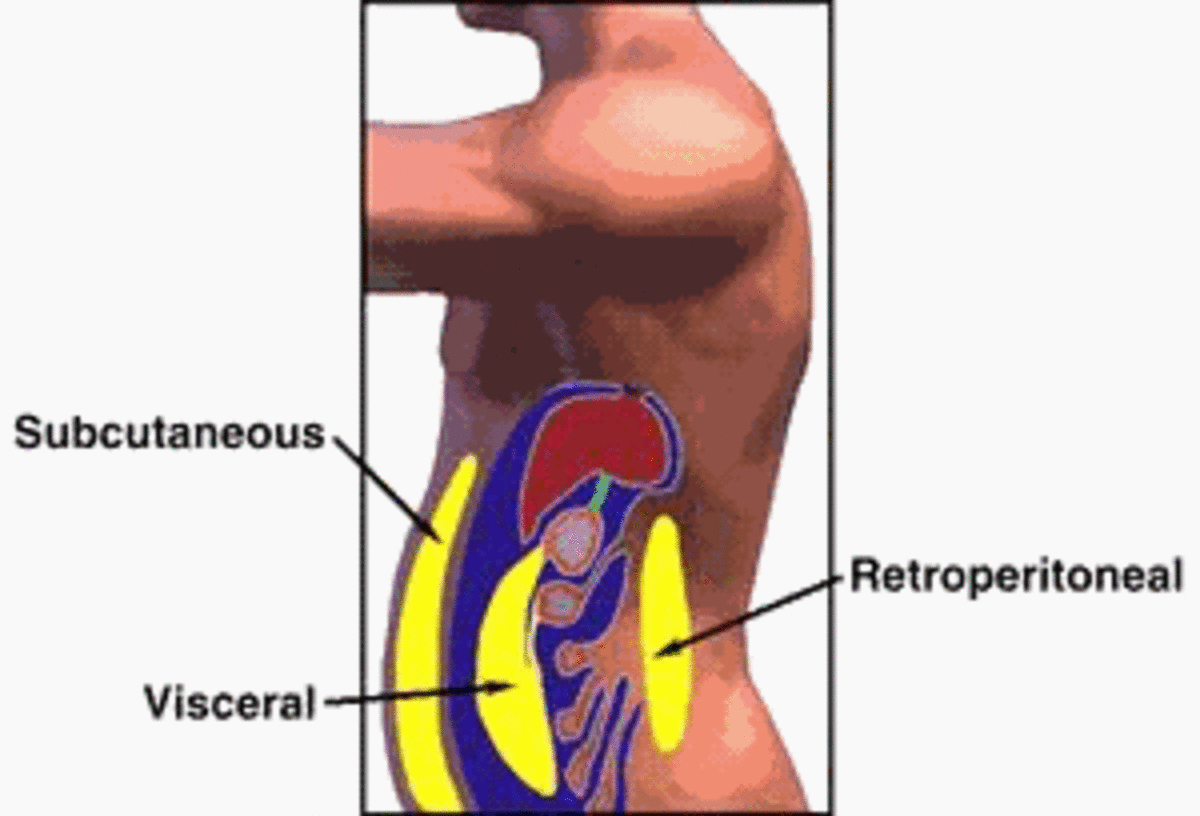
Obesity in Adults, Children and Pregnant Women
Some Facts from WHO (World Health Organisation)
- There are more than 500.000.000 obese people in the world
- Over 40.000.000 preschool children are overweight
- Obesity and overweight are connected to more deaths than underweight
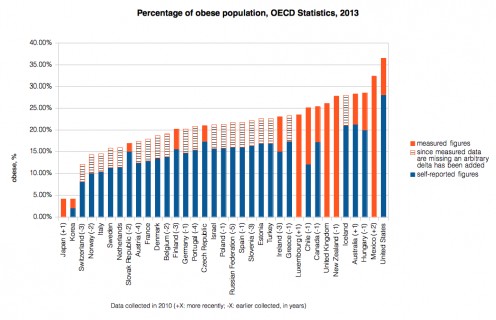
Overveight/Obesity In Some Contries, Ages 20+, Both Sex
Country
| Prelevance of obesity
| |
|---|---|---|
USA
| 31.8
| |
Canada
| 24.3
| |
UK
| 24.9
| |
Germany
| 24.3
| |
Egypt
| 34.6
| |
Norway
| 19.8
| |
Bolivia
| 18.9
| |
China
| 5.6
| |
Bangladesh
| 1.1
|
Source WHO (World Health Organisation)
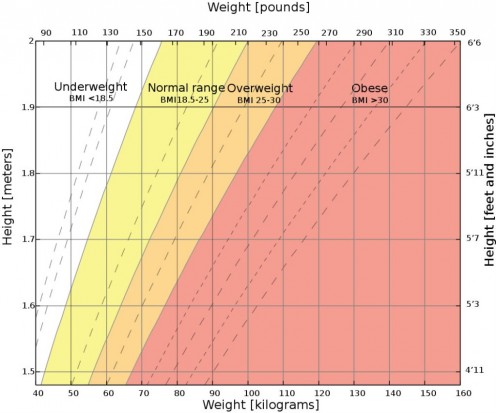
Body Mass Index Chart
Obese Population 2010
Obesity
Obesity is a disease of the modern world. What is obesity and what are the causes of obesity in adults, pregnant women and children? How do people get fat and the importance of fat cells? The impact of obesity to human health. These are some of the most common questions.
