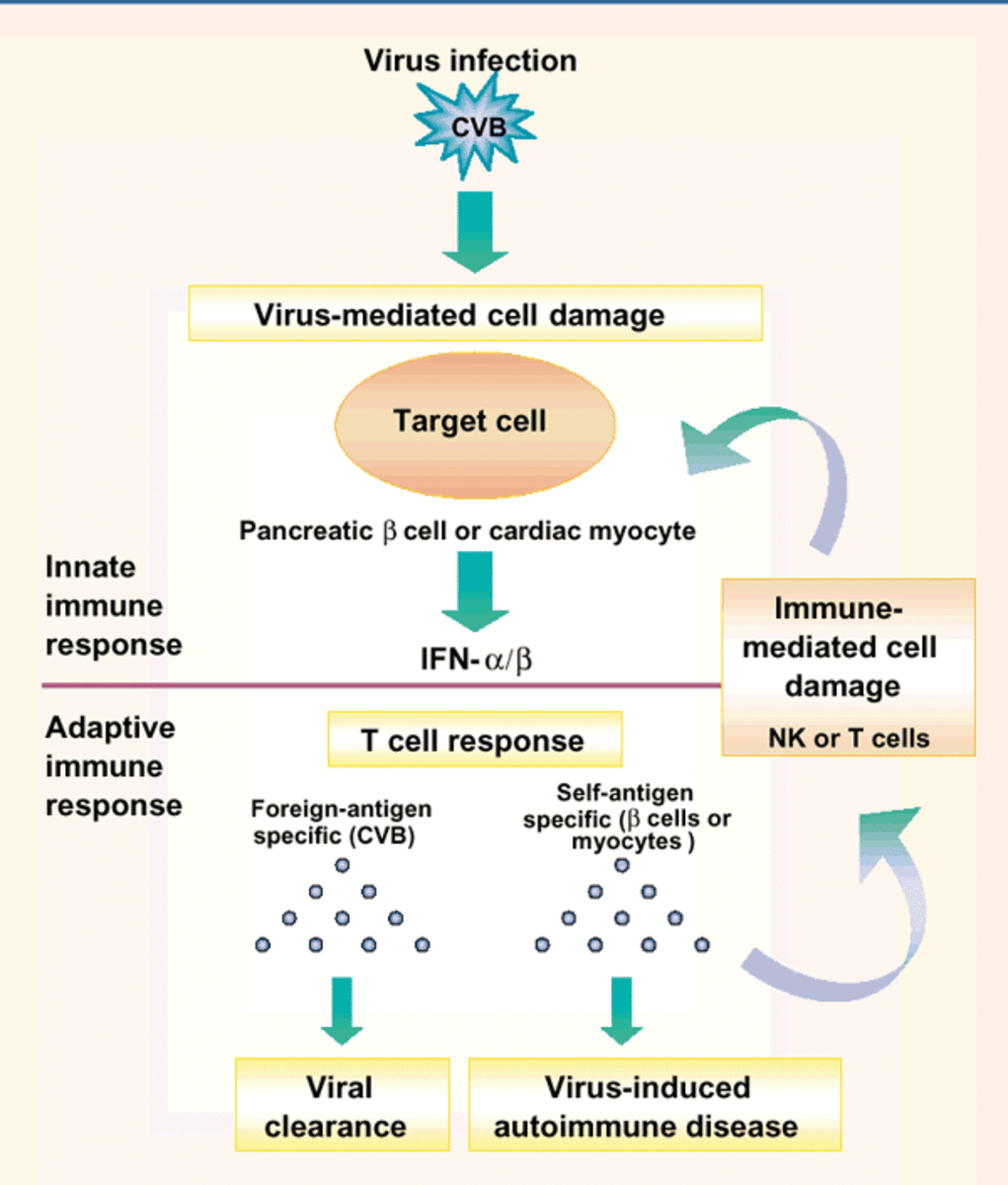
Immunology investigation; Autoimmune diseases causes and cures - Natural antibiotics VS lab organisms.
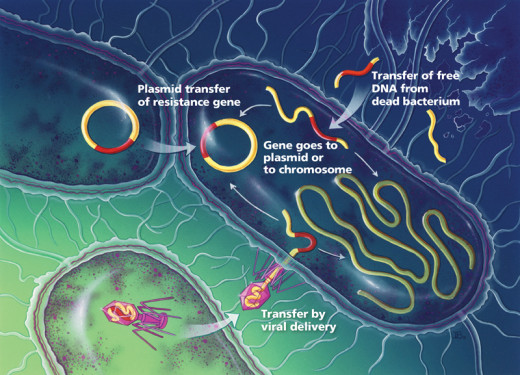
Nearly every disease known to medicine has become resistant to at least one antibiotic and several are immune to more than one. One of the MOST alarming things about the cholera epidemic, which as killed as many as 50,000 people in Rwanda, is that it involves a strain of bacterium which cannot be treated with standard antibiotics. Tuberculosis, too, has learned how to outwit doctors. Tuberculosis is an unusually touch microbe. Several strains of TB have emerged in the U.S. that cannot be treated with common antibiotics. Even infections such as staph and strep have become harder to treat as they have acquired resistance to standard antibiotics. One strain of hospital-dwelling staph can now be treated only with a single antibiotic and public health officials have no doubt that it will soon become immune to that one as well. Hospitals could become dangerous places to go and even more so if strep develops universal resistance.
