Cancer of Lens of the Eyes: Causes and Counter
Mutation causes retinoblastoma that can be controlled by natural agents
By Conrado D. Fontanilla
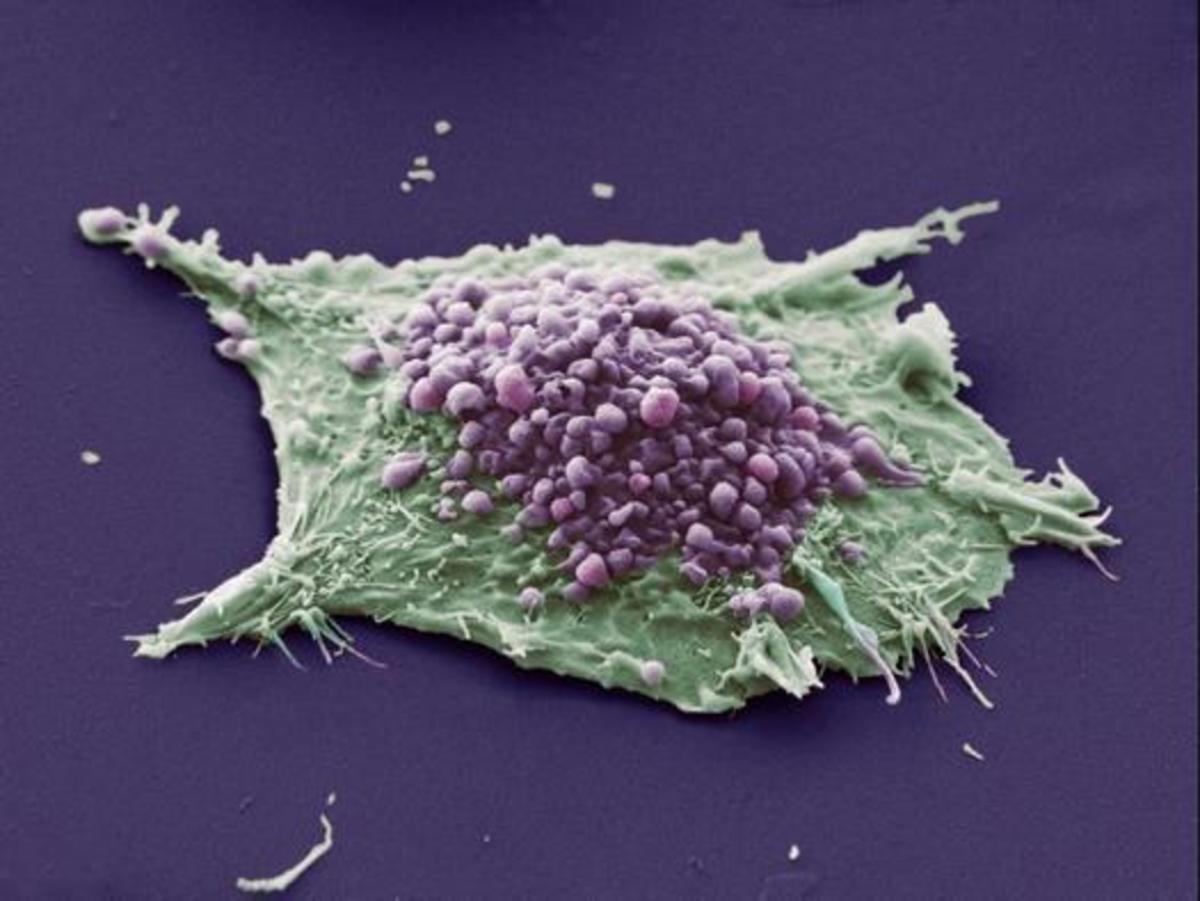
Retinoblastoma (cancer of the retina) afflicts children one to three years old. Retina is the layer of the eye that is sensitive to light. One child in 14,000 births is a victim of retinoblastoma; or one child in 20,000 births is a victim. There are two forms of retinoblastoma. inherited and sporadic.
