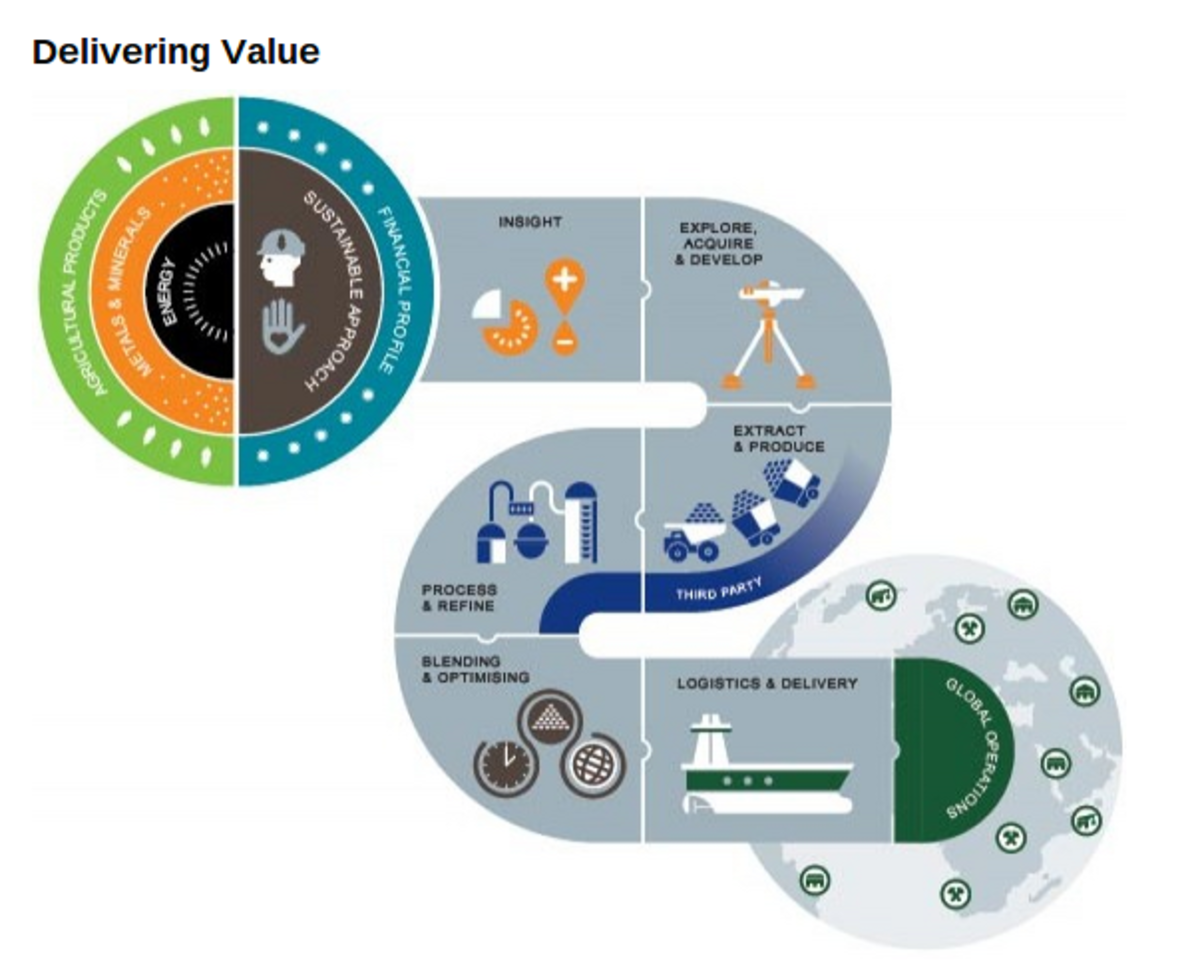
How Are Commodities Traded? How is a Physical Commodity Traded? Commodity Trading in Stock Market