The Discovery of Bacteria.
The Dutch merchant and amateur scientist Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1632–1723) was the first person to observe bacteria and other microorganisms. Using single-lens microscopes of his own design, he described bacteria and other microorganisms (calling them "animalcules") in a series of letters to the Royal Society of London between 1674 and 1723. Bacteria are generally classified into three groups based on their shape. They are described as spherical (coccus), rodlike (bacillus), or spiral or corkscrew (spirochete [pronounced SPY-ruh-keet] or spirilla). Some bacteria also have a shape like that of a comma and are known as vibrio. Bacteria most commonly reproduce by fission, the process by which a single cell divides to produce two new cells. The process of fission may take anywhere from 15 minutes to 16 hours, depending on the type of bacterium. A number of factors influence the rate at which bacterial growth occurs, the most important of which are moisture, temperature, and pH. Most bacteria require a pH of 6.7 to 7.5 (slightly more or less acidic than pure water). Other bacteria, however, can survive at a pH more severe than that of battery acid.
it is now well known that the use and overuse of antibiotics has resulted in increasing resistance by causing breeding of microorganisms agents. in 2010, health care providers in the United States prescribed 258 million courses of antibiotics in the outpatient setting; this translates into 833 prescription per 1000 persons, and these numbers do not include the use of these drugs in hospitalized patients.
Annually, more than 2 million individuals are infected with antibiotics-resistant organisms. these individuals are at increased risk of acquiring autoimmune disease as the organisms infiltration through the GI tract progresses.
The excessively widespread use of antibiotics has created many threats. A well-known problem is the increasing bacterial resistance to antibiotics, which has clearly become a worldwide challenge to the effective control of infections by many pathogens. But, beyond affecting the pathogenic agents for which it is intended, antibiotic treatment also affects the mutualistic communities of microbes that inhabit the human body. As they inhibit susceptible organisms and select for resistant ones, antibiotics can have strong immediate effects on the composition of these communities, such as the proliferation of resistant opportunists that can cause accute disease. furthermore, antibiotic-induced microbiota alterations are also likely to have more insidious effects on long-term health. In the case of the gut microbiota, this community interacts with many crucial aspects of human biology, including the regulation of immune and metabolic homeostasis, in the gut and beyond. It follows that antibiotic treatments bear the risk of altering these basic equilibria.
Group A streptococcus (GAS) outbreaks occur as a result of the emergence of dominant clones, which arise through the horizontal acquisition of DNA that encodes toxins and antibiotic resistance determinants or through more subtle genetic changes.
Antibiotic resistance bacteria have been found in tissue from patients with sarcoidosis. ... inflammation and other autoimmune diseases.
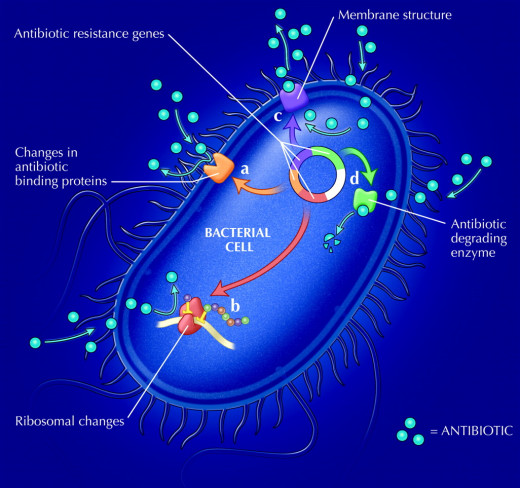
Resistance of bacteria to antibiotics occurs in a variety of ways.
“Antibiotic therapy is not an effective treatment against autoimmune inner ear infection and rates of recurrent infection are significantly higher in children who have been treated with antibiotics.”
Journal of the AMA
Our bodies contain complex and powerful disease-fighting weapons, consisting primarily of the immune system which works 24 hours a day attacking and destroying foreign invaders such as bacteria and viruses. When this system is functioning at an optimum level, the body can best combat invading microbes. Many of the characteristic symptoms of illness, such as fever and swollen glands, are signs that the immune system processes are proceeding on schedule.
the key to fighting and preventing illness is by strengthening the degree of natural immunity, the natural body defenses and the overall vitality of the individual.
“There is no healing force outside of the human body.”
Dr. Isaac Jennings.

Conventional medicine does not effectively address the fact that most individuals’ health is determined by three things: day-to-day behavior; access to health-defining resources like unprocessed food and regular exercise; and how lifestyle choices affect the body, about which education levels are shockingly low amongst all socioeconomic demographics.
“Conventional medicine does not focus on curing your illness, but on suppressing the side-effects so that you feel better - not so that you are better”. The guardian.

In 1914, the inhibitory effect of garlic on mycobacteria was reported by Dr. MW. McDuffie of the Metropolitan Hospital in New York. He compared garlic with 55 other treatments for TB and concluded that it was the most effective. He affirmed “Garlic contains a volatile oil, called allyl sulphide, and its medical properties depend on this oil, strongly antiseptic, it seems to have a remarkable power of inhibiting the growth of the Koch’s bacillus, eliminated by the lungs, skin, kidneys and liver, and oxidizes into sulphonic acid in the system. Applied locally, it is freely absorbed by the skin and penetrates the deeper tissues. Garlic gave us our best results, and would seem equally efficacious, no matter what part of tile body affected, whether skin, bones, glands, lungs or special parts”