Hypertension and Its Management
Definition:
Hypertension can be defined as persistent raised blood pressure of 140/90 mmHg or higher. Hypertension is another name for high blood pressure. It can severely impact the quality of life and it increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, and death.
Blood pressure is the force exerted by the blood against the walls of the blood vessels. How great the pressure depends on the work being done by the heart and the resistance of the blood vessels.
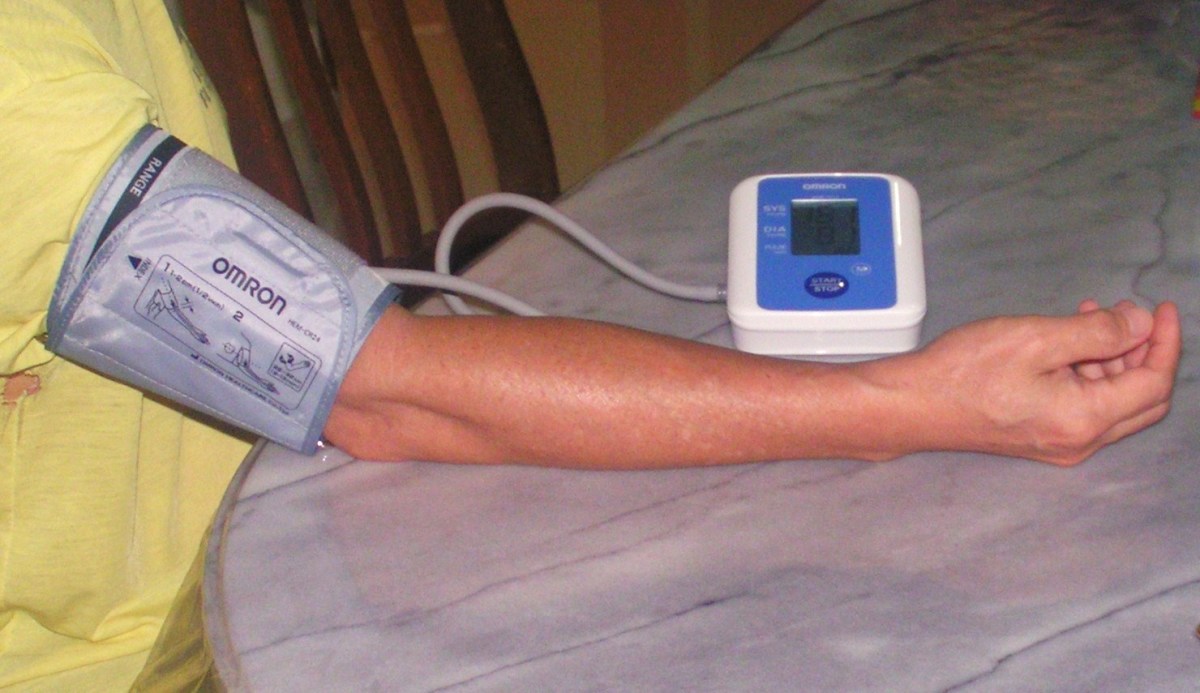
The blood pressure must have been taken on more than one occasion. The patient must have had good rest and in a comfortable position. Must not have taken coffee, cigarette or meal ½ an hour before measurement.
Normal sphygmomanometer with the appropriate size of the cuff for the arm. Reading is taken in both arms at the 1st visit and using the arm with higher reading in the subsequent measurement. The decision is based on multiple readings over weeks.
Normal blood pressure is 120 over 80 mm of mercury (mmHg), but high blood pressure is higher than 140 over 90 mmHg. The systolic reading of 140 mmHg refers to the pressure as the heart pumps blood around the body. The diastolic reading of 90 mmHg refers to the pressure as the heart relaxes and refills with blood.
