Polycystic Ovary Syndrome | Symptoms & Treatments of PCOS
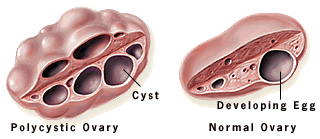
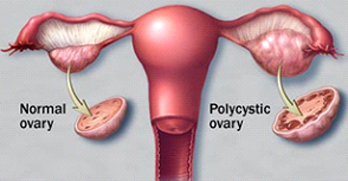
What are Ovarian Cysts?
Ovarian cysts, also known as Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), is a condition which is a relatively common reproductive endocrine disorder affecting approximately 10 to 15% of women of reproductive age. Although metabolic disorders such as Type II Diabetes, as well as certain atherosclerotic conditions (thickening and hardening of certain blood vessels) and obesity can contribute to the development of ovarian cysts, a strong familial link often plays an important role.
Symptoms can include Infertility, Irregular Periods & Acne
The main symptoms that women with ovarian cysts may experience are:
* Lack of ovulation (which may lead to infertility)
* Irregular periods that can be extra light or extra heavy
* Excess body hair and acne which occurs due to elevated testosterone levels
* Obesity which affects mainly the top half of the body and the abdominal area particularly
* Insulin resistance can be present which eventually results in high insulin levels in the body
* Enlarged ovaries can be seen on an ultrasound
Additionally, the risk of developing certain cardiovascular conditions (such as high blood pressure and heart attack) is higher if you are affected by ovarian cysts. High levels of fatty acids and cholesterol in your system will also increase the risk of developing not only heart conditions but also PCOS, but the good news is that abnormal cholesterol levels can be improved through a healthy diet and regular exercise.

Can PCOS affect my pregnancy?
Women with ovarian cysts who are pregnant have a higher possibility of developing gestational diabetes (this is a condition where women who have previously not suffered with high glucose levels, first show elevated blood sugar levels during their pregnancy).
This risk is greatest in women who are severely overweight, and who required ovulation induction to become pregnant, hence keeping your weight within normal ranges will decrease your chances of developing gestational diabetes.

Is there a link between Ovarian Cysts and Cancer?
If severe abnormalities in the menstrual cycle are present (i.e. lack of menstruation or excessively heavy bleeding), it can in some cases lead to overgrowth of the endometrium tissue (the inner tissue lining of the womb/uterus is referred to as the endometrium) and this can eventually lead to carcinomas.
To explain a little further, the female body contains two major hormones involved in the reproductive cycle; oestrogen and progesterone. Lack of ovulation (caused by cysts in the ovaries) can lead to a lack of menstruation, which in turn increases the levels of oestrogen, causing the endometrium to thicken. Repeatedly high levels of oestrogen combined with low levels of progesterone can predispose to endometrial cancer.

Is there anything I can do to reduce the risks associated with PCOS?
Yes. Regular exercise (and weight loss) is particularly beneficial for a number of reasons. It results in a lower BMI (body mass index), it lowers the risk of developing cardiovascular conditions, and it can normalize glucose metabolism and therefore reduce the chances of you developing Diabetes.
Furthermore, a reduction in weight improves frequency of ovulation thus improves fertility, and it lowers androgen levels thus decreasing hirsutism (excess hair growth) and acne.
Drug therapies can improve the situation also; ‘insulin-sensitizing agents’ such as Metformin can reduce insulin resistance hence lowering the risk of developing Diabetes. If you are having problems ovulating, Clomiphene may be used to induce ovulation, as well as injectable gonadotrophin medication.
Oral contraceptives (sometimes in combination with other medications such as spironolactone) may also be given to reduce hirsutism and acne, maintain regular menstruation, prevent endometrial cancer, and also prevent pregnancy (if it is not an immediate concern).
The other option is surgery – it can improve ovulation, and normalize androgen levels, leading to an increase in fertility and the resumption of a normal menstrual cycle.
2. Warfarin (Coumadin) | What you Need to Know about Blood Clotting, Interactions & Side Effects
Warfarin is referred to as an oral anti-coagulant drug which essentially stops the blood from clotting. The way in which Warfarin does this is by decreasing the production of Vitamin K, a vitamin that is involved in forming clots in the body.
It takes around 48-72 hours for the anticoagulant effect to be seen, but the effect of Warfarin on the blood needs to be carefully monitored because the blood must not lose its ability to clot completely (this could cause massive blood loss, both internally and externally, if you are injured or receive some sort of trauma)... Read more.
Recommended Reading
You can also browse through some of my other Health based articles. They provide some valuable insights into causes, prevention and remedies you can try out to improve the quality of your life in those times when your health is not 100%.
1. Joint Health | Reduce Your Joint Pain & Stiffness using Natural Supplements
My last few years working as a pharmacist has made me aware that one of the most common complaints many patients tend to have is joint pain or joint stiffness, with the most common areas being affected are the knees, the finger joints or the wrist & shoulders. This is a particularly important issue as it affects the quality of life; imagine consistent pain or stiffness in the joints, or imagine waking up in the morning and realising you cant jump out of bed without wincing with pain..
Doesn’t sound very pleasurable or bearable for that matter! This hub is designed to make you aware of various natural supplements that you can take to improve the overall health of your joints, no matter what your age might be... Read more.
© 2011 CONSCIOUSNINJA