How to Protect a Child’s Hearing
Hearing Protection: Save Your Child's Hearing

While approximately 3/1000 children are born with a congenital, permanent hearing loss, many children acquire a hearing loss in childhood due to noise exposure, certain infections, medical treatments, or traumatic injuries. While some causes of hearing loss are unavoidable, there are ways to reduce or prevent acquired, environmental hearing loss in children.
What is Noise Induced Hearing Loss?
The most common cause of preventable hearing loss in children is noise-induced hearing loss. Exposure to loud volumes causes damage to the delicate inner hair cells of the inner ear. Once these outer hair cells are damaged, they cannot regenerate: the loss of these cells causes a permanent, irreversible hearing loss.
Teens and tweens are at a particular risk for noise induced hearing loss, as they use MP3 players with earbuds, attend rock concerts, and have more exposure to high noise volumes over a long period of time.
Young children are also using headphones and electronic entertainment systems at a higher rate than previous generations. The use of in-car DVD players and hand-held gaming systems places young children at a higher risk of developing noise-induced hearing loss.
Infants are not immune to the effects of damaging noise: many baby toys are equipped with electronic sounds that are unsafe at close range. Since babies tend to hold toys close to their face, the volume of the sound is louder and may damage hearing. Many baby toys exceed 85dB in volume and may damage delicate hearing cells.
Noise Volume and Time Exposure Limits
Volume
| Maximum Allowable Time Exposure
|
|---|---|
85dB
| 8 hours
|
90dB
| 4 hours
|
100dB
| 1 hour
|
105dB
| 30 minutes
|
110dB
| 15 minutes
|
115dB
| 0 minutes
|
How Loud is Too Loud?
If your child is 3 feet away and you have to shout to hear each other, the background noise is at a dangerous level: in general, background noise is above 85dB in this situation. Hearing loss will occur when a person is exposed to 85dB for 8 hours per day.
Noise levels of 115dB or greater greatly increase the chance for acquired hearing loss: exposure to this noise level will cause hearing damage within 5 minutes. An Apple iPod is usually near 100-115dB when played at maximum volume.
Noise above 140dB causes pain and immediate hearing loss. A gunshot is over 140dB when fired at close range, as is a jet plane at take-off.