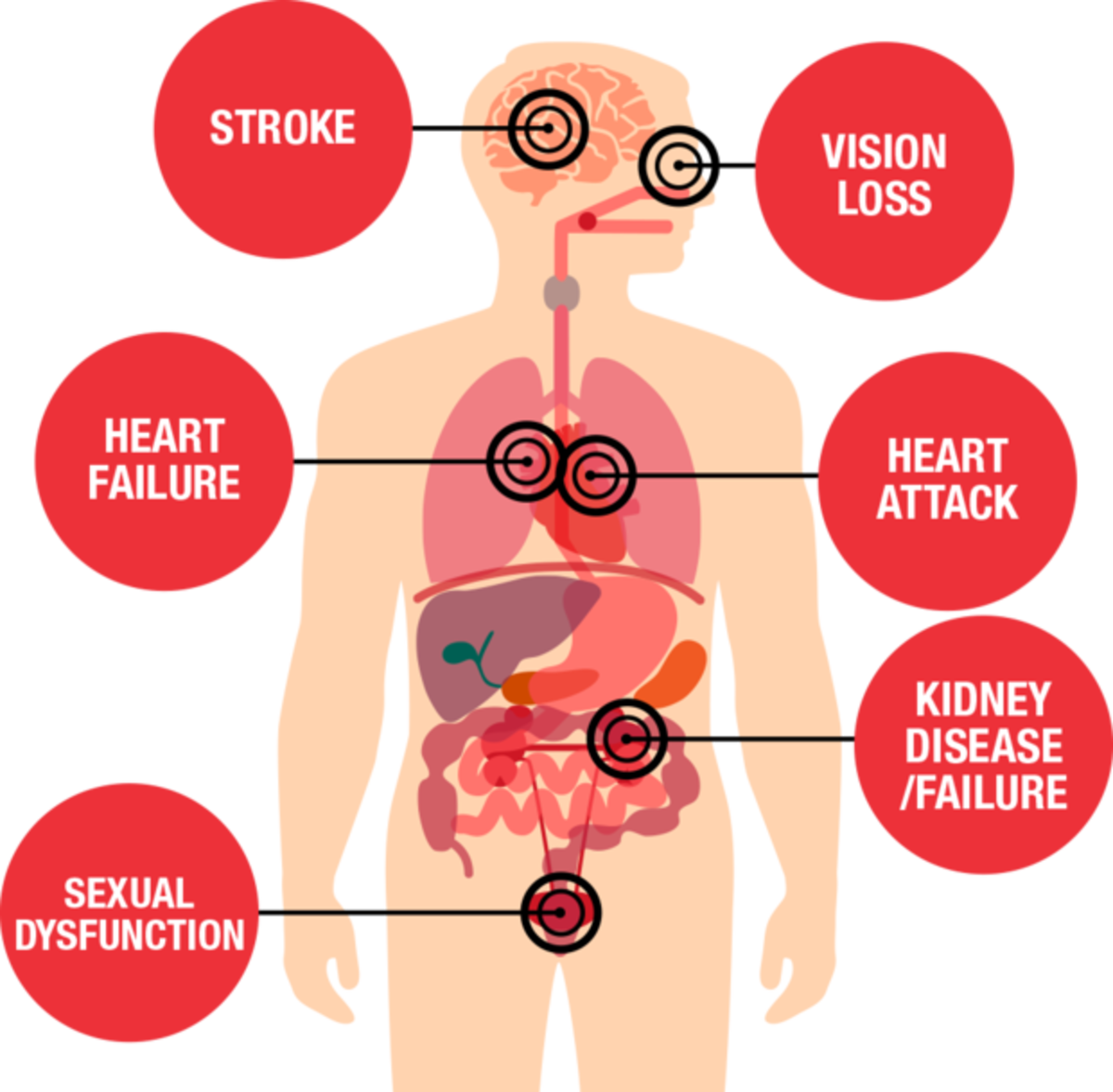
Acute causes of high blood pressure include stress, but it can happen on its own or it can result from a condition, such as a kidney disease. A heart attack, stroke, and other problems can be the result of unmanaged hypertension. The best way to address high blood pressure is the lifestyle factors.