Inheritance
The basis of inheritance is the chromosome. A human being has 48 chromosomes (numbered 1 to 48) in each cell. A chromosome is composed of genes. A chromosome is like a pod of string beans. The seeds are like genes. The pod has a divider that is sometimes located at the middle, sometimes near one end. That is why a chromosome has a short arm and a long arm. The gene of retinoblastoma (RB1) is located in the long arm of chromosome 13 (Cummings, M. Human Heredity, Principles and Issues. 1998:292-314). A gene comes in pairs, one fellow is called allele. Furthermore, a gene is a string of nucleotides arranged in a sequence by nature (normal) or by mutation (abnormal). A gene is like two open pearl necklaces laid side by side. A nucleotide is like a bead. Three nucleotides in sequence encode an information, called genetic information, that controls the production of protein. Most of these proteins make up the human body. A change or mutation in a nucleotide or in the sequence of nucleotides results in abnormal protein that mostly shows as tumor or cancer.
Inherited form of retinoblastoma
The gene involved in retinoblastoma is tagged as RB1 which is located in the long arm of chromosome 13. In the inherited form, a person inherited a copy of a gene, an allele, that is mutated; chromosome 13 has a deletion in its long arm (Cummings, same source as above). That is, the abnormality consists of a deletion of one allele. When its twin, the normal allele, in a retinal cell is also mutated or inactivated, the person develops cancer of the retina. The chance that this person, now with both alleles of RB1 mutated in one retinal cell, develops retinoblastoma is 85% to 90% in both eyes (Cummings, M. Human Heredity, Principles and Issues. 2009:289).
All the cells of a person who had inherited a mutated RB1 carry a mutated or inactivated allele of RB1. It is highly probable that one nucleotide had been deleted, or missing. Remember three nucleotides compose a genetic information that is expressed as a protein like insulin, or hemoglobin; when one of three nucleotides that are supposed to be together is mutated the result is an abnormal protein like tumor, or cancer, etc. When the other normal RB1 allele in just one cell, other than a retinal cell, in the body of a person is mutated or inactivated he develops cancers of the bone, lung, and bladder.
Sporadic form of retinoblastoma
No mutated allele of RB1 is inherited. Both alleles are normal in all cells of the child. However, both alleles, in one retinal cell, may incur changes or mutations due to sporadic causes, including environment. In this form, one eye usually develops a tumor. The chance of this tumor to develop into other kinds of cancer is low.
Two-hit model of retinoblastoma development
Retinoblastoma develops in two ways. In one way, a person inherited a mutated allele of RB1. When the other allele in a retinal cell is also mutated by sporadic factors, retinoblastoma develops. That is, two events had been involved. One inherited, the other due to sporadic factors. Given that one allele is already abnormal, it only takes a few mutations in the other normal allele to become abnormal as well. Thus retinoblastoma develops in both eyes.
In the other way -- the sporadic form of retinoblastoma -- both alleles of RB1 are normal. However, when both alleles in one retinal cell sustain mutations due to sporadic factors, retinoblastoma develops. It takes a long time for mutations in two alleles to occur that is why a child develops retinoblastoma later in his childhood.
This two-hit model was proposed by Alfred Knudson and his colleagues (Cummings, M. Human Heredity, Principles and Issues. 2009:289).
Spontaneous mutation
To recall, a gene consists of nucleotides. Three nucleotides make up a genetic information that is expressed in the production of a protein. A tumor or cancer is protein. A spontaneous mutation consists in (1) a deletion (loss) of a nucleotide, or (2) substitution of a nucleotide, or (3) rearrangement of nucleotide sequence, or (4) frameshift mutation. A spontaneous mutation occurs during meiosis or fertilization. The mutated RB1 comes either from the sperm of the father or egg of the mother.
