How to Alleviate Bad Back Pain
9 out of 10 adults experience back pain at some point in their life. Lower back pain is the 5th most frequent reason people visit a physician.
Treatments for back pain can be divided into medical and non-medical categories. Whether you are experiencing acute (less than 3 months) or chronic back pain (more than 3 months), you would be wise to seek out a doctor that can accurately determine the source of the pain (muscle, nerve, bone, tendon, ligament, or joint) and who will create an individualized, multi-faceted treatment plan that does not simply incorporate prescriptions and/or surgeries.
Back pain treatments include:
- Prescriptions
- Surgery
- Electrical Stimulation
- Physical Therapy
- Chiropractic Treatment
- Cognitive Behavior Therapy
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is often prescribed to back pain sufferers and is an excellent adjunct to other treatments. Physical therapists (PTs) help people with back pain improve the muscle strength that supports the injured area and help identify, correct, or prevent movements that could cause more pain or disability. PTs teach you how to keep your back and stomach muscles strong, use good posture, and learn the safest way to lift heavy objects. PT may include massage therapy.
PTs normally design an individualized program for your particular area and cause of pain, as previously determined by your physician.
Physical therapy can continue as long as needed.
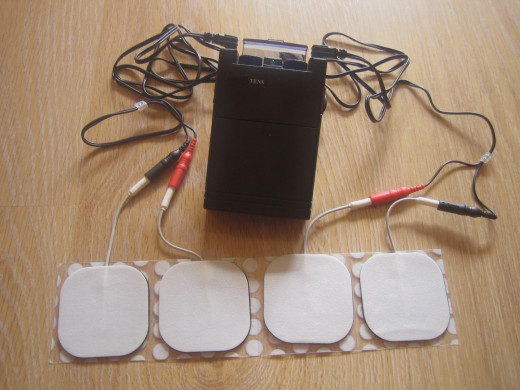
Electric Nerve Stimulation
Found to be more effective than surgery, counterirritation involves stimulating pain in one area of the body to reduce pain in another. Spinal stimulation has proven quite effective in reducing back pain in many patients. Often a transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) unit is used. The TENS unit is applied near the painful area of the back or where the nerve fibers of the painful area enter the spinal cord. The person in pain adjusts the voltage and frequency. When used correctly, the TENS unit produces a feeling of numbness in the pain area.
More invasive is stimulation-produced analgesia (SPA). SPA involves delivery of electrical impulses via electrodes implanted directly in the areas of the brain known to be rich in opioid receptors. Patients self-administer the electrical impulse, stimulating endorphin neurons that activate the brain's natural analgesia system. The benefits of SPA include its effectiveness, lack of disruption of other senses, and lack of confusion that often occurs with opioid analgesia.

Guided Imagery
Unlike visualization, guided imagery uses all of a person's senses to promote a change in their perceptions. Guided imagery is actually a form of self-hypnosis, involving focused concentration and attention. It involves relaxation techniques and mental rehearsal, where the patient imagines a surgery or treatment, thereby ridding themselves of unrealistic fantasies about the potential pain or side effects.
Used mostly with those experiencing low to moderate levels of back pain, the process involves teaching the patient relaxation techniques, wherein they can divert their attention from pain to other mental pictures.
Prescriptions
Besides muscle relaxants and epidural steroid shots, analgesics are the basic go-to drug for back pain management. They are either opioid (like morphine), which are central acting, or non-opioid (like ibuprofen), which are peripherally acting chemicals that focus their pain-relieving and anti-inflammatory properties at the actual site of the pain.
Nonopioid Analgesics
Nonopioid analgesics include aspirin, acetaminophen, and ibuprofen, also called NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs). NSAIDs work by blocking a chemical chain reaction that is triggered during an injury. NSAIDs prevent the production of prostaglandin, which sensitizes spinal neurons to pain.
The benefits of NSAIDs are that they produce pain reduction (for low-grade pain) without sedation, and they reduce inflammation. However, some people can't tolerate the annoying side effects of NSAIDs (like stomach pain and intestinal issues), and some have experienced severe side effects such as liver failure from taking large doses of NSAIDs over a period of time.
