My Heart is Racing! Could I Have Hyperthyroidism Even if My Lab Results are Normal? The Symptoms of Thyroid Disease
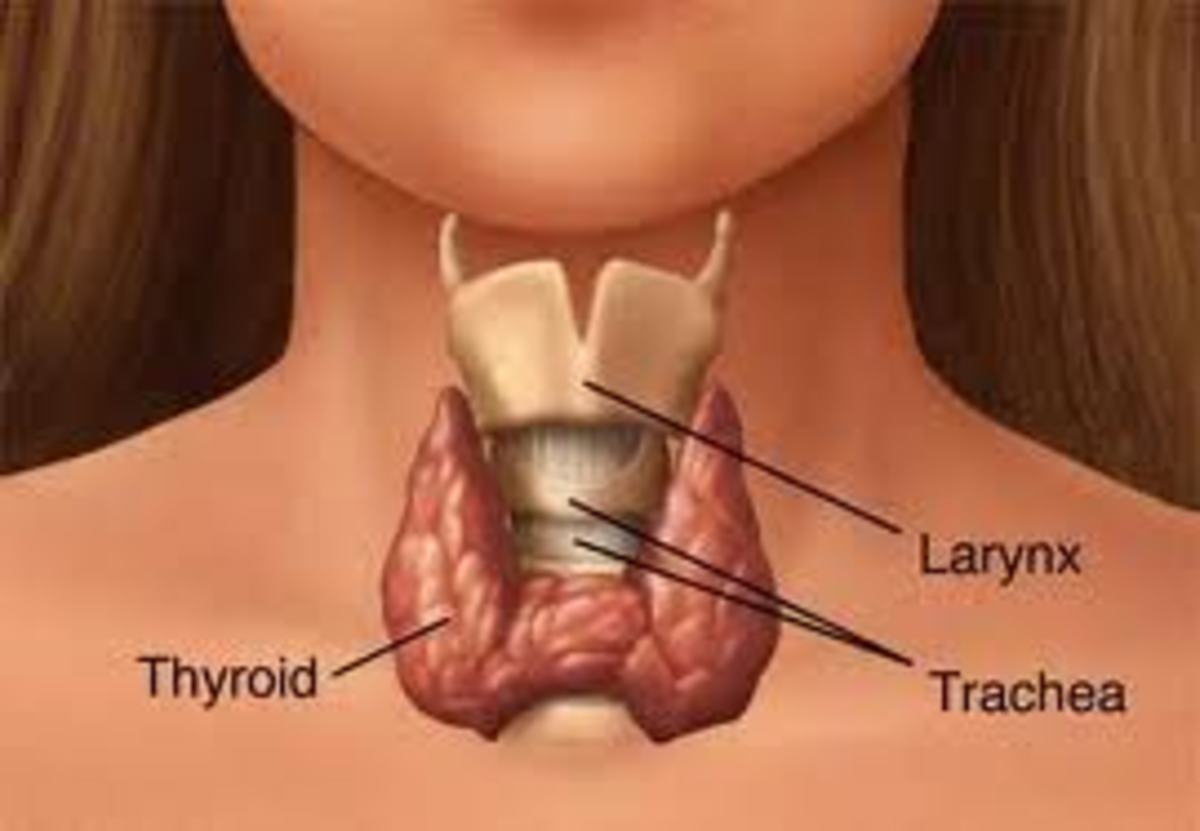
What is the Thyroid Gland?