Using the analogy of a necklace of pearls: in deletion of nucleotide, a bead is lost; in substitution, a necklace made of white pearls, one pink pearl replaced one white bead; in rearrangement, if the beads were numbered 1, 2, 3, rearrangement means that the new order is now 1, 3, 2. These changes produce abnormal proteins like tumor and cancer.
Sporadic mutation
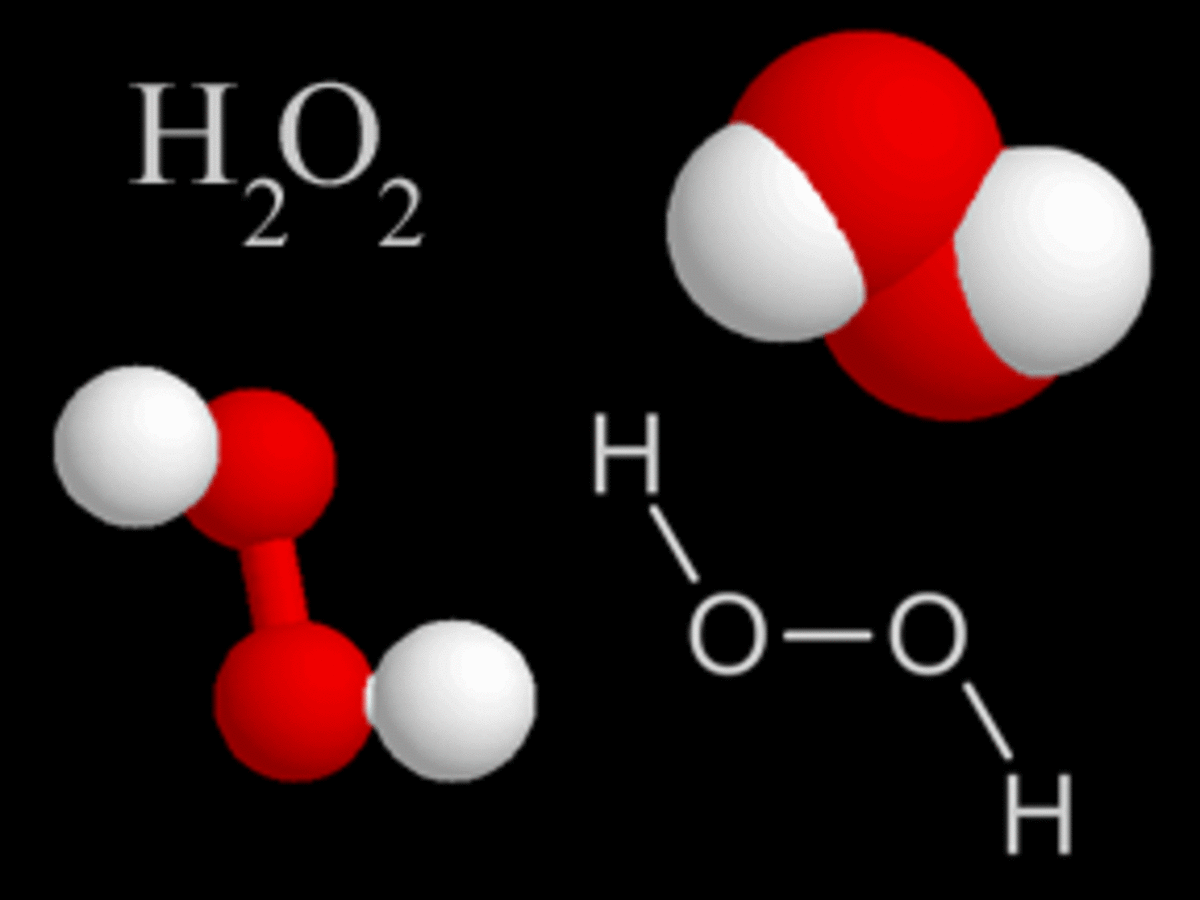
Sporadic factors include free radicals like molecular oxygen, superoxide, hydrogen peroxide, hydroxyl, and singlet oxygen. Sporadic factors are found outside the human body or outside the cell, or inside the cell.
