Managing Risks with Futures and Options

Introduction
Currency risk is a form of financial risk that arises due to unanticipated fluctuations in the exchange rates between two currencies. For a firm that have assets and liabilities denominated in foreign exchange, managing currency risk is very important. Even crypto currencies such as the notable Bitcoin can be subjected to currency risks, especially with their booming growth in recent years. The crypto currency crash in 2018 is a good example. The prices of cryptocurriences fell by a sharp 80% from their peak in the start of the year and was widely considered to be worse than the tech bubble crash in the late 1990s.
A good way of managing such risk is to make using of currency futures and options.
Using Currency Futures to Manage Currency Risk
Currency futures are standard size contracts of a particular currency that are exchanged on a fixed settlement date. Currency futures allow a firm to hedge transaction exposure by locking the price to buy or sell a foreign currency. There are two techniques of using currency futures to manage risk.
The first technique is to buy currency futures to hedge payables in a foreign currency, if appreciation of the foreign currency is expected. The other is to sell currency futures to hedge receivables, if depreciation of the foreign currency is expected.
Buying Futures to Hedge Payables
For example, ENG PLC based in England has a payment of 12.5 million JPY to be made in 2 months’ time to JPN Private Limited based in Japan. Assuming a current spot rate of £0.0048:
£0.0048 * ¥12,500,000 = £60,000
The payment is expected to be £60,000. However, if the Yen appreciates and the spot rate increases to £0.00514 in 2 months’ time:
£0.00514 * ¥12,500,000 = £64,250
The payment will increase to £64,250 instead. The additional payment can be offset if ENG PLC hedges its payables initially by buying a futures contract for JPY 12.5 million. Assuming a futures rate of £0.00468:
£0.00468 * ¥12,500,000 = £58,500
In home currency (Pounds), the futures price is calculated to be £58,500, which is lower than the unhedged payment of £64,250. Thus, ENG PLC will not have to worry about adverse fluctuations in the spot rate as the price is effectively locked in.
Selling Futures to Hedge Receivables
Assuming ENG PLC exports products overseas to countries such as the United States and Thailand. Therefore, receivables in the form of foreign currency can be expected for the company. Its financial performance is therefore affected by currency risk and hedging its transaction exposure can diminish this risk.
In order to do so, ENG PLC can sell currency futures to hedge its receivables. For example, if ENG PLC sells 45,000 pairs of roller-blades at 4594 Baht per pair to its retailer in Thailand and with a current spot rate of £0.0153:
45,000 * 4594 Baht = 206,730,000 Baht
£0.0153 * 206,730,000 Baht = £3,162,969
ENG PLC can expect forthcoming receivables worth £3,162,969. However, due to market instability, depreciation of the Thai Baht occurs and the spot rate falls from from £0.0153 to £0.0133:
£0.0133 * 206,730,000 Baht = £2,749,509
The value of the receivables will decline from £3,162,969 to only £2,749,509 in value. This is a loss of £413,460! However, if the firm sells currency futures to hedge its receivables, it would be protected from this unanticipated depreciation. For example, if the firm sells a 3 months currency futures contract at a rate of £0.0143:
£0.0133 * 206,730,000 Baht = £2,956,239
It would be guaranteed £2,956,239 in receivables that offsets the spot market losses.
Using Currency Options to Manage Currency Risk
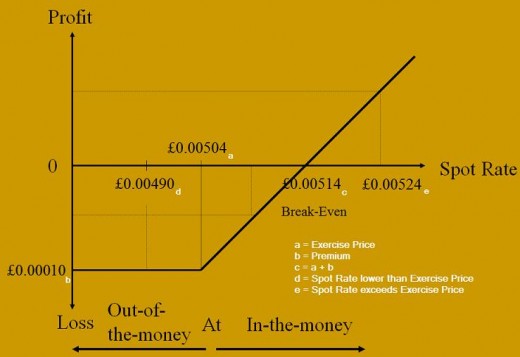
Currency options grant the right to buy or sell an asset at a specified price (known as strike or exercise price) at or within a given time, before expiration. There are no obligations as the contract does not have to be fulfilled and can be lapsed. For currency options, a premium must be paid, even if not exercised.
There are two categories of currency options, call and put options. A firm can make use of a call option to hedge payables, exercising rights to buy a specific amount of foreign currency. This ensures the firm will not have to pay more than a maximum price. A firm can also make use of a put option to hedge receivables, exercising rights to sell off a specific amount of foreign currency, ensuring a minimum amount of receivables.
Using Currency Call Options to Hedge Payables
As described in the example earlier, ENG PLC has payables in JPY (Japanese Yen). An appreciation of the Yen can result in the firm paying more than the expected amount. ENG PLC can make use of currency call options to hedge these payables. Call options will have an exercise price in which it can exercise rights within a given period of time; ensuring payment will not exceed a maximum price.
Unlike currency futures, the price is not locked in as there no obligations to buy. If the spot rate upon payment is lower than the exercise price, the firm can choose to lapse the call option and purchase Yen at the cheaper spot rate. However, if the spot rate exceeds the exercise price, the firm can exercise the call option, purchasing Yen at the exercise price.
For example, assuming an exercise price and premium at £0.00504 and £0.00010 respectively and the spot rate increases to £0.00524:
£0.00504 + £0.00010 = £0.00514
Even with premium included, the rate of £0.00514 is still lower than the appreciated spot rate of £0.00524. The maximum loss that ENG PLC can suffer is the premium of £0.0001 to purchase call options contract initially.
Using Currency Put Options to Hedge Receivables
ENG PLC has receivables in foreign currency from its export business as described earlier. For example, if the company sells 50,000 pairs of roller-blades at $80 each in the United States, it can expect receivables of $4 million in sales. Assuming a current spot rate of £0.66:
£0.66 * $4,000,000 = £2,640,000
ENG PLC can expect receivables worth £2,640,000. If there is depreciation of the US Dollar, the firm will receive less than what is initially expected. For example, if the spot rate decreases to £0.56:
£0.56 * $4,000,000 = £2,240,000
The firm will receive a smaller amount at £2,240,000 instead. To manage this risk, the firm can use currency put options to hedge its receivables, exercise its rights to purchase at the exercise if necessary. There is no obligation for the firm to sell at the exercise price. When receivables are due and the spot rate is higher than the exercise price, the firm can lapse its put option. The firm can then sell the foreign currency at this prevailing spot rate. However, if the spot rate falls, the firm can exercise its put option to sell at the exercise price. Assuming an exercise price of £0.68:
£0.68 * $4,000,000 = £2,720,000
ENG PLC will be guaranteed £2,720,000 in receivables, regardless of spot rate fluctuations. Note that a premium is still required and will have to be deducted accordingly to calculate the profit.