The Effects of Noise Induced Hearing Loss
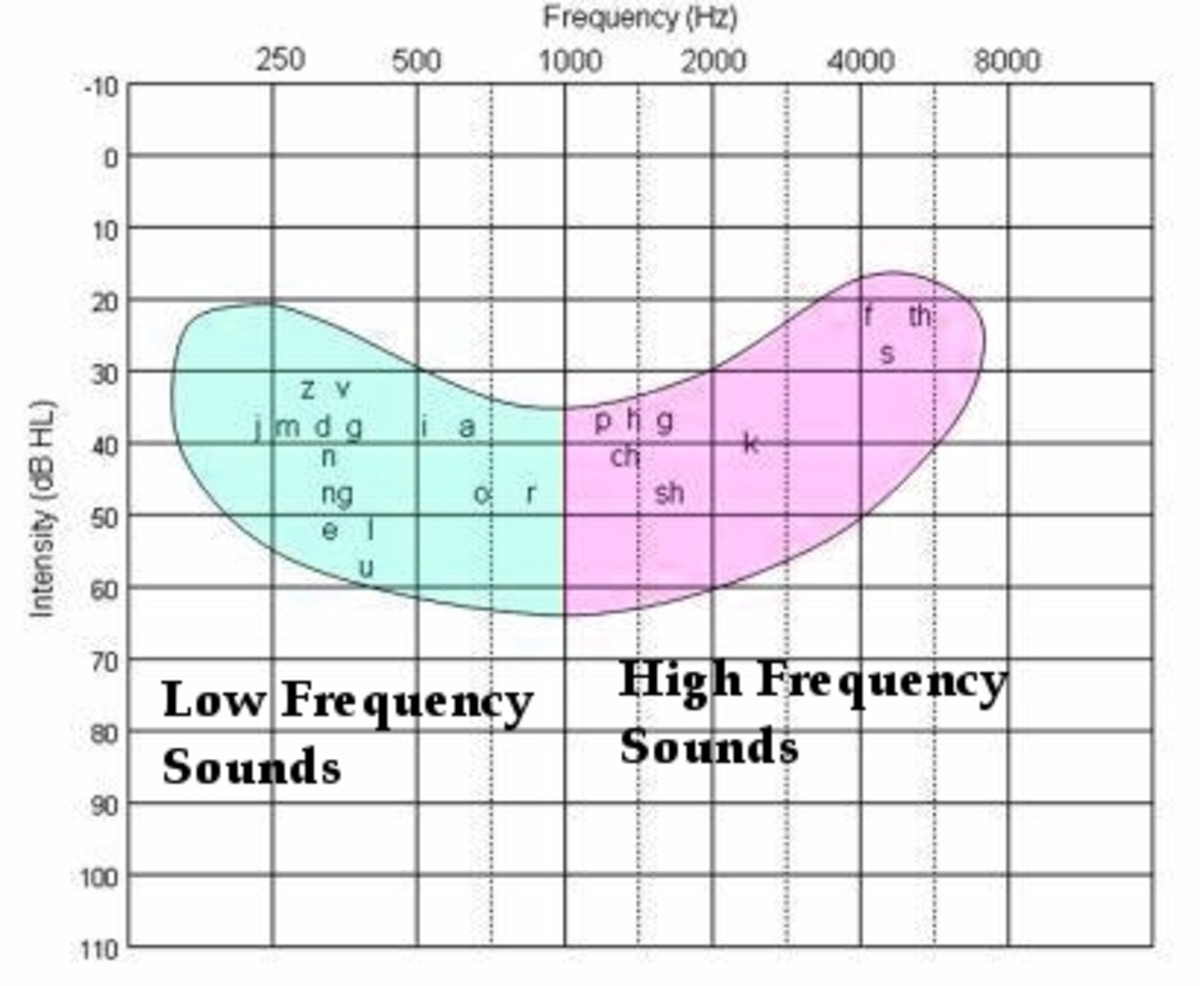
The first hair cells to encounter a sound wave are the ones responsible for hearing high-pitched sounds. In speech, these are the sounds “S,” “F,” and “TH.” These hair cells are the first to become damaged with prolonged noise exposure: many people with noise induced hearing loss will claim they can “hear” someone speaking, but can’t understand what the person is saying.
dB Meter App for Android
Noisy Toys Damage Children's Hearing
Prevent Noise Induced Hearing Loss in Children
Children who listen to MP3 players may not recognize how loud the music is: as hair cells become damaged in the inner ear, children may become “used to” the volume level and begin increasing the decibels. Most MP3 players have a volume limiting application build into the software.
Apple iPods and iPhones, for example, have a setting which allows users to set a maximum volume limit. Simply go to the settings menu and set the volume limit. iPod Shuffles must be connected to iTunes to adjust the volume limit: simply go to settings, then select “limit maximum volume.” Adjust the slider bar to lock in the maximum allowable volume. Limit your child’s use of ear buds and headphones to less than 4 hours per day: the longer a child listens to noise, the greater the likelihood of hearing damage.
Purchase toys without sound, or toys with acceptable volume limits. There are several dB meter apps for tablet computers and smart phones. Use this app to determine how loud a toy is: if it is uncomfortably loud when held up to your ear, it will damage your child’s hearing.
Children exposed to continuous loud noise (such as rock concerts, shooting ranges, or lawnmowers) should wear hearing protection. Over-the-ear headphones or foam insert earplugs are available at drug stores or online. This is the easiest way to prevent hearing damage in young children!
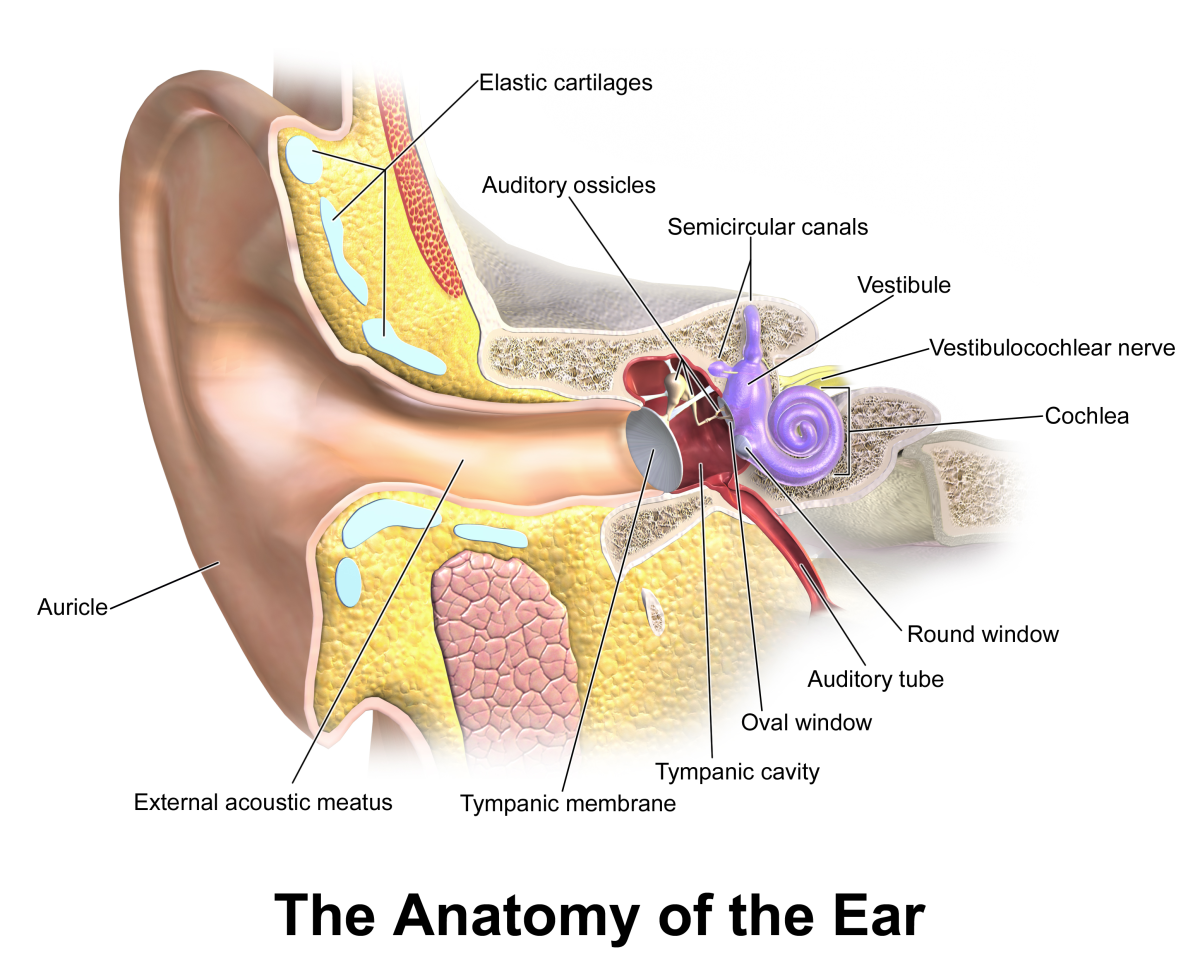
How the Ear Works
Treat Ear Infections
Some children have fluid that builds up in the middle ear, which prevents the transmission of sound from the eardrum to the tiny middle ear bones (and consequently, to the inner ear). Frequent ear infections and fluid in the middle ear causes a temporary, conductive hearing loss. Unfortunately, untreated ear infections may cause a thickening of the eardrum over time, and may damage the delicate middle ear bones: this can lead to a