We breathe molecular oxygen. It is used in the metabolism of glucose in the production of energy. In this metabolism, one molecule of glucose (or blood sugar) is split into two, each goes in separate paths. At the start of each path an atom of hydrogen is involved with its electron separated from its proton. The electron is passed down like water in a waterfall. At the foot of the waterfall, a molecular oxygen is waiting. One of its oxygen atom catches the electron and forms a molecule of water. The other oxygen atom becomes a superoxide that has one unpaired electron. One glucose yields 38 units of energy called adenosine triphosphate (ATP). This superoxide is a free radical that is hungry to satisfy its one free electron. It grabs another electron that usually belongs to a tissue. This tissue is injured and this injury results in a tumor or cancer.
In the case of retinoblastoma, superoxides grab electrons from the normal allele of the RB1 gene, thus initiating changes or mutations in the allele. The cell of the retina with both alleles mutated develops retinoblastoma.
Tumor or cancer starts in one cell only. A tumor is non-malignant; it starts and grows uncontrolled in one cell. A tumor may graduate into cancer when it grows uncontrolled beyond the capacity of the matrix surrounding a cell; its basement broken allowing escape of abnormal cells to invade neighboring cells or cells in other parts of the body. The process of breaking out and invasion is called metastasis. (I have another Hub "Genes of Heritable Breast Cancer Found: How To Counter Its Causes").
The usual free radicals that hit the cells of the retina are singlet oxygen, and the reactive oxygen species hydroxyl and hydrogen peroxide. A singlet oxygen is formerly a molecular oxygen with the spin of one of its unpaired electrons having been reversed by heat coming from the sun. (A molecular oxygen has two unpaired electrons spinning in their outermost orbitals in parallel directions.) A singlet oxygen has two unpaired electrons spinning in opposite directions. A hydroxyl is derived from a molecule of water that had been heated, usually by the sun. A hydrogen peroxide is derived from molecules of superoxide that had not been dismantled by the enzyme glutathione peroxidase into safe water. Hydroxyl and hydrogen peroxide behave like free radicals in that they also grab electrons.
Why focus on free radicals?
Why should we focus on the sporadic (environmental) that includes free radicals? The reason is that 60% to 70% of all cases of retinoblastoma are caused by sporadic factors (Encyclopedia Britannica 2009). Only about 40% to 30% cases are caused by inherited, spontaneous mutation. To be repetitious, an inherited mutated allele alone does not graduate into cancer. The other normal allele must be mutated also -- by sporadic factors. That is, a person carrying an inherited mutated allele will not develop retinoblastoma unless hit by sporadic factors that mutate the normal RB1 allele. Another reason is that damage due to free radicals is preventable. Free radicals can be located by means of the electron spin resonance spectrophotometry and the free radical load of the human body can be tested (Sharma, H., MD. Freedom from Disease. 1996). In addition, means of controlling free radicals are available and cheap (food, fruits, vegetables, vitamins, minerals). A little expensive but effective is infusion chelation therapy involving EDTA (ethylene-diamine-tetra-acetate). Besides, the application of most of them does not need a prescription from the doctor. The minimum goal in dealing with free radicals is to have a balance between free radical load of the body and the antioxidants in the body. There will always be free radicals in the body because they are a by-product of body processes, production of ATP, for example. A free radical load greater than available antioxidants results in oxidative stress.
I have a hypothesis that most of the so-called spontaneous mutation (deletion, substitution, rearrangement of nucleotide sequence, frameshift) are caused by free radicals. My hypothesis runs as follows:
“Free radicals grab electrons from the hydrogen of DNA.”
In this hypothesis, the concepts are free radicals, electrons, hydrogen, and DNA; the relationship is “grab.”
Statements of fact that relates to sense-experience are:
1. The DNA consists of several hydrogen atoms and hydrogen bonds (Cummings, M. Human Heredity, Principles and Issues:2009).