Hypertension and heart disease are global problems. The World Health Organization (WHO) suggests that the growth of the processed food industry has impacted the amount of salt consumed and that this plays a role in hypertension.
Around 85 million people in the United States (U.S.) have high blood pressure.
1. Epidemiology:
Hypertension is highly prevalent worldwide. In the United State of America, about 20% of White Suburban population have Bp>160/95mmHg and about 5% have Bp>140/90mmHg according to Framingham data report.
The prevalence in Nigeria is reported to be 12%-22% in people above 15 years.
Global disease modality 2002:
Cardiovascular disease is a major cause of death globally.
2. Parthenogenesis of Hypertension:
Arterial Blood Pressure (ABP) is a product of cardiac output (CO) and Systemic Vascular Resistance (SVR).
Cardiac Output= stroke volume x heart beat per minute.
Systemic Vascular Resistance = force opposing the movement of blood within the blood vessels.
Anything that will alter any of these parameters will affect the blood pressure. There are some inbuilt mechanism that regulates blood pressure.
1. Sympathetic nervous system.
2. Vascular endothelium.
3. Renal system.
4. Endocrine system.
1. Sympathetic Nervous System (SNS):
Sympathetic Nervous System (SNS) releases a chemical norepinephrine- this will react with some target cells receptor within seconds to cause increase heart rate, increase cardiac contractility and wide spread vasoconstriction in peripheral arterioles.
It also promotes the release of renin in the kidneys.
2. Vascular Endothelium:
This is the single cell layer that lines the blood vessels. It produces vasoactive substances which help to maintain low arterial tone at rest. It also inhibits the growth of the smooth muscle layer.
Some are the potent vasodilator and others are vasoconstrictor. Endothelial dysfunction contributes to atherosclerosis and primary hypertension.
3. Rena System:
The renin system controls Na+ excretion and extra cellular fluid volume. The kidney does this via the renal renin angiotensin aldosterone system.