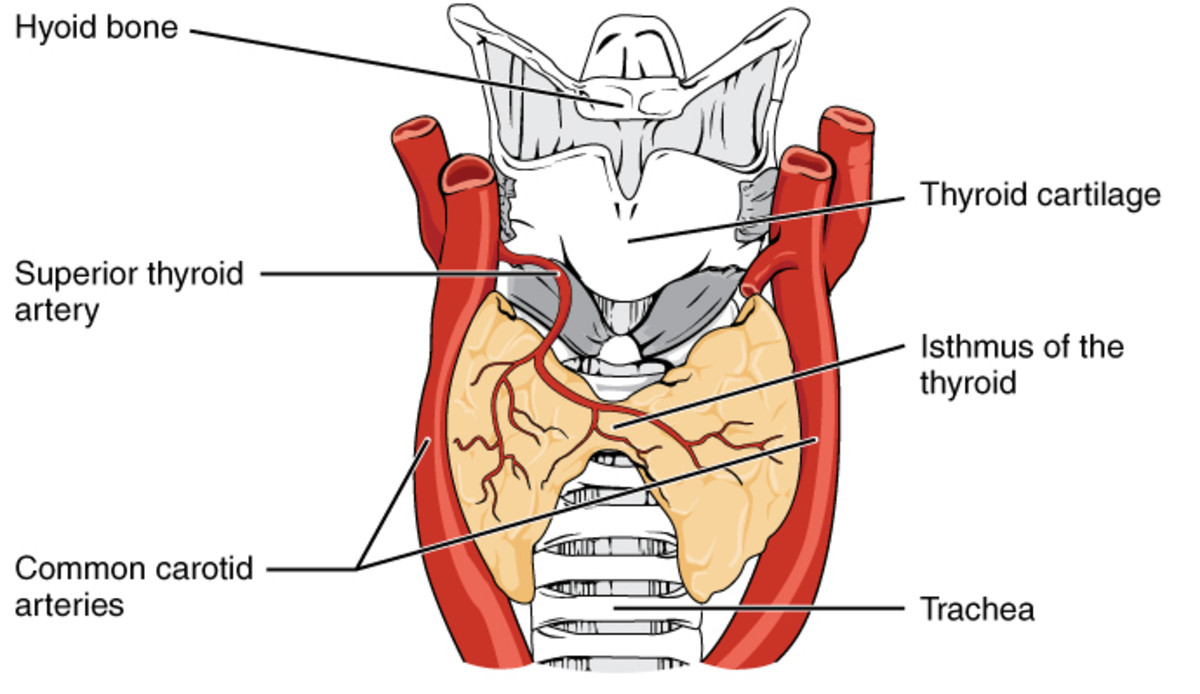
The thyroid is a small gland located in the front of your neck, just below your voice box, or “Adam’s Apple”. It’s a small gland, but its duties in regulating your metabolism and maintaining your health are tremendous. The basic idea behind a working thyroid gland is that it takes up iodine from the foods we eat and, in combination with the amino acid Tyrosine, converts it into thyroid hormones. These thyroid hormones are known as triiodothyronine, most commonly referred to as T3; and thyroxine, most commonly referred to as T4. From there, T3 and T4 are distributed throughout the body and regulate our metabolism. An excess or insufficiency of thyroid hormones can lead to many overlapping symptoms that become progressively worse if left untreated.
What is Hyperthyroidism?
Hyperthyroidism is a condition that occurs when your thyroid gland becomes over-active producing too much thyroid hormone. This can occur for several reasons. It may be that you are taking in too much iodine, maybe your thyroid has become enlarged or nodules have grown on it, or maybe its as simple as taking in excessive levels of thyroid producing medication to treat an under-active thyroid gland. Whatever the reason, the result is the same. Your metabolism speeds up to an unmanageable level, and every system in your body speeds up along with it. Left untreated for a long period of time, hyperthyroidism can be very dangerous, and rarely even fatal.