Trading Commodities with Futures and Options Contracts
The sale and purchase of commodities contracts is carried out through futures contracts and options contracts on exchanges that standardise the quantity and minimum quality of the commodity being traded. On a commodity exchange, it is the underlying standard stated in the contract that defines the commodity, not any quality inherent in a specific producer's product. In this case there is not normally a physical delivery of the commodity. This is where the majority of commodity investment speculation occurs and is the main opportunity for the investor to enact an investment strategy.
Futures traded commodities are fungible and have the following attributes:
One tranche (contract) of the commodity is indistinguishable from and interchangeable with the next (fungible).
The commodity is traded publicly and openly on an auction-style futures exchange where the price is determined by current market conditions and the opinion of the traders on the exchange.
Only commodities that are of global economic interest and having inherent worth are traded on the futures exchanges.
Commodities exchanges are located on all continents. This leads to a diverse range of commodities that are traded on these exchanges. See “What are Commodities?” for a full list of the commodities that are traded on the worlds commodity exchanges.

Beginners Introduction to Commodities Futures Trading - History
Commodity Futures - Hedging Price Risk
The Futures Contract
Trading Commodities Physically
- As tangible assets commodities, in addition, can be traded physically between a buyer and seller just like any import / export transaction. The difference being that commodities are traded in huge quantities and in the unfinished state i.e. no manufacturing process has usually occurred. In this instance a contract or sale and purchase agreement (SPA) is drawn up between the contracting parties where all of the physical attributes of the commodity and the procedure for exchange and delivery (the delivery schedule) are determined. Although commodities are deemed to be uniform as a definition in practice there are subtle differences between commodities of the same general definition and these differences must be taken into account in order for an acceptable price to be agreed. There is not necessarily an absolute set quantity that can be traded for any particular commodity traded in it's physical form, although in general shipping quantities usually increase in quantities of 12,500 metric tons for the major commodities.
Similarly, commodities can be traded in their physical form on the spot market or as spot trades. The only difference here to a contract for physical delivery is that delivery is almost immediate and payment is made for a single shipment or deliverable quantity.
For physical delivery there are a number of interested involved parties: owners, buyers (possibly traders), mandates for both sides, facilitators, brokers and intermediaries. As this series of articles is developed each of these parties will be defined and discussed fully. Also involved will be shipping companies, testing companies, warehousing and storage facilities and a plethora of other supporting operations that ensure a timely and safe conclusion to a complex operation.
For a comprehensive list of the general classifications of physically traded commodities see “What are Commodities?”.
Both trading commodities physically and through the medium of futures are high cost, high returns strategies. For this reason few investors are willing or able to enter the commodities arena. There are however, other alternatives that are less risky and less costly to enter.

Trading Commodities Through Commodity Stocks
In addition to trading commodities on the futures market or physically you can also effect a strategy of investment in commodities on a less risky basis by investing in a portfolio of Commodity Stocks (or Shares).
On the FTSE 100 companies such as Anglo American, BHP Billiton, BP, Cairn Energy, Drax, International Power, Kazakhmys, Lonmin, Rio Tinto, Petrofac, Scottish & Southern Energy and Vedanta Recources can be traded if you wish to invest in high-capitalisation stocks.
In the US there are innumerable commodities companies quoted on the various stock markets in order for you to gain a holding in commodity stocks.
However, the speculative profits are with the smaller cap stocks in the mining, energy and oil exploration categories.
Trading Commodities Through Exchange Traded Funds (ETF's) or Investment Trusts
There are two more practical methods of gaining access to commodities apart from futures, physical purchase or purchase of commodity stocks and these are:
- Commodity ETF's (Exchange Traded Funds) - these funds reflect the underlying price changes of the held commodities. There are funds for oil, gold, silver and baskets of commodities. These allow you to diversify away from your general equity market exposure.
- Commodity Stock ETF's - these are funds that are invested in the stocks of commodity producers rather than the commodities themselves. There are funds in gold mining stocks, oil producers and agri-stocks etc. These have a high correlation to the overall equity market in general.
Both of these are known as Investment Trusts in the UK.