Obesity is a condition of increased body weight that occurs as a result of the accumulation of superfluous fat tissue. An immediate cause of obesity is getting in the body more food than the body needs.
Diet and Obesity
Food is the basis of existence, for the all living things, together with human. The necessity to satisfy the hunger is one amongst the essential human instinct. Life, physical development, physical and mental health depends on proper nutrition. All necessary components for the development and growth of the organism, proteins, fats, carbohydrates, minerals, vitamins, a person gets from food. Food provides to man a necessary "fuel". Food ingredients are "burned" by digestion and metabolism within the cells. It's further metabolized to simpler chemical compounds, and then the energy is released. The released energy is measured in calories.
The number of calories that contains one gram of basic nutrients varies. If the body is given one gram of the protein, the organism will produce on the average, four calories. An equivalent number of calories offer carbohydrates, while one gram of fat, release up to nine calories. Though the fat contains more than twice as much energy from carbohydrates, and proteins. Carbohydrates are the main source of calories in the food. They provide fifty to seventy percent of the total amount of calories. This proportion in poorly developed countries are higher as a result of the fact that carbohydrates are the most affordable supply of energy: potatoes, bread, pasta, beans. In most countries, significant source of calories is alcohol, which in the form of alcoholic beverages, sometime even regularly, is an integral part of the meal.
Daily caloric needs depend on the physical activity and the range varies from 2200 to over than 5000 calories. Persons who sit while at work, easier physical labor, spend daily from 2300 to 2500 calories. A stronger physical activity needs about 3,000 calories, significant physical labor 4000 calories, while during the most difficult physical tasks (e.g., miners, lumberjacks) are spent over 5000 calories.
The energy expressed in calories is spent continuously, but not equally. Light physical work spends only about a hundred calories per hour, sitting seventy five calories, while the sleeping consumes even less. Exhausting physical labor consumes over four hundred calories per hour. Mental work, despite being terribly tiresome, spends very few calories. The doctor has performed an experiment on himself and found that "one hour of mental work does not consume more calories than they have in half a peanut."
A healthy person unconsciously maintains the balance between their caloric needs, as well as the amount and calorific value of some foods. To a healthy person, the amount of calories of consumed food is equal to consumed energy. Once the organism receives more additional calories than the body requires, obesity occurs. Any excess of "eaten" calories, no matter whether they are the fat, carbohydrates, protein, or alcohol, are stored as a reserve within the fat cells of the body. For each nine calories of energy the body produces one gram of fat reserve. That means, if a person gets only 500 calories a day above their needs, within a week will increase the body weight for one pound. We could say that the body uses the time of abundance to create a reserve for "lean days." However, these reserves are excessive fat in obese patients. Many obese individuals have a few hundred thousand spare calories deposited in fat tissue. In the present conditions of life, such an accumulation of fatty tissue is not only unnecessary and pointless, but it is very harmful to health.
How To Calculate BMI (Body Mass Index)
Metric Units: BMI = Weight (kg) / (Height (m) x Height (m))
English Units: BMI = Weight (lb) / (Height (in) x Height (in)) x 703
Example:
Someone who is 1.80 m and weights 80 kg has a BMI of
BMI Calculation = 80 / (1.8 x 1.8) = 24.69 Normal category.