permanent, conductive hearing loss. Some children who experience long-term, untreated ear infections may develop a permanent sensorineural hearing loss (damage to the outer hair cells of the cochlea). It is vital to address chronic ear infections and fluid in the ears: if your child has had fluid in the ear for more than three months, it is time to get a referral to an Ear, Nose, and Throat doctor.
Fluid in the ears is simple to treat with a short, outpatient surgery: tiny tubes can be placed in the eardrums, which allows the Eustachian tubes to function properly and drain ear fluid out of the middle ear space. These ear tubes (also known as tympanostomy tubes or grommets) prevent fluid accumulation and often restore hearing levels to normal in children who suffer from chronic ear infections.
The Effects of Congenital Rubella Infection
Get Vaccinated
Vaccination is controversial among some parenting circles. From a hearing loss perspective, however, there is little controversy: if you want to prevent deafness from infectious diseases, vaccination is vital. Rubella was the leading cause of acquired deafness from an infectious disease in the 1960s, caused by an outbreak in the years 1963-1965. Thousands of children experienced a profound hearing loss from this infection. Due to a successful vaccination program, very few children are deaf due to Rubella in the modern era.
Measles, meningitis, and mumps can all cause deafness. Helen Keller became deaf and blind from a disease described as "an acute congestion of the stomach and brain," which may have been meningitis or scarlet fever (caused by a strep infection). All of these diseases are treatable or preventable in modern society.
Protect the Ears From Injury

Prevent Traumatic Injury to the Head and Ears
Traumatic injury is another cause of acquired hearing loss in children. My sister, at the age of 8, rode a bike down a steep hill and decided to attempt riding without touching the handlebars. She wasn't wearing a helmet, and the resulting crash fractured her jaw and tore through her eardrum. Fortunately, her eardrum healed without permanent hearing damage, but the potential for traumatic deafness was very high.
Children should always wear helmets when participating in contact sports or while riding a bike or skiing. While it is not possible to prevent every trip and fall throughout childhood, a helmet goes a long way toward protecting those little ears (and brain)!