Stress leads to the immediate production of vasoconstrictor producing the immediate increase in systemic vascular resistance. If prolonged will stimulate adrenal cortex to produce aldosterone which causes Na+ water retention. Renal modular sent prostaglandin with vasodilator effect.
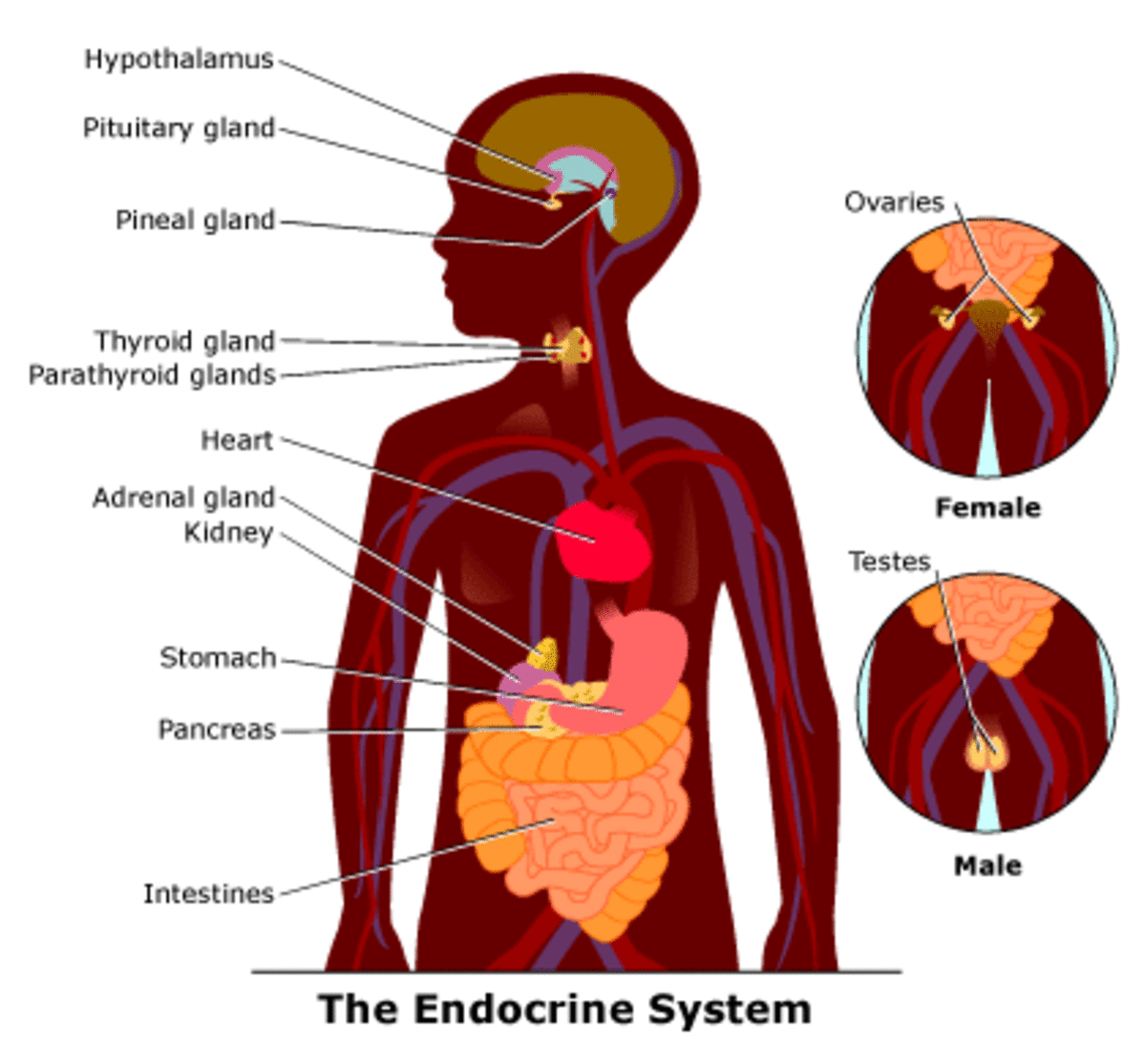
4. Endocrine System:
Endocrine system stimulates the sympathetic nervous system with epinephrine which increases heart rate and contrarily. Other hormones are involved in complex activities that regulate the Blood pressure in an individual. Regulating mechanism in a person in good health function to the demand of the body.
When there is a defect in the function of one or more of the regulating mechanism i.e.
1. Symphatic nervous system.
2. Vascular Endothelium.
3. Renal System.
4. Endocrine System.
Hypertension will develop.

3. Forms of Hypertension:
Hypertension can be primary or secondary. If high blood pressure is not caused by another condition or disease it is referred to as primary, or essential, hypertension. If it occurs as a result of another condition, it is called secondary hypertension.
1. Primary Hypertension:
Primary hypertension is elevated blood pressure without an identified cause. This accounts for about 95% of all cases of hypertension. Primary hypertension can result from multiple factors, including blood plasma volume and activity of the hormones that regulate of blood volume and pressure. It is also influenced by environmental factors, such as stress and lack of exercise.
Contributing factors to primary hypertension.
The following have been found to be contributing factors to primary hypertension.
i. Age
ii. Alcohol use
iii. Cigarette smoking
iv. Diabetes mellitus
v. Elevation serum lipid
vi. Excess sodium salt intake in diet
vii. Gender
viii. Family history
ix. Ethnicity
x. Sedentary life style
xi. Poor social economic status
xii. Stress
xiii. Hereditary- the interaction of genetic, environmental and demographic factor- increases the risk of hypertension.
High sodium diet increases water and sodium reabsorption noted in 20% of patient with hypertension.
Stress and increased sympathetic nervous system activity lead to high risk of developing hypertension.