Using Body Mass Index (BMI) to Estimate Overweight and Obesity
BMI of Adults Age 20 and Older
| Classification
| |
|---|---|---|
< 18.5
| Underweight
| |
18.5 to 24.9
| Normal weight
| |
25 to 29.9
| Overweight
| |
30 +
| Obesity
|
The BMI is used because it correlates with the amount of fat in the body.
Physical And Mental Disorders Of Obese Persons
Obesity is a disease. The main cause is poor and excessive diet.
According to the consequences for human health and life, obesity is comparable to malnutrition or diseases of insufficient nutrition. It has been proved that obese people live shorter than people with normal weight. As higher is the degree of obesity, the mortality rate is higher. Men with a body weight that's increased by 20 percent, have a mortality of up to 50 percent higher than a man with normal body weight. In women, the consequences are not so serious, although obesity is more common than among men. Obesity adversely affects the functioning of the many organs within the body, the heart and vascular system, kidneys, liver, lungs, intestines.
Obesity significantly burdens the heart, especially senior individuals. Adipose tissue permeates the heart muscle, the heart becomes larger, but not stronger. The heart of obese individuals should endure a greater effort, not only as a result of increased body weight, but also as a result of many of the newly created blood vessels that supply the surplus fat. The heart of obese individuals is burdened with movements and increased physical effort. Therefore, obese people quickly get tired, and their working ability significantly are reduced. Due to the difficulty in walking, such individuals are sitting more, causing a further reduction in consumption of calories within the body. It's understandable that with an equivalent quantity of food, weight continues to rise. This creates a closed circle with no way out without proper treatment.
Obese persons have increased fatty substances in the blood: cholesterol, triglycerides (hyperlipidemia), which are deposited on the walls of blood vessels and accelerates the development of atherosclerosis. The fatty substances are deposited in the blood vessels of the heart muscle and brain. For obese people more likely is to develop coronary sclerosis. The consequence is occasional pain in the heart, and may develop a heart attack. Modified blood vessels in the brain leads to bleeding in the brain.
High blood pressure is several times more common in obese than in people who have an ideal body weight.
Breathing of obese individuals is troublesome, exhausting and superficial. "Armor of fat" on the chest complicates its expansion. The expansion of the chest is hampered by the weakness of intercostal muscles, which spreads the rib cage, because they are very permeated with fatty tissue. The high position of the diaphragm muscles, which are also involved in respiration, even more impairs breathing. Accumulated fat within the abdominal cavity raises the diaphragm within the chest. The diaphragm then pushes on the heart and causes heart issues. During breaths, the diaphragm cannot be sufficiently lowered in the abdominal cavity, that is filled with fatty tissue, which results in reduced inhalation. The total amount of the inhaled air is significantly reduced. Reduced supply of air to the lungs complicates filling the heart with blood. During the time, it develops damage and chronic heart failure. Hampered gas exchange in the lungs, leads to the accumulation of carbon dioxide within the blood, which leads to a constant sleepiness. Weakened »pulmonary ventilation" is additionally a reason why at obese people are much more likely to occur pneumonia than in those with normal weight.
Obese individuals are at risk of other diseases: diabetes, liver damage, blood coagulation within the blood vessels (thrombosis), distortion of the bone system, joint inflammation, varicose veins in the legs, inflammation of the gall bladder, appendix, gallstones. There are digestive disorders as bloating, belching, diarrhea.
But all these physical changes, obese individuals don't relate to their excessive weight. Many are more concerned about physical appearance than the disturbed state of health, particularly if it comes to younger people. Concern for his or her look, poor mobility, decreased ability to work, it all leads to mental disorders: a sense of inferiority, depression, withdrawal.
Some Warning Facts
- More than 300.000 people die every year due to obesity.
- Persons with BMI larger than 30, have a 50 - 100 % increased risk of premature death
- Heart disease is increased in people who have BMI larger than 25.
- Gaining more than 20 pounds from age 18 to midlife, woman doubles their risk of postmenopausal breast cancer
- The risk of developing type 2 diabetes is increased to twice, at persons who gain weight of 11 to 18 pounds then at persons with normal body weight.
Brain's Role In Obesity
There's a direct cause of obesity with excess calories consumed with food, it can be said that a person is becoming obese because he eats too much. There's no doubt that in connection with such assertion, we could ask a series of questions: Why do some people eat too much, why people can consume huge amounts of food and keep slim, while others with much smaller amounts of food are becoming fat? Why somebody who nearly eats nothing cannot lose weight?
