- HubPages»
- Personal Finance»
- Tax & Taxes»
- Income Tax
Filing Requirements For A Federal Income Tax Return

For many people tax season is a time of confusion and shear frustration. We struggle over what to include and what to exclude from our tax return. Even if we know what to include on our tax return we may struggle to determine which forms to use and how to present it on our Form 1040. However, before one struggles through the myriad of tax forms, we should first check to see if we even have a filing requirement to begin with. This article will go over several reasons why you “must” file a tax return. There may be other reasons why you “may want” to file a tax return when you are not required to do so. Some people file merely to get a refund of an over payment of taxes or to fulfill a FAFSA Form (One files FAFSA forms in order to help individuals get college financial aid). This article will only focus on the reasons why you must file. This article will NOT discuss the filing requirements for those who could be claimed as a dependent on another taxpayer's return.
Gross Income Requirements: Based on your filing status and age you may be required to file a tax return if your “gross income” is above a certain threshold. Gross income includes all income wherever earned that is not “exempt” from taxation. It is important to note that “exemption” from taxation is different from “excluded” from taxation. Exemption from taxation means the income is never to be included in gross “taxable” income on your tax return; however, you may need to list the income as “non-taxable” income on the return. An example of this would be “tax-exempt” interest, which one includes on line 8b of the Form 1040 – Individual Income Tax Return, but is not included on line 8a “taxable Interest income” on the Form 1040. Excludable Income is income, which you would include on a Form on your tax return, but would then back out as an offsetting entry. An example of this would be income subject to the foreign income exclusion rules or main home-sale gain exclusion rules. Under the Foreign Income exclusion rules taxpayers, if they meet certain requirements, which can be found in the instructions to IRS Form 2555, can reduce the amount of gross income earned outside the U.S. The Home-Sale Exclusion rules allows people to exclude a certain amount of gain from the sale of their “Main Home” so long as they meet certain criteria. Excludable income “must” be included in the “Gross income Test” for filing without the offsetting exclusion being accounted for. Gross income also included the gains, but not losses, from the sale of investments; and the gross income from Schedule C –Self-Employed income, but not the expenses form the Schedule C business;
Please also note that the income for the gross income test includes any income you made in any form including money, property, goods or services.
**Additionally, you should not "net" income you earn from investments. For instance, some people who invest in foreign stocks may find that they need to pay taxes on capital gains and/or dividends before the owner may receive the proceeds of the gain or dividend. If this occurs you must figure out the gross capital gain and/or gross dividend and claim that on your tax return. You can then try and take a foreign tax credit or deduction on the income you paid. If you are not sure if your foreign investment required you to pay taxes upfront, then you should contact your broker to see about how to retrieve this information.
Gross Income Thresholds - Tax Year 2015
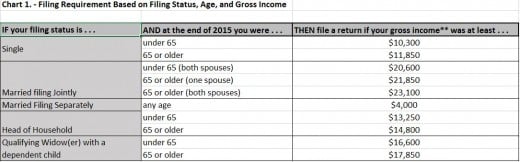
Additionally, you must file a return if any of the special taxes below apply for 2015:
You owe any special taxes, including any of the following.
-
Alternative minimum tax.
-
Additional tax on a qualified plan, including an individual retirement arrangement (IRA), or other tax-favored account. However, if you are filing a return only because you owe this tax, you can file Form 5329 by itself.
-
Household employment taxes. However, if you are filing a return only because you owe this tax, you can file Schedule H by itself.
-
Social Security and Medicare tax on tips you did not report to your employer or on wages, you received from an employer who did not withhold these taxes.
-
Recapture of first-time homebuyer credit. See the instructions for line 60b.
-
Write-in taxes, including uncollected social security and Medicare or RRTA tax on tips you reported to your employer or on group-term life insurance and additional taxes on health savings accounts. See the instructions for line 62.
-
Recapture taxes. See the instructions for lines 44, 60b, and line 62.
You must also file a tax return if any of the following issues are present.
- You (or your spouse, if filing jointly) received health savings account, Archer MSA, or Medicare Advantage MSA distributions.
- You had net earnings from self-employment of at least $400
- You had wages of $108.28 or more from a church or qualified church-controlled organization that is exempt from employer social security and Medicare taxes.
- Advance payments of the premium tax credit were made for you, your spouse, or a dependent who enrolled in coverage through the Marketplace. You or whoever enrolled you should have received Form(s) 1095-A showing the amount of the advance payments.
Please note that in this section of the filing requirement rules you see another mention of Schedule C income. This is due to the fact that one can be subject to filing a Federal Return if the “Gross Income” from your Schedule C business, whether alone or cumulatively with other gross income, exceeds the “Gross income” requirement; or if the “Net Income” from your Schedule C business (Gross income from Schedule C less Expenses from your Schedule C business) equals or exceeds $400.
Hopefully, this article will help clear up a little bit of the confusion concerning the Federal Income Tax filing requirements for individuals. If you still need more information you can go to the IRS' website at www.irs.gov to look over filing requirements for the Form 1040 - Individual Income Tax Return.
To learn more about various areas of taxation, click the articles below:
More about tax rules:
- Mortgage Interest Deductions: Mortgage Interest Deductions are "itemized deductions" which may help you lower your taxable income, and therefore your tax liability. Mortgage Deductions are subject to several limitations.
- Gambling Loss Deductions: Gambling Loss Deductions are "itemized deductions" which may help you lower your taxable income, and therefore your tax liability. Gambling Losses may only be taken up to the amount of Gambling winnings.
- Contributions to a Traditional IRA: Contributions to a traditional IRA "may or may not" result in a deduction to gross income. One's filing status, modified adjusted gross income, earned income, and whether they are covered under a retirement plan at work can effect one's ability to take a deduction for a contribution to a traditional IRA.
- Student Loan Interest Deductions: Payments of one's student loan interest may result in a tax deduction based on whether the interest is on a qualifying student loan, and the taxpayer meets certain eligibility requirements.
- Roth IRA Contributions: Contributions to a Roth IRA do not result in tax deductible savings on one's tax return. However, Roth IRA investments have other great tax benefits later on in life, such as being able to possibly take distributions from the account (both contributions and income earnings) tax free "if" the recipient meets all of the requirements.
Do you find tax time stressful?
Quiz: Do not assume information not listed in question
view quiz statistics© 2016 James

![TurboTax Deluxe 2015 Federal + State Taxes - Tax Preparation Software - PC Download [Old Version]](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/413zyZhyIkL._SL160_.jpg)