Opioid Analgesics
Opioid analgesics used to be called narcotics. They are actually agonists (excitatory chemicals) that act on the brain to reduce pain message intensity or the response to pain.
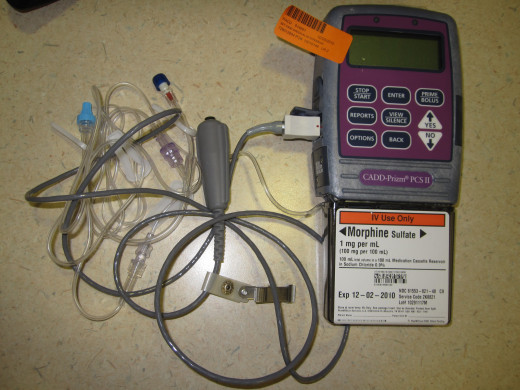
The most powerful and probably most widely-used prescription for severe back pain is morphine, which can be administered in a variety of ways. Basically, morphine binds to certain cells in the brain and at the back of the spinal cord to produce intense analgesia, indifference to pain, a state of relaxed euphoria, reduced apprehension, and a sense of tranquility. No wonder it is so addictive.
So, today, rather than giving one dose per day or per time period, with the patient quickly developing a tolerance, physicians that treat intense, chronic back pain may implant a small morphine pump at the site of the pain. The patient self-administers a small dose as needed.
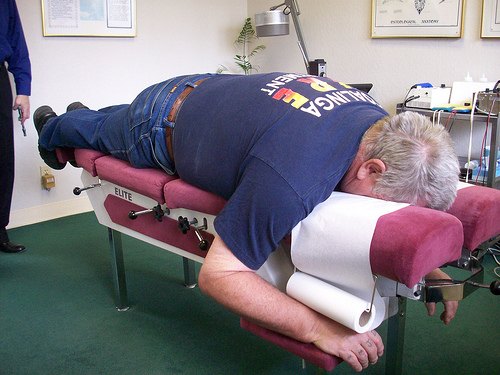
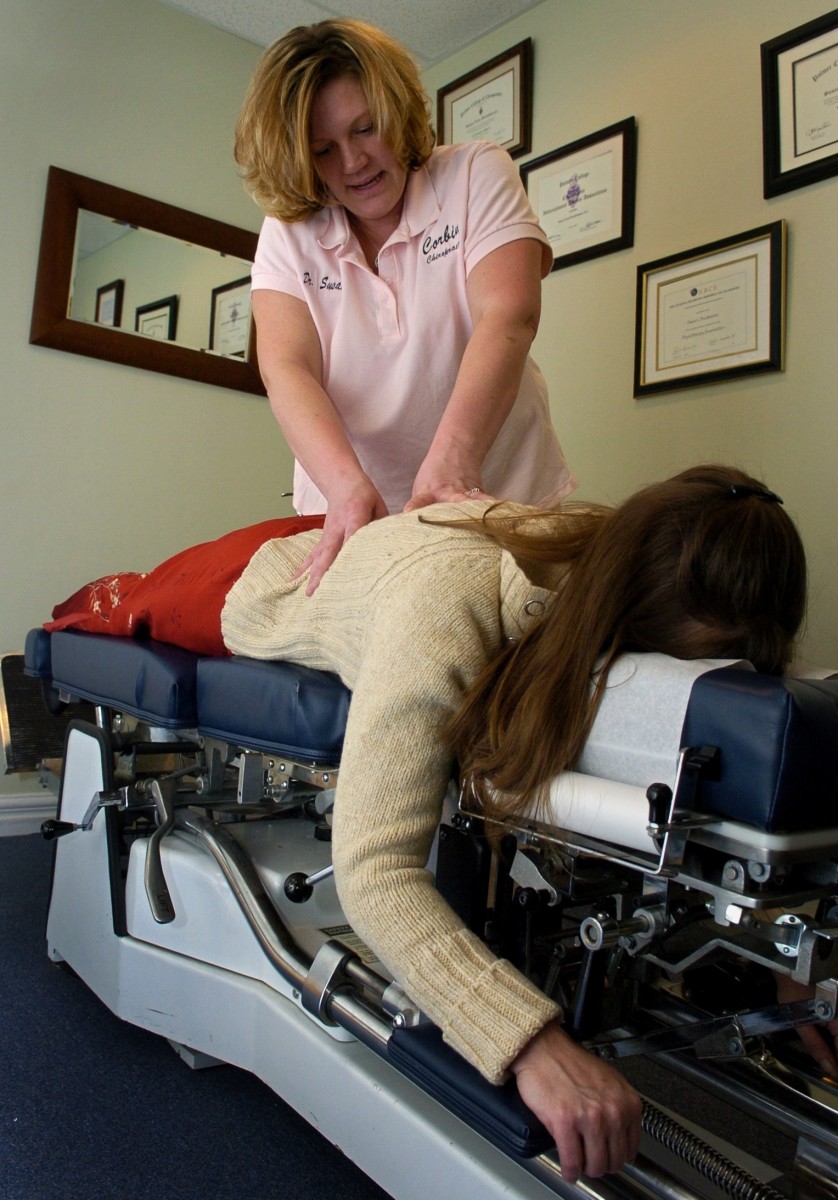
Chiropractic Treatment
Although the efficacy of chiropractic treatment is widely debated, the current status of acceptance for spinal adjustments performed by well-trained chiropractors for relief of back pain is evidenced by its wide coverage by insurance companies, including Medicaid and Medicare. Studies have shown that 1/5 of back pain sufferers have been treated successfully by chiropractors.
There are large risks, however, which may suggest that previous diagnosis of the cause of back pain be determined before seeking chiropractic care. For instance, spinal adjustments can cause severe damage if you have a spinal fracture or tumor.

Cognitive Behavior Therapy (CBT)
CBT aims to change a person's pain experience by changing their thought process and behaviors and lowering their stress levels. Strategies include the following:
Education and Goal-setting
CBT counselors often start with a brief course designed to explain the difference between acute and chronic pain; the mechanisms of gate control theory; and the contributions of depression, anxiety, lack of activity, and other controllable factors related to back pain. Counselors normally encourage the patient to keep a 'pain diary' that records pain frequency, duration, and intensity, medication use, and mood and activity levels. This allows the patient and counselor to discover pain patterns and develop specific and measurable goals for pain intervention.