2. Secondary Hypertension:
The specific cause of secondary hypertension can be identified. This is responsible for about 5% of cases of hypertension. It has specific causes and is a complication of another problem.
Causes of secondary hypertension:
Causes will include the followings;
i. Pregnancy induced hypertension (PET).
ii. Congenital narrowing of the aorta (Coarctation of the aorta).
iii. Renal disease.
iv. Endocrine disorders e.g. Cushing syndrome.
v. Pheochromocytoma.
vi. Hyperaldosteronism.
vii. Neurological disorder e.g. a brain tumour.
viii. Head injury.
ix. Medication- sympathetic stimulants steroids.
x. Oral contraceptive.
xi. Erythropoietin.
4. Classification of Hypertension:
Stage 1 hypertension and need treatment If your blood pressure is between 140/90 and 159/99.
Stage 2 hypertension is 160/100 or higher. ... Blood pressure lowering therapy is likely to prevent stroke and death in patients with uncomplicated.
Stage 1 hypertension. The systolic pressure is 140 to 159 mm Hg or your diastolic pressure is 90 to 99 mm Hg.
Stage 2 hypertension, is diagnosed when your systolic pressure is 160 mm Hg or higher or your diastolic pressure is 100 mm Hg or higher.
5. Clinical Manifestation:
Hypertension in most cases may not present with any symptom. Hence it referred to as “Silent killer”. Many cases are picked up of routine examination for other reasons. Many will present for the first time with signs of complications.
However, the following symptoms may be associated with hypertension.
i. Headache.
ii. Dizziness.
iii. Palpitation.
iv. Chest pain.
v. Difficulty in breathing.
vi. Tiredness on mild exertion.
vii. Epistaxis
viii. Tinnitus.
xi.Fainting.
Examination of a patient with hypertension may not show any other sign apart from the high blood pressure. The physician during the encounter with the patient with hypertension may ask questions about the family history of hypertension.
The family history of hypertension. The life style of the patient and past medical history to identify any predisposing factor and identifiable life study that may be contributing to the high blood pressure.
Then the patient will be evaluated for target organ damage and assess other diseases that may be associated.
6. Symptoms
Hypertension is a "silent killer." A person with hypertension may not notice any symptoms. Hypertension can cause damages to the cardiovascular system and internal organs, such as the kidneys.
Long-term hypertension can cause complications, where the formation of plaque results in the narrowing of blood vessels, through atherosclerosis. As the heart must pump harder to deliver blood to the body.This makes hypertension worse.
7. Laboratory investigations:
Diagnosis of hypertension is made by measuring blood pressure over at least 3 clinic visits using the upper-arm cuff device called a sphygmomanometer.
The doctor will take a history and perform a physical examination before diagnosing hypertension.
Some additional tests can help identify the cause of high blood pressure and determine any complications.
- PVC
- Renal function test.
- Renal serum and urine creatinine clearance.
- Blood glucose.
- Serum lipids
- ECG.
- Renal Ultrasound
- CX-ray
More tests will be required in secondary hypertension

8. Management of Hypertension:
Management of hypertension is lifelong. Hence there is a need to involve the patient and the family in the management plan. Some types of hypertension can be managed through lifestyle and dietary choices, such as engaging in physical activity, reducing alcohol and tobacco use, and avoiding a high-sodium diet.
The aim of treatment of hypertension includes:
i. Maintain blood pressure at near optimum level for each category of patient.
ii. Encourage compliance with therapy.
iii. Prevent end organ damage.
iv. Prevent complications
Life style modification may be adequate in the patient with the Blood pressure of between 130-139 systolic and 85-89 diastolic.
Above this level, drug therapy will be required in addition.
Listed below are some life style modifications that can lower Blood pressure:
i. Weight reduction.
ii. Reduction of salt intake
iii. Increased physical activity
iv. Diet rich in vegetable and fruits
v. Diet low in saturated fats
vi. Stress management.
© 2017 ODEWOYE FRANCIS SUNDAY