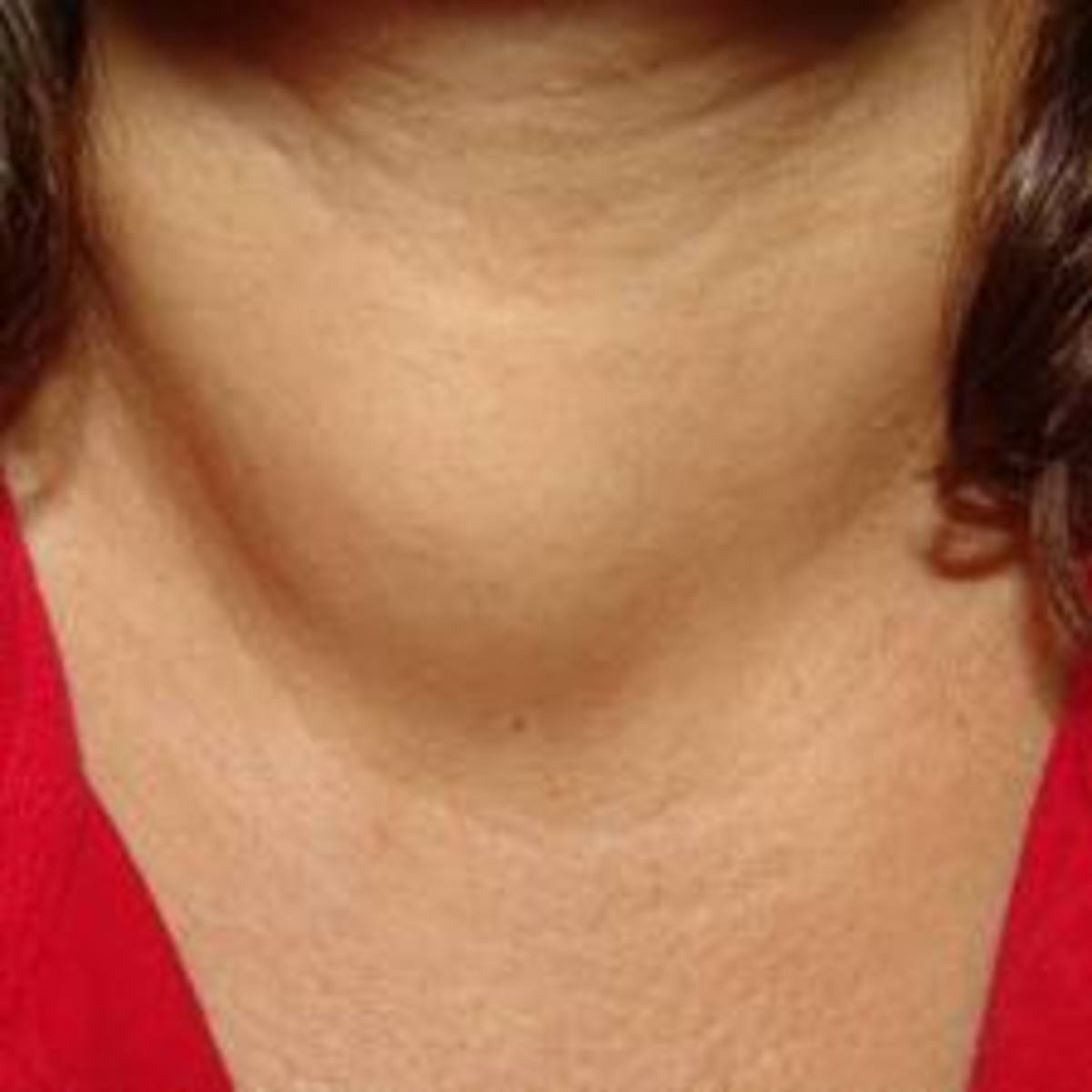
What are the Common Signs and Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism?
Think of your body as a car. When you have hyperthyroidism, your body speeds up, much as pushing the gas pedal of a car. Before you know it, the gas is all the way down and the brakes have given out. When the brakes give out, the only way to stop is to crash. Scary analogy, but very on point. You may notice only a few symptoms at the onset, but as time passes, the symptoms become more plentiful and become progressively more prominent.
