The Dangers of Stagflation for Our Global Economy
Understanding Stagflation
So what is Stagflation? This is an interesting big word as far as economic terms go. It is basically comes from the words stagnation and inflation. In plain terms it describes an economy that is experiencing a recession (get it a stagnating economy) together with a high level of inflation.
A proxy figure for the seriousness of the recession is the unemployment rate. While the CPI is usually use as the proxy for the inflation rate experience by the population.

Introducing the Misery Index?
The Misery Index is a good proxy measurement for the degree of stagflation. Unfortunately it this Index seems to be coming back into fashion again.
The misery index is calculated by adding the unemployment rate with the inflation rate. Another more useful way is probably to calculated Misery Index as a product of the unemployment and inflation rate. You you think about it, intuitively the unemployment multiplies the effect of inflation and vice versa, so it makes more sense to multiply them together.
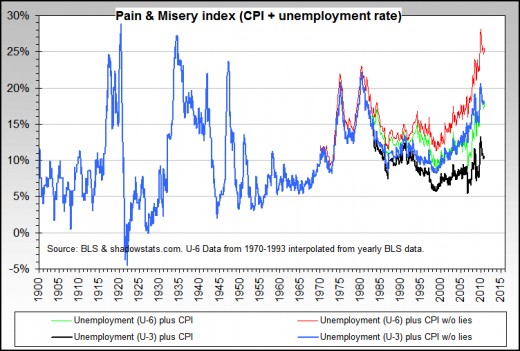
- Daily chart: Misery and happiness: Misery returns | The Economist
But in 2011, with almost every big economy facing high unemployment or inflation ...
Why is it So Difficult to Solve?
The tricky thing about Stagflation is that there is no easy way out of it once the economy is already experiencing it. Trying to solve either the recession or the inflation will usually more the other thing worse.
If the government decides to stimulate the economy by increasing spending and funding it with a loose monetary policy (just a nice way of saying they will print money non-stop) then the inflation will become much worse.
If the government tries to curb inflation by increasing the interest rate then the recession and unemployment will most likely become worse. Therein lies the dilemma.
Historical Context of Stagflation
"Stagflation, a portmanteau of 'stagnation' and 'inflation,' emerged as a significant economic phenomenon in the 1970s, challenging conventional economic theories and policies. The term was first coined by British politician Iain Macleod in 1965 during a period of economic stress in the United Kingdom. The most notable instance of stagflation occurred in the United States during the 1970s. This period was characterized by:
High inflation rates, reaching double digits by 1974
Slow economic growth
Persistently high unemployment, peaking at 9% by May 1975
Several factors contributed to this economic predicament:
The 1973 OPEC oil embargo, which disrupted supply chains and led to soaring oil prices
Unsustainable economic policies by the Federal Reserve in the late 1950s and 1960s
The collapse of managed currency rates
High budget deficits and lower interest rates
The stagflation of the 1970s posed a significant challenge to policymakers, as traditional economic theories suggested that high inflation and high unemployment shouldn't coexist. This period led to a transformation in macroeconomic theory and policy approaches, ultimately influencing how central banks manage monetary policy today. The resolution of stagflation came in the early 1980s under Federal Reserve Chair Paul Volcker, who raised interest rates dramatically to combat inflation. This period marked a significant shift in economic thinking and policy-making, with lasting impacts on how governments and central banks approach economic challenges."
Chances of stagflation in 2025
the chance of stagflation in the United States in 2025 varies among different sources and experts, but there is a notable concern about this economic scenario. Here's a summary of the different probabilities and factors:
- Wells Fargo estimates the probability of stagflation to be lower than 28%.
- A forecaster group consensus puts the chance of stagflation in the US at 25%.
- Jamie Dimon, CEO of JPMorgan, estimates a 35% chance of stagflation.
- Using Epoch's time-invariant Laplace rule, one forecaster estimated a 6.4% chance of stagflation until 2025.
Factors that could increase the risk of stagflation include:
- Potential inflation from President-elect Donald Trump's policies, particularly tariffs.
- Fiscal expansion leading to higher deficits, estimated at 8% of GDP.
- Reduced net migration potentially dampening growth and increasing wage pressures.
- Oil price shocks, with WTI oil averaging above $75 increasing stagflation risk to 23%.
- A top-10 US bank failure, which could increase stagflation risk to 22%.
It's important to note that while stagflation is a concern, many economists still see a "soft landing" or continued economic growth as more likely scenarios for 2025. The Federal Reserve's ability to manage inflation without triggering a recession will be crucial in determining the economic outcome.
My Hand Picked Articles on Stagflation
- RealClearPolitics - The Return of Stagflation
- UPDATE 1-Slowing UK economy to flag stagflation-lite fears | Reuters
* Q4 GDP growth seen 0.5 pct at best, down from 0.7 pct Q3 * Public finance figures to show if austerity plan on track * BoE's King gets chance to hit back at inflation critics (Adds Business Secretary - Economic Future: US, Europe Heading For Stagflation | Markets | Minyanville.com
A combination of stagnation and inflation is considered to be the worst of all of the potential outcomes for an economy.