The Centers that regulates food consumption are located within the brain. There are so called »Center for hunger", whose stimulation causes hunger and need for food intake, the "satiety center", whose stimulation causes the person no longer feels hunger. A healthy person unconsciously maintains a balance between the two centers, so the amount of calories of entered food is equivalent to the amount of consumed energy.
If the balance is disturbed, it may be two types of consequences:
- Insufficient intake of food, results in the loss of body weight, with the time to develop a state of malnutrition.
- Excessive intake of food, creates more calories than are consumed, which leads to increase in the weight, the obesity.
There are a variety of known and unknown factors that act on the brain centers. Fleeting hunger will occur as a result of reductions in blood sugar, spasms and painful movement of the stomach, while, as an example, stretching the abdomen can cause a sense of fullness. It's believed that there are three main disorders that permanently have an effect on the centers: disorders within the brain, hereditary factors and psychological disorders. All these factors can create disequilibrium and lead to obesity.
Disorders within the brain can cause obesity if they occur within the area of the brain, where are centers of hunger and satiety situated. It is known that these centers are placed in a part of the brain called hypothalamus. Experiments have shown that animals stop to eat if "center for hunger" were destroyed. If it's destroyed "satiety center," opposite reaction happens, the animal stops to eat. As a result of the damage of that part of the brain at humans, can suddenly appear excessive hunger, taking huge amounts of food and obesity, regardless of the fact that such a person for many years had a normal body weight. A similar situation may occur, sudden and complete loss of appetite with a sense of constant fullness. The result is a rapid loss of body weight. Such conditions occur after brain injury and inflammation rarely as a result of brain tumors.
Environment's Influence On Obesity
In the occurrence of obesity, heredity (genetic factor) is not as important as was formerly thought. Behind the so-called hereditary obesity, there is actually an impact of environment and family. Many obese people were raised in the families where the dish was represented as the only satisfaction in the life, where they have created the cult of dishes. The habit of taking large quantities of food from childhood, remains for later. Large portions, gradually made the satiety center less sensitive. In addition, overeating in the early childhood, has caused the creation of a large number of fat cells.
Link Between Obesity and Mental Health
Emotional and other mental disorders could directly have an effect on the centers of satiety and hunger. It is known as the phenomenon of intemperate habits of eating after a stressful event, after dissatisfaction, conflict within the family or in the work, after failing to solve some important problems in life. Taking food reduces the "mental tension" of such persons, who actually by overeating resolves their internal problems and situations. If such mental disorder persists or becomes permanent, the pleasure of eating can become their only satisfaction in the life.
New Era and Obesity
The modern way of life affects obesity. The body weight gain, is characteristic of the people in the civilized and wealthy countries. In underdeveloped and poor countries, a major part of the energy (calories) is consumed at the workplace, on the way to the workplace and in the preparation of food, while the people in rich and urban environments consume less calories.
Dietary habits?
How Difficult You Find Changing Of Dietary Habbits?
Many Obesity-related Health Conditions Are Now Being Seen in Children
- high blood pressure
- early symptoms of hardening of the arteries
- type 2 diabetes
- nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- polycystic ovary disorder
- disordered breathing during sleep
Being overweight during childhood can accelerate the development of heart disease.
Obesity Campaign Poster

Child Obesity
Adult obesity is closely related to obesity in the childhood. In more than one-third of the cases, adult obesity is just a continuation of obesity in the childhood. Such cases are also the most difficult forms of adult obesity.
Science has uncovered the facts that indicates how and in what way the inheritance and external environmental influences, affects obesity in childhood. Fat as a "reserve fuel" have accumulated in the special fat cells, called adipocytes. Increased weight and body weight depends not only on whether the fat cells are more or less filled with grease, but also on the total number of fat cells in the body. The number of human fat cells might be determined as same as the blood cells can be determined in the blood. The total number of fat cells in the human body is an average of about 300 billion.
Will the number of fat cells be a higher or lower, determines the hereditary factor, but even more a way of eating in the first days, months and years of life. Excessive nutrition at a young age has a major influence on the fat cell growth, especially overeating in the first days and first weeks of life. As a child is getting older, the influence of diet on the number of fat cells is getting smaller, so around 23 years of age, the number of fat cells gets stabilized and did not change anymore throughout the life.
