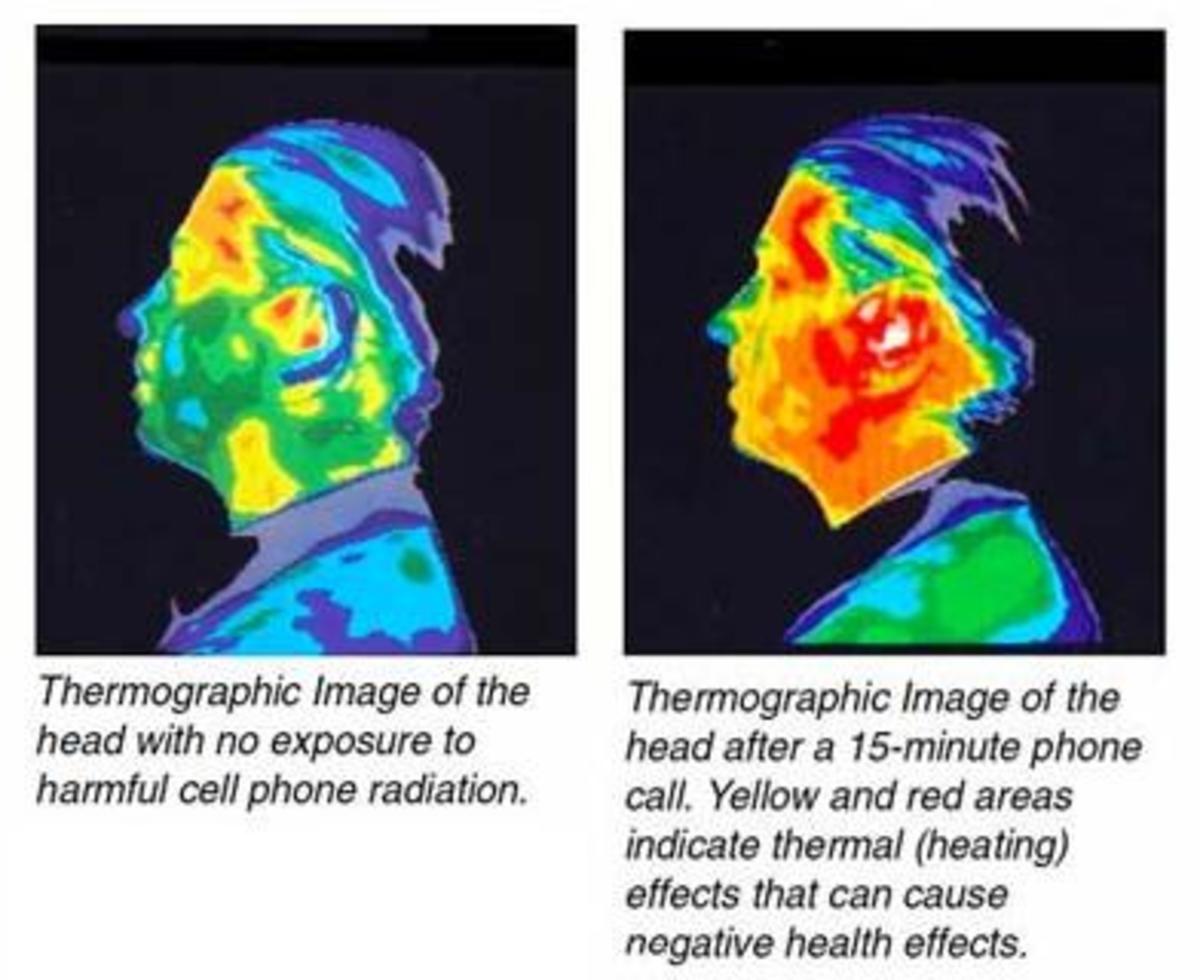
Sun protection
Sun Protection
We all need daylight; small amounts of UV are beneficial for people and essential in the production of vitamin D, necessary for calcium balance. Sun exposure also kills certain germs and boosts our mood. In fact, people who lack daylight can develop SAD –Seasonal Affective Disorder which is a form of depression caused by the lack of sunlight during winter. UV radiation is also used to treat several diseases, including rickets, psoriasis, eczema and jaundice. Unfortunately, overexposure to the sun rays damages the skin irreparably and prolonged exposure to solar UV radiation may result in acute and chronic health effects on the skin, eye and immune system.
Overexposure to the sun (without appropriate sun protection) :
- Causes sunburn and tissue destruction.
- Causes people sensitive to ultraviolet light to react with redness, rashes and itching just after a brief exposure to sunlight.
- Increases the risk of skin cancer
- Damages the skin collagen resulting in premature aging of the skin.