Some of the more common symptoms are:
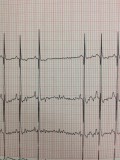
- Increased heart rate (Tachycardia)
- Mitral valve prolapse
- Bulging Eyes
- Sweating
- Issues with pregnancy/possible miscarriage
- Goiter (Swelling of the thyroid)
- High blood pressure
- Unintentional weight loss (rarely, you may see weight gain)
- Difficulty concentrating
- Difficulty staying on task
- In Women, lighter or no menstruation
- In Men, breast development
- Nervousness
- Hand Tremors
- Intolerance to heat
- Moodiness
- Muscle fatigue/weakness
- Extreme energy, to the point that you seemingly become exhausted for no reason
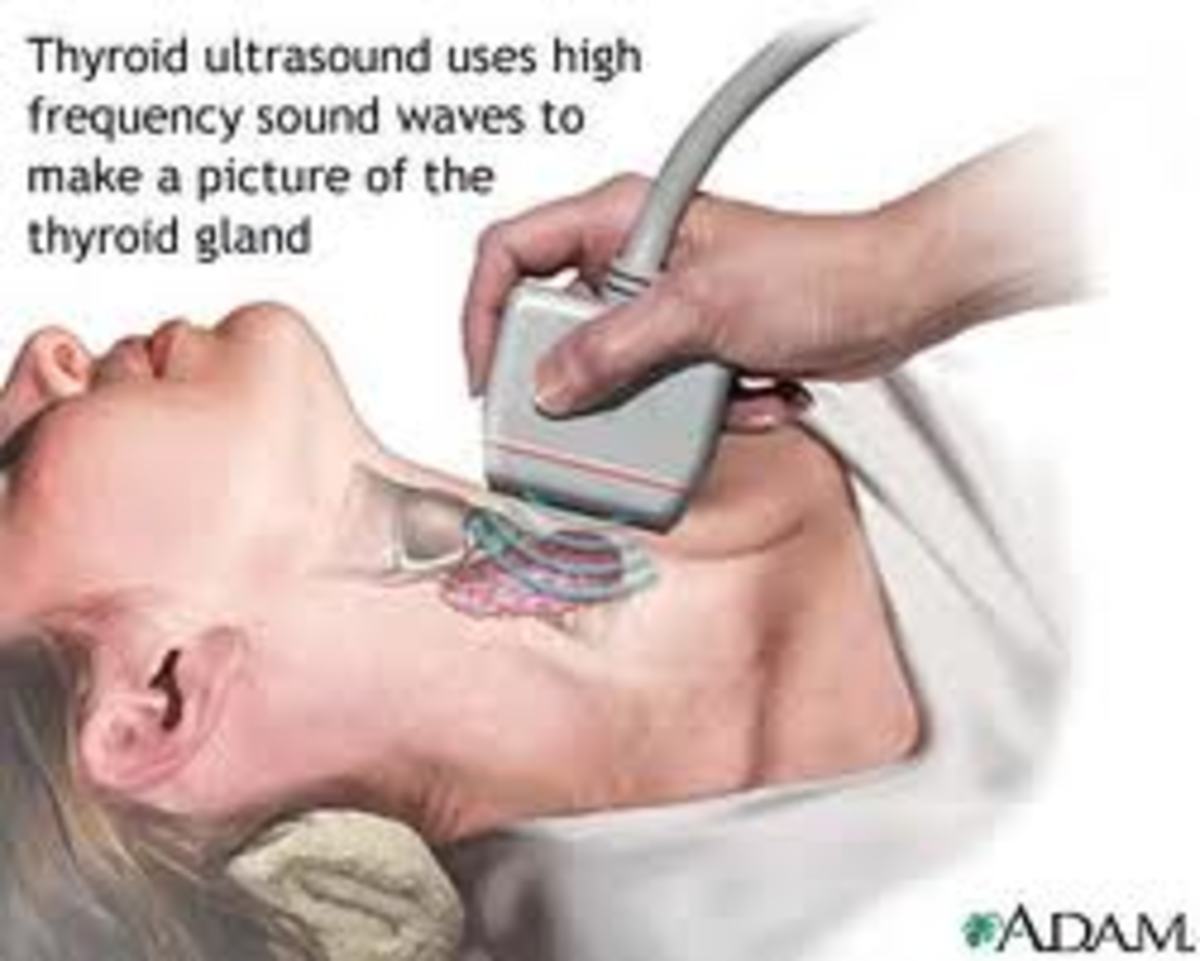
Tests to Determine if you have Hyperthyroidism
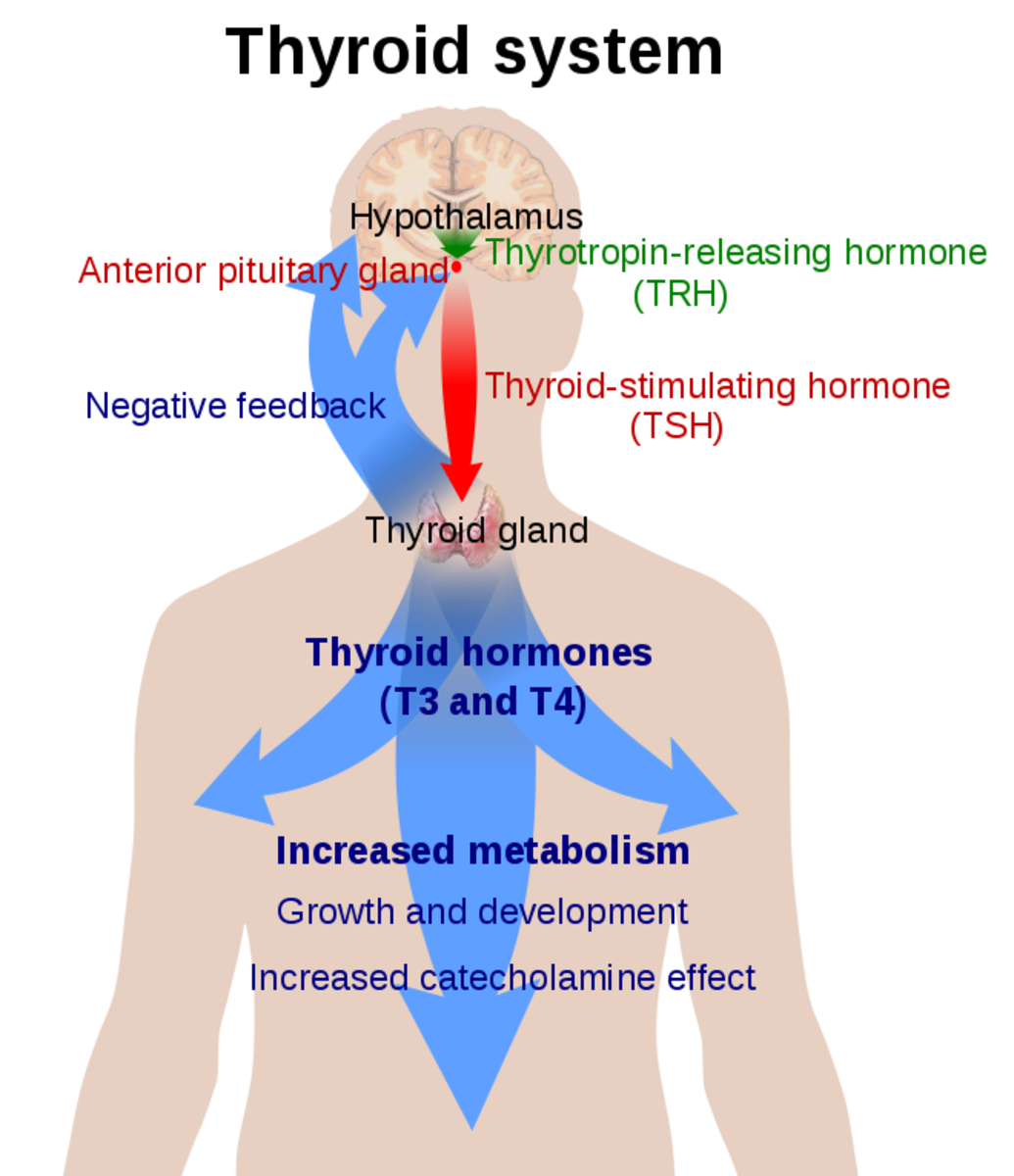
Your doctor will feel (palpate) your thyroid to check for any nodules or swelling. He will order a simple blood test to check the levels of your thyroid hormones. Many doctors will order a test of your TSH and T4 levels. A TSH test measures your Serum Thyrotropin, which is a thyroid stimulating hormone. TSH is produced by your pituitary gland and is the hormone that prompts your thyroid gland to release T3 and T4. If your TSH level is low and your T4 is high, there is a good indication that your thyroid is overactive and is producing too much thyroid hormone, driving your metabolism out of control. Most labs consider a TSH of under .5 to be too low, however, it is now being recommended that anything between a .3 and 3 is considered normal. Many people feel better with a TSH around 1. Even if your lab values show a normal range, talk to your Doctor about your symptoms. Many labs place normal values that are only indicative of an average. You could still have hyperthyroidism, and more and more labs are changing the levels that are considered normal to reflect a smaller range.