So that obesity in childhood creates the preconditions for later obesity, not only in eating habits but also in thenumber of fat cells.
Fat cells are not equally distributed throughout the body. That's why some gets fat on the side, and another gain weight at legs. Someone is fatter in the face, at the other "everything goes in the belly." On such a layout, affects hormones and secretions of some glands.
A lower degree of obesity of children occurs when their body weight does not exceed 10 to 20 percent above normal weight. Obesity is when a child's weight exceeds 20 percent above the weight that is considered normal for that age, gender and height of the specific body. The main culprits in the obesity of children are their parents. The widespread opinion is that the child is healthy as fatter. The truth is the opposite: obese children become ill before than children with normal weight, and even a child who is considered to be thinner. Many parents feed their children believing that in this way they shows true love.
Obese children become awkward, immobile. They cannot equally participate in children's games, they become an object of mockery and abuse. Obese kids avoid the company of other children, withdraw into themselves, they have a sense of inferiority, and they do nothing else but to continue to over-eat. The consequence is an increase in body weight. Preventing excessive feeding in the first months of life, prevention of obesity in the pre-school and school age, provides to children happier childhood, at the same time reducing adult obesity.
Obesity in America
Too Little Or Too Much Weight Gain Linked To Child's Obesity
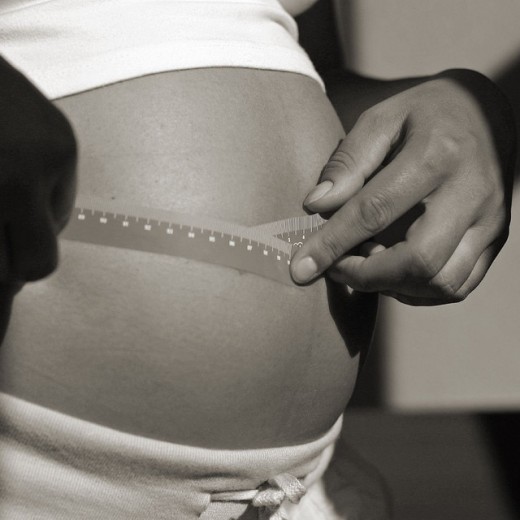

Obesity Of Pregnant Women
While in pregnancy, the body weight of women is gradually increasing. That increase of body weight in a healthy and normal pregnancy woman on average is ten to thirteen kg. Only half of the body weight refers to the baby and also the female internal reproductive organs, the rest is generally adipose tissue which accumulates to serve as a "storage" for baby and breastfeeding. Only 1 to 2 kg refers to the accumulated liquid. Weight gain during pregnancy depends on the type of the feminine body, diet, diseases of pregnant women and children. Weight of some women will increase only slightly more than the weight of the child, and the others gain more than twenty kg.
Amount Of Weight That Women Are Recommended to Gain During Pregnancy
BMI before pregnancy
| Recomended weight gain
| |
|---|---|---|
BMI less than 18.5
| 28 to 40 pounds
| |
BMI between 25 and 29
| 15 to 25 pounds
| |
BMI of 30 or greater
| between 11 and 20 pounds
|
justmesuzanne tells you What Is Ideal Body Weight & Should You Achieve It?
- What Is Ideal Body Weight & Should You Achieve It?
You may be very healthy & weigh far more than your supposed ideal weight. Healthy weight is determined holistically by taking an inventory of your level of exercise, overall health record & more.
A Way Out
You can lose weight through increased physical activity, changes in dietary, by increasing physical activity and changes in behavior. Medications or weight-loss surgery may be options in some cases. Weight-loss surgery can be solution for severely obese patients who have one or more obesity-related health problems, such as high blood pressure, diabetes or sleep apnea.
Consult specialist about obesity screening and your treatment for weight loss.
What is Obesity and What Does it Mean? by Gabriel Wilson
- What is Obesity and What Does it Mean? Are You Killing Yourself by Being Fat? Is Your Weight Killing
Informative article about obesity and the dangers of being obese. Face the facts; why are you fat? And how to get help.
This content is accurate and true to the best of the author’s knowledge and does not substitute for diagnosis, prognosis, treatment, prescription, and/or dietary advice from a licensed health professional. Drugs, supplements, and natural remedies may have dangerous side effects. If pregnant or nursing, consult with a qualified provider on an individual basis. Seek immediate help if you are experiencing a medical emergency.
© 2014 Nikolic Predrag