and would pay it off over time.
- Families weren't the only ones doing that, though. Countries were too!
- [Point to Germany on a map.] Who lost during World War I? (Central Powers including Germany) The Allies told Germany that because Germany had kind of started World War I, they had to pay back all the damage that was done to the other countries. It's kind of like if you draw on your kitchen wall with a Sharpie marker and your mom makes you scrub and scrub and scrub the wall until all the Sharpie marker is gone. Only what Germany had to do was much, much, much bigger and harder to do!
- [Pass out the fake money to each student until you don't have any left.] Do you think Germany had enough money to pay back all the Allies for all the buildings they'd blown up and all the people they'd killed? No, they didn't. How could they get the money? They borrowed it from places like American banks!
- For a few years Germany tried to slowly pay the money to the Allies, but eventually they said, "We can't do this anymore. We can't pay that money back." Uh oh.
- [Show a picture of wheat or show a piece of bread.] On top of that, during and shortly after World War I, farmers were able to sell lots of grain to countries in Europe who were fighting in World War I and couldn't spend the time to grow their own crops because they were fighting or cleaning up after fighting. Eventually the countries in Europe were able to grow their own food again and didn't need to buy it from American any more. The farmers in America, some of whom had bought farming equipment on credit, couldn't make enough money to pay their bills because not enough people were buying their wheat.
- By the late 1920s, some people weren't making as much money, so they weren't spending as much money. That meant businesses weren't making as much money. It got so bad that many companies began to close.
- Businesses got so bad that something called a "Stock Market Crash" happened.
- Let's first talk about the Stock Market. Who buys things from amazon.com? It's a huge company and makes lots of money, right? Wouldn't you like to make some money from amazon.com? Well, you can get some! Amazon.com needs money to run its company, so people like you, called investors, can buy a "stock" in amazon. That means you give some money to amazon.com for them to use for their company. If they make money, they give you some...but if they lose money, guess what? You lose some...or all of your money.
- That's what happened in 1929. Companies were losing money, so the people who were hoping to make lots of money when those companies made money lost A LOT or ALL of their money.
- People got scared, so they rushed to banks to get their money from the banks. Guess what happened. The banks ran out of money! Unlike today in which some banks are FDIC insured, banks could just close down and never give you your money. That's what happened to lots and lots of people. They lost their money from the stock market crash and from the run on banks, people rushing to get money from banks!
- This caused something called "The Great Depression." Lots of people lost their money. Lots of businesses closed. Lots of dads lost their jobs. Lots of families didn't have enough to eat. It was a sad time.
You will need:
- Fake money (such as copies of the German Reichsmark pictured above - at least 1 per student), a world map to show Germany, & a picture of wheat or show a piece of bread
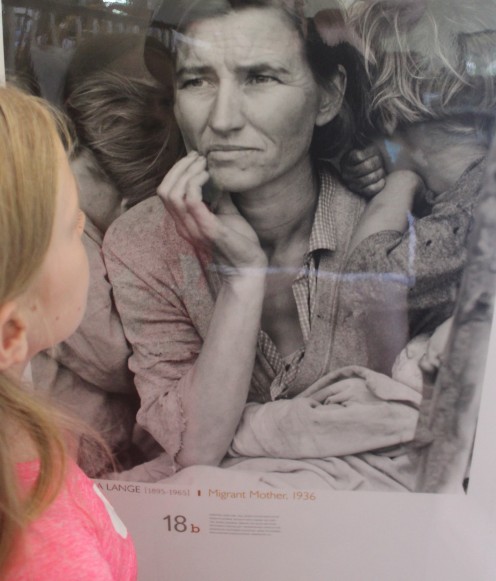
Migrant Mother, 1936 & Dorothea Lange