There are many other thyroid tests that can be ordered depending on your doctor, but the above are the most common. In addition to a blood test, your doctor may order an ultrasound of your thyroid gland to check for any abnormalities. This is usually done in cases where the doctor feels an abnormality when he palpates the gland at your visit.
Treatment of Hyperthyroidism
Luckily for hyperthyroidism patients, it is easily treatable. It may only require treatment with a daily anti-thyroid medication. If that approach doesn't work well, you may have to take a dose of radioactive iodine. Your thyroid will absorb the radioactive iodine, and much, if not all of your thyroid will be destroyed. Rarely, the best option may be to have your thyroid gland surgically removed. If your thyroid has to be removed or destroyed with radioactive iodine, you will begin a daily treatment of synthetic thyroid hormone pills. The pills are small, and side effects are EXTREMELY rare. Normally your doctor will start with a low dosage, and then re-test your thyroid levels in 6-8 weeks. If your levels aren't right, he will adjust your dosage and re-test again until your lab results come back normal. During this period, you may experience some symptoms of hypothyroidism. The best thing is that as the hormone adjusts to the correct levels, your symptoms will begin to correct themselves. Slowly but surely, you will get back to normal. Remember, though, that current TSH lab values are not quite in line what the American Association of Endocrinologists is currently recommending.
Common Lab Values of Thyroid Blood Tests
TEST SHORT NAME VALUE
- Serum thyroxine T4 4.6-12 ug/dl
- Free thyroxine fraction FT4F 0.03-0.005%
- Free Thyroxine FT4 0.7-1.9 ng/dl
- Thyroid hormone binding ratio THBR 0.9-1.1
- Free Thyroxine index FT4I 4-11
- Serum Triiodothyronine T3 80-180 ng/dl
- Free Triiodothyronine l FT3 230-619 pg/d
- Free T3 Index FT3I 80-180
- Radioactive iodine uptake RAIU 10-30%
- Serum thyrotropin TSH 0.5-6 uU/ml
- Thyroxine-binding globulin TBG 12-20 ug/dl T4 +1.8 ugm
- TRH stimulation test Peak TSH 9-30 uIU/ml at 20-30 min
- Serum thyroglobulin l Tg 0-30 ng/m
Hyperthyroidism News and Research
- Hyperthyroidism - MayoClinic.com
Hyperthyroidism Comprehensive overview covers symptoms, causes, treatment of an overactive thyroid gland. - Hyperthyroidism - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
- Hyperthyroidism WebMD: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments
What is hyperthyroidism? Hyperthyroidism means your thyroid makes too much thyroid hormone. Your thyroid is a gland in the front of your neck. It controls your metabolism, which is how your body turns food into energy. - THE MEDICAL NEWS | from News-Medical.Net - Latest Medical News and Research from Around the World
from News-Medical.Net - Latest Medical News and Research from Around the World - http://www.thyroid.org/patients/brochures/Hyper_brochure.pdf