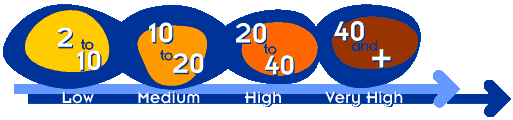
Sun Creams Explained
Sun creams containing titanium reflect or block ultraviolet light. The degree of protection is expressed as a factor number. For example a Factor 6 sun cream means that you can be exposed for 6 times longer than the length of time in which unprotected skin would burn.
In extreme sunlight, you really need a Factor 25 or higher depending on your skin type.
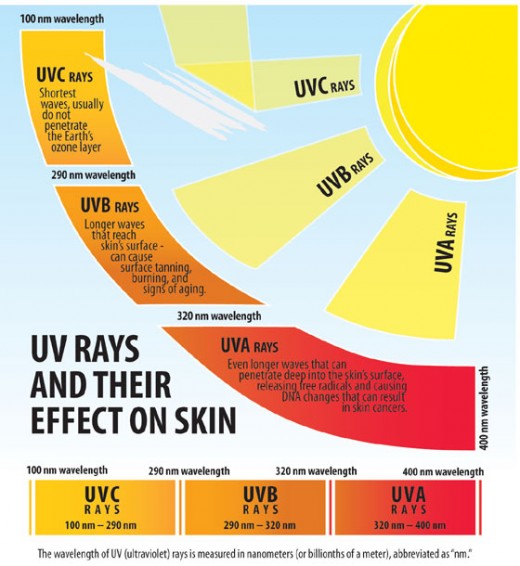
Ordinary sunscreens protect against medium wavelength ultraviolet light, known as ultraviolet B, which is the one that causes sunburn. Unfortunately, they don’t protect against longer wavelength ultraviolet light, known as ultraviolet A, which is the culprit for long term skin aging and cancer. For complete protection you should use both a UVB and UVA sunscreen or cover up with sun protection clothing.
UV Rays and their effects on the skin
What's your skin type?
Moisturizer Sunscreens

Do:
- Know your skin type and protect yourself accordingly.
- Cover up with sun hats and sunscreen protection both UVB and UVA.
- Try to apply sunscreen 15-30 minutes before going out in the sun. Reapply soon after to ensure that you get even coverage. Think of it as painting a wall – the first coat fills in any rough bits and the second gives an even layer
- Let your skin get used to the sunshine progressively. Take it slow for the first few days of exposure.
- Use sun protection products as part of your daily beauty routine. You can find everyday use moisturizers and tinted moisturizers with a high content of sun protection.
- Avoid direct exposure during the midday sun.
- Remember to re-apply sunscreen when exercising or playing sports in the sun.
- Stay away from surfaces that reflect sunlight back at you like water, snow and sand - or else increase your sun protection.
- Encourage your children to enjoy being outdoors but protect them with sun protection clothing and a good sunscreen lotion appropriate for their age and skin type.
- Watch your skin and report any unusual changes to your doctor.
- Choose sunglasses with a a UV 400 label or a a statement that the sunglasses offer 100% UV protection
SunSmart...Quiz on Sun protection
Checking for skin cancer
Examine Your Skin
Sun Protection DON'Ts:
Don’t
- Swim at midday thinking that water protects you from sunburn… it doesn’t.
- Forget to re apply your sunscreen lotion or sunscreen cream after swimming and every couple of hours according to the factor number you are using.
- Go for short intensive sunbathing holidays. A short and intensive exposure is more aggressive and damaging to your skin than a long exposure with only a few hours at a time.
- Do not store sunscreens in very hot places as extreme heat can ruin their protective chemicals.

My favourite swimwear:
- Animal Print Swimwear
"Animal prints never goes out of style" - Crochet Swimwear