Cognitive Restructuring
Cognitive interventions challenge a patient's maladaptive beliefs about their pain and redefine pain as an experience that is more manageable.
Cognitive restructuring challenges illogical beliefs such as:
- Catastrophizing
- Overgeneralizing
- Victimization
- Self-blame
- Dwelling on the pain
Surgery
Currently, back surgery is really a last resort attempt at pain control. There are so many major risks, costs, and side-effects, that results are unpredictable, are often short-lived (because our nervous system is able to regenerate, allowing transmission of pain impulses to the brain via many different pathways), and sometimes make the pain even worse.
If surgery is recommended, it is normally for lumbar disc herniation, degenerative disc disease, lumbar spinal stenosis, scoliosis, or a compression fracture. The surgeries are classified as nerve decompression, fusion of body segments, or deformity correction surgeries.
Be wary of doctors who jump immediately to this recommendation, due to the reasons stated above and due to the fact that other treatments have been proven to be more effective.
Future Back Pain Treatment
Due to the high rate of back pain and its treatment costs, research is plentiful. A few promising areas of research are described here:
- Recently, pain researchers have discovered that many patients who suffer from chronic back pain have lower levels of endorphins in their spinal fluid. Currently, clinicians are experimenting to see if injections of synthetic endorphins (beta-endorphins) are effective. So far, most trial participants are reporting excellent, long-lasting pain relief.
- In addition, surgeons are conducting research on ways to disrupt incoming pain messages before they reach the spinal cord and the brainstem.
- Researchers are finding that it is possible to restore an intervertebral disc or prevent its further degeneration through biological treatments using stem cells from the patient's own bone marrow to stimulate the discs to regenerate.