Futures Spread Betting (First Part)
Trading Commodities Through Spread Betting
Another method of getting an exposure to commodities is to have an account with one of the many spread betting companies that are now available over the internet. The volatility of the market gives opportunities for good profits but also high losses. The speculative nature of this mechanism is given away in the name. This is betting on the price movement of a commodity. There is a lower access cost than for physical or futures trading and the range of commodities available for betting against includes:
- Metals - Gold, Silver, Palladium, Platinum
- Energy - Crude Oil, Gasoline, Natural Gas
- Agricultural - Soybeans, Soybean Oil, Soybean Meal, Corn, Wheat, Oats
- Meats - Pork Bellies, Lean Hogs, Live Cattle, Feeder Cattle
- Softs - Cocoa, Coffee, Sugar
- Miscellaneous - Cotton, Lumber and Frozen Orange Juice
The same research as you would need to do for all the other commodities trading mechanisms are required for spread betting.

Standardising Commodity Trading
As an aid to standardisation of physical commodity trades, economists use a statistical definition for commodities based on a trade classification systems: SIC Codes and HS Codes.
SIC Codes
The relevant SIC Codes for the types of commodity we are interested in are:
Division A: Agriculture, Forestry and Fishing
Industry Group 011: Cash Grains
0111 Wheat
0112 Rice
0115 Corn
0116 Soybeans
Industry Group 013: Field Crops, Except Cash Grains ·
0131 Cotton
0132 Tobacco
0133 Sugarcane and Sugar Beets
Division B. Mining
Industry Group 101: Iron Ores
1011 Iron Ores
Industry Group 102: Copper Ores
1021 Copper Ores
Industry Group 103: Lead And Zinc Ores
1031 Lead and Zinc Ores
Industry Group 104: Gold And Silver Ores
1041 Gold Ores
1044 Silver Ores
Industry Group 106: Ferro-alloy Ores, Except Vanadium
1061 Ferro-alloy Ores, Except Vanadium
Industry Group 109: Miscellaneous Metal Ores
1094 Uranium, Radium, Vanadium Ores

Harmonised System (HS) Codes
The relevant Harmonised System (HS) Codes for the types of commodity we are interested in are:
06-15 Vegetable Products
10
CEREALS
- 1001 wheat and meslin
- 1002 rye in the grain
- 1003 barley
- 1004 oats
- 1005 corn (maize)
- 1006 rice
- 1007 grain sorghum
- 1008 buckwheat, millet & canary seed, cereals nesoi
05-27 Mineral Products
25 SALT, SULPHUR, EARTH & STONE, LIME & CEMENT
- 2503 sulfur of all kinds nesoi
- 2523 portland cement, aluminous cement, slag cement etc
26
ORES SLAG & ASH
- 2601 iron ores & concentrates, including roast pyrites
- 2602 manganese ores & concentrates inc mangnfrs iron ores
- 2603 copper ores and concentrates
- 2604 nickel ores and concentrates
- 2605 cobalt ores and concentrates
- 2606 aluminum ores and concentrates
- 2607 lead ores and concentrates
- 2608 zinc ores and concentrates
- 2609 tin ores and concentrates
- 2610 chromium ores and concentrates
- 2611 tungsten ores and concentrates
- 2612 uranium or thorium ores and concentrates
- 2613 molybdenum ores and concentrates
- 2614 titanium ores and concentrates
- 2615 niobium, tantalum, vanadium & zirconium ore & conc
- 2616 precious metal ores and concentrates
27
MINERAL FUELS, OILS, WAXES & BITUMINOUS SUB
- 2701 coal, briquettes, ovoids etc, mfr from coal
- 2704 coke etc of coal, lignite or peat, retort carbon
- 2705 coal gas, water gas, prdcr gas etc, ex pet gs & othgs
- 2709 crude oil from petroleum and bituminous minerals
- 2710 oil (not crude) from petrol & bitum mineral etc,
- 2711 petroleum gases & other gaseous hydrocarbons
- 2713 petroleum coke, petroleum bitumen & other residues
- 2714 bitumen & asphalt, natural, shale & tar sands etc.
39-40 Plastics / Rubbers
40
RUBBERS
& ARTICLES THEREOF
- 4001 natural rubber, balata, gutta-percha, guayule, chicle and similar natural gums, in primary forms or in plates, sheets or strip

____To Tweet_______To Flag______To Like______To Thumb's Up
_________________JUMP back to the beginning
_______These pencils are for your personal use for comments_____.
__________________PLEASE DO NOT REMOVE________________