2. The hydrogen bond that binds hydrogen atoms together, and hydrogen with other elements of the DNA (like phosphates, nitrogen, and sugars) is weak. It is only as much as 5% that of the covalent and ionic bonds. "This property is of special significance as it accounts for the temporary bonding between certain atoms of large complex molecules such as proteins and nucleic acid" (Tortora, G.F and J.D. Becker. Life Science, 2nd edition. 1978:14). Nucleic acid is a component of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). Atoms of molecular oxygen are bound together by covalent bond. Atoms of salt (sodium chloride) are bound together by ionic bond. The atoms of water are bound together by hydrogen bond. The reason why water is a solvent is that the hydrogen bonds are easy to stretch that allow other atoms to get between the atoms of hydrogen and oxygen.
3. The mass of hydrogen being small and the hydrogen bond being weak make the hydrogen electron the weakest prey for a free radical (or reactive oxygen species) to grab.
A hydrogen atom whose electron is lost “dies.” The ordinary hydrogen (in contrast to isotopes of hydrogen like deuterium) has one electron and one proton – no nucleus. The orphaned proton most probably becomes part of another molecule like water when one atom of molecular oxygen takes one electron and one proton. This occurs during metabolism of glucose.
DNA is destroyed when several hydrogen electrons had been grabbed, consequently several of its hydrogen bonds were broken.
4. Destruction of DNA results in mutation.
If all these statements of fact are true, my hypothesis would turn into a theory. It is easy for a chemist to test items 1 to 4 in a laboratory. (I have a Hub “A Theory of How The Salk Killed-virus Vaccine Kills Polio Virus It Marked with Antigen.”)
Natural controls
Superoxide is converted to hydrogen peroxide by superoxide dismutase. Hydrogen peroxide is dismantled to safe water by glutathione peroxidase. These occur in the cell.
Free radicals can be prevented from inflicting damage by simply satisfying their hunger for electrons. Enzyme antioxidants do this. Examples of enzyme antioxidants are superoxide dismutase, glutathione peroxidase, glutathione reductase, catalase and glutathione synthetase (that makes glutathione from nutrition). Enzyme antioxidants (built-in to the cell) are recyclable because they are not destroyed in the reactions that they accelerate. Supplement antioxidants like vitamins A, C, E, and B-complex do this. Supplement antioxidants are a sacrifice; they die once they had donated their electrons. Vitamin C can recycle some vitamin E; NADH can recycle some vitamin C. That is why supplement antioxidants must be supplied continuously.
Colored natural food like carrot absorb the heat thus neutralizes singlet oxygen.
In a test tube experiment using drops of human blood mixed with extracts from the pulp of ripe duhat fruit (colored dark brown or black) done in the University of the Philippines at Los Baños, some chromosomes of blood sustained gaps, breaks, condensations, and loose sister chromatids. (A chromosome is composed of two chromatids.) The duhat (Syzyggium cumini L.) extract caused these aberrations in the chromosome. It means that if the chromosomes were chromosomes of tumor or cancer cells, these tumor or cancer cells would stop growing. The reason is that a cell with chromosomal aberrations cannot assemble proteins to grow. Fruits, vegetables, and other natural food containing antioxidants provide protection against retinoblastoma.
Colored glasses worn during sunny days protect against retinoblastoma.
Unfortunately, conventional medicine does not mention about free radicals because it ignores them as causes of disease.
Fortunately, stem cell therapy, the emerging treatment and cure for several diseases recognizes that free radicals are causes of disease (Bellomo, M. Stem Cell Divide. 2006). The stem cell for use in growing an earlobe, for example, must be free from free radical damage, otherwise it is pre-aged. The stem cell used in cloning Dolly, the cloned sheep, could have been pre-aged that is why Dolly did not live long.
So, you must get pieces of advice for natural control of retinoblastoma from doctors familiar with holistic medicine or naturopathy.