10. Flip through and quickly summarize (or read) Dorothea's Eyes: Dorothea Lange Photographs the Truth by Barb Rosenstock.
You will need:
Dorothea's Eyes: Dorothea Lange Photographs the Truth by Barb Rosenstock or other book on Dorothea Lange (such as
Dorothea Lange by Carole Weatherford)
11. Study Migrant Mother, 1930, by Dorothea Lange. Ask questions such as these from Picturing America:
- What do you first notice when you look at this photograph? Why do you think you notice that?
- Describe the woman's clothing. What does her clothing suggest about the woman and her children?
- Look at the expression on the woman's face. How do you think she feels? What might she be thinking?
You will need:
- a copy of Migrant Mother, 1930, by Dorothea Lange
- (optional) Above coloring page of Migrant Mother
12. New Deal: Mention that Dorothea Lange took this photo and it was quickly used around the country to show how desperate many families were because of the Great Depression.
- President Franklin D. Roosevelt used photographs like this to insist that the government needed to use lots and lots and lots of tax dollars to create programs to help people who were going through difficult times. This was called the New Deal.
- Many historians feel like Franklin D. Roosevelt's New Deal prolonged the Great Depression by having the government rather than individuals, churches, businesses, and charities be the ones to help.
Great American Dust Bowl

13. If life wasn't difficult enough for farmers in the West, the 1930s also experienced the Great American Dust Bowl during which dust storms blew up across the West. Summarize The Great American Dust Bowl: A Graphic Novel by Don Brown by quickly flipping through a few pages.
You will need:
The Great American Dust Bowl: A Graphic Novel by Don Brown or other book on the Great American Dust Bowl of the 1930s
14. Review: In the late 1920s what type of building were architects racing to design and build? (a skyscraper; the tallest building) Name a skyscraper that was built during that time. (Chrysler Building or Empire State Building) Which country borrowed lots of money from other countries and from American banks but then couldn't pay back all the money they borrowed? (Germany) What happened in 1929 when lots of companies and then lots of people lost lost of money? (Stock Market Crash) Because of the Stock Market Crash of 1929, lots of people didn't have much money so they didn't have much food; what was this time period called? (The Great Depression). President Franklin D. Roosevelt used photographs like The Migrant Mother by Dorothea Lange to insist that the government needed to use lots and lots and lots of tax dollars to create programs to help people who were going through difficult times; what was this called? (the New Deal) Meanwhile, what happened on lots of farms on the West because they hadn't been using good farming practices? (Dust Bowl)
15. Assign next week's biography report on Dwight D. Eisenhower.
Eating Depression Cake

16. Allow students to taste Depression cake.
You will need:
- disposable forks and plates
Joke

A Book to Read Each Day

We read through lots of books. In addition to the books we used in the above lesson, we also enjoyed:
Herbert Hoover by Mike Venezia
You Wouldn't Want to Be a Skyscraper Builder! : A Hazardous Job You'd Rather Not Take by John Malam
Eleanor Quiet No More : The Life of Eleanor Roosevelt by Doreen Rappaport
Make Your Mark, Franklin Roosevelt by Judith St. George
Born and Bred in the Great Depression by Jonah Winter
What Was the Great Depression? by Janet B. Pascal (short chapter book we read over a few days)
Thanks to Frances Perkins: Fighter for Workers' Rights by Deborah Hopkinson
Looking for all my lessons?
AMERICAN HISTORY FOR EARLY ELEMENTARY:
Native Americans & Columbus Lesson
Jamestown Lesson
Pilgrims Lesson
Thirteen Colonies Lesson
French and Indian War Lesson
Colonial Period & Revolution Rumblings Lesson
Boston Massacre & Boston Tea Party Lesson
First Shots & Declaration of Independence Lesson
American War for Independence Battles Lesson
Valley Forge & Battle of Yorktown Lesson
American Literature Lesson & American War for Independence Review
Colonial Christmas Party
Constitution Lesson
Three Branches of Government Lesson
President George Washington Lesson
Louisiana Purchase Lesson
War of 1812 Lesson
Monroe Doctrine Lesson
Trail of Tears Lesson
Oregon Trail & Battle of Alamo Lesson
California Gold Rush & Pony Express Lesson
American Industrial Revolution Lesson
Underground Railroad Lesson
Abolitionists & Women Suffragists Lesson
Civil War: The Confederate States & Abraham Lincoln Lesson
Civil War Battles Lesson
Civil War Party & End of Year Review Game
BONUS LESSONS (if you have room for a few extra classes):
Reconstruction Lesson
Wild West Lesson
Immigrants Lesson
Tycoons & Theodore Roosevelt Lesson
World War I Lesson
Roaring Twenties Lesson
Great Depression and the 1930s Lesson
World War II Lesson
ALL MY LESSONS:
Fun, Free Hands-on Unit Studies (My Lessons in All Subjects)
© 2025 Shannon








