- HubPages»
- Technology»
- Computers & Software»
- Computer Software
CMMS Software System Analysis Tools
What Analysis Features Should You Expect to Have in a CMMS?
The basic components of a computerized maintenance management system are: work orders, preventive maintenance, inventory management, purchasing management and equipment downtime tracking. All of these basic components should have a corresponding analysis and reporting module. Charting data obtained from the CMMS gives the user a quick view of trouble spots in the maintenance system.
It makes sense to be able to import analysis data into another application such as Excel. By using Excel to further analyze analysis data the maintenance manager leverages the usefulness of the original analysis data. Additionally Excel is an OLE automation server that exposes advanced capabilities to the reporting software enabling sophisticated data presentation.
Equipment Failure Tracking and Analysis
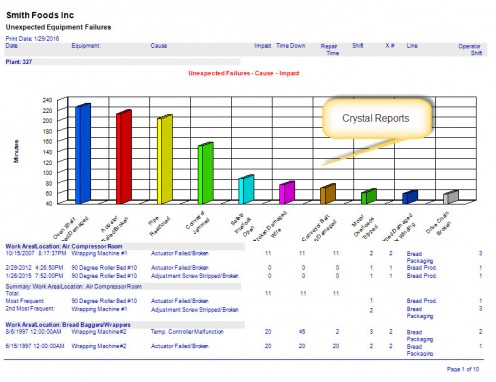
With regards to downtime analysis some of the more advanced systems also offer reliability analysis and other equipment failure analysis tools. Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) leverages downtime data to generate three useful KPIs:
- Quality: reflects the percentage of defective units produced. Often defects can be attributed to equipment issues and should be logged as equipment downtime.
- Availability: Is a measure of planned vs. unplanned (downtime) stoppages. This is basically a measurement of the ratio of potential production time compared to actual production time.
- Performance: This KPI measures how close to the equipment's expected product output is to its actual output. Lagging performance also may indicate downtime. Although an equipment item is still running, if not running at capacity due to an equipment problem then this should be logged as downtime.
Reliability analysis is another useful tool for determining equipment reliability and therefore effectiveness of operation. Few CMMS software programs actually implement reliability analysis. Integrating reliability metrics such as, Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF), into the preventive maintenance system is a powerful way to determine how well labor resources are being used. Mean Time Between Failure (MTBF) guides the maintenance manager towards optimized preventive maintenance intervals by examining the downtime interval and comparing it to the maintenance interval. In some cases this means adding labor in other cases labor may be reduced for a particular preventive maintenance item. Either way efficiencies are optimized.
Work Order and Preventive Maintenance Analysis
Analyzing work performed provides the maintenance manager with the information needed to allocate resources properly and efficiently. Below are several useful Key Performance Indicators (KPIs).
- Percentage completion of assigned preventive maintenance tasks by technician.
- Percentage completion of assigned preventive maintenance tasks by equipment item.
- Overdue work orders by technician, work order type, work order priority or status.
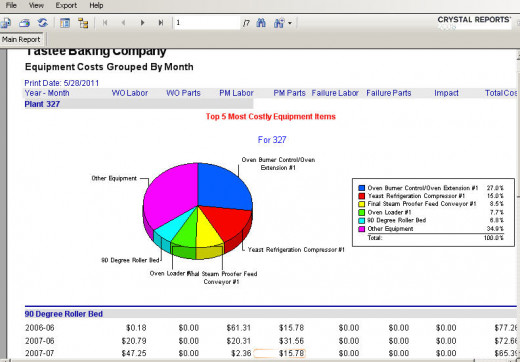
- Overall cost of preventive maintenance labor and parts by equipment item.
- Average late days (for completion of preventive maintenance tasks) by technician.
Some of the above KPIs referred to late completion or overdue assignments. This is useful information, however your CMMS should have the ability to remind technicians if their work is behind schedule. These timely reminders should be automated and issued by email or text message.
Purchasing and Inventory Analysis
Basic inventory management software capabilities typically include:
- Physical inventory variance audit.
- Notifying under stock.
- Inter-Plant inventory search, transfer request and transfer approval process.
- Adequate user-defined fields to enhance the software flexibility.
- Basic fields such as: restocking quantity, restocking level, minimum and maximum stock.
- Capability for pictures or better yet file attachments linking to each inventory item if needed.
Reporting by cost center, account, equipment and who requisitioned inventory are basic reports needed by most maintenance or inventory management users. Cost reports, restocking lists, over/under stock reports and audit reports are useful as well. These reports guide the user towards optimum stock levels and timely restocking of critical spare parts.
What are Best Practices for to CMMS Analysis Reporting?
CMMS software guides the maintenance manager to where labor and other assets should be allocated. Having a selection of various analysis tools offers a better chance to have the correct tool for increasing maintenance efficiencies. All this analysis data if useful, but only if this data may be reported on easily and through various shareable formats. At the very least analysis data should be available in the following shareable formats so that users who do not have the software application may still be informed.
- Web Page (.html)
- Adobe Acrobat (.pdf)
- Excel (.xls)
- Microsoft Word
- Picture formats (.jpg, .png, .tiff, .bmp)
Additionally reporting is best automated by using a built-in report scheduler. Report schedulers are only useful if the reports use a floating date range. The reason for this is that once date sensitive report is defined it should report only on date-appropriate information. This saves the maintenance manager the time and trouble of editing the report definition and truly automates the reporting process.
In short, planning now for CMMS software data analysis later should be a high priority. Let your software reward you with answers that improve your maintenance operation through thoughtful planning of data analysis and reporting.
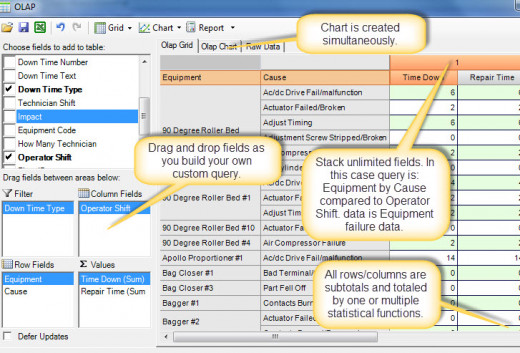
OLAP (data cube analysis)