Difference Between Native Mobile Applications and Web Mobile Applications
Mobile Applications
Today, in the era of smartphones and downloads, we often come across mobile applications. Mobile applications or apps as we call them, are applications that are designed to run on mobile devices.
There are mainly two types of mobile applications:
- Mobile Web Apps
- Mobile Native Apps
There is also a third kind of mobile applications that are called Hybrid Apps, which are the combination of both mobile web apps and native apps.
Let's discuss each type and see what are the main differences between the two.
Mobile Web Apps
A mobile web app is nothing but a web application that is designed for mobile phones and other electronic devices but is used through a web browser. This means that web browsers such as Google Chrome, Safari, Firefox etc. are required to run the application. The app runs through a URL and is generally written in web languages such has HTML5.
So for it to run, your device must be web-enabled and must have an active internet connection. The application then can be downloaded from a central server each time you want to run it.
These are generally cheaper and easier to design. These are often used where the app has to run on multiple types of devices at the same time. This is one of the key advantages of web apps over native apps.
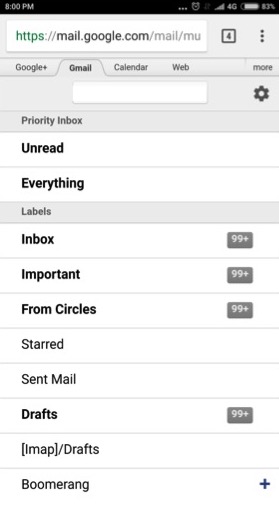
Example of a Mobile Web Application
An example of a mobile web application is the Gmail Web App that is available once you put the URL in the web browser that can be seen in the above image.

Native Mobile Apps
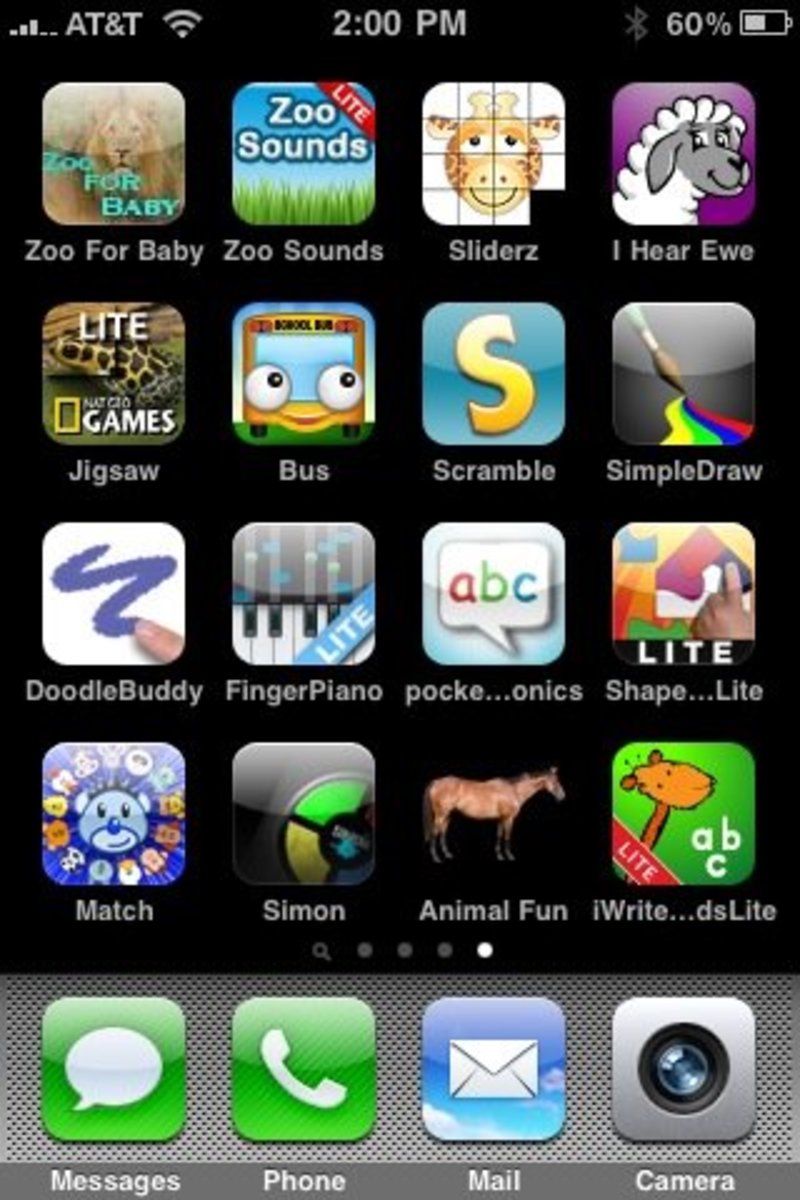
A native mobile app is an application software that is designed for a specific kind of device, according to the operating system of that device. One can download the app from a web store that is usually pre-downloaded on the device (e.g. Apple's App Store). This then requires an installation. You can identify this as small icons on the screen of the device, as shown in the image on the left.
You then do not need to access the app over the web browser as in the case of a Web Mobile App.
To run the application, you need not necessarily have an active internet connection. However, for updates and for downloading the application itself, you may require an internet connection.
These are a little more expensive and difficult to build as compared to a web mobile app because of the intricacies involved in building the app itself. It becomes even more expensive if it has to be made for a wide range of devices. Also, they are designed to use the device's features such as the camera, GPS, contacts etc.
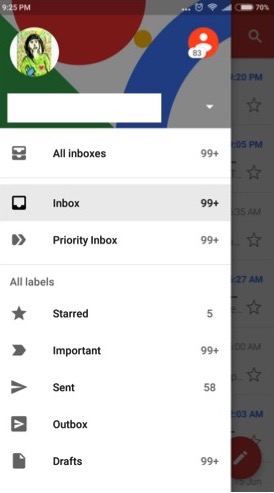
Example of a Native Mobile Application
An example of a native mobile application is the Gmail App that is available on the web store. As seen above it has various features, and once the mail is downloaded you can view if offline as well.
It has a different interface as compared to the mobile web application.
Below is a tabulation of the key differences explained briefly.
Key Differences Between Mobile Web Apps & Mobile Native Apps
Parameters
| Mobile Web Apps
| Mobile Native Apps
|
|---|---|---|
Cross Platform Compatibility
| Enables cross-platform compatibility
| Separate versions of the app are required for the app to work across multiple devices .
|
Time And Cost Involved
| Relatively cheap, easy, and fast to build (Some device-specific customization may be required).
| Time and cost involved is monumental for developing apps on multiple mobile platforms.
|
Maintenance & Promotion
| Easier to maintain.
| Huge maintenance and promotion costs may be occurred.
|
Access
| Simple and universal access (downloading is not required).
| Downloading is required to run the app.
|
Access to On-Board Hardware & Software
| Generally cannot access the on-board hardware and software on a mobile device.
| Native apps can make use of full features of the device such as GPS, camera, etc.
|
Heavy & Complex Graphics
| Heavy/complex custom graphics (gaming, etc.) cannot be supported.
| Heavy/complex custom graphics (gaming, etc.) can be supported.
|
Ability to Run Offline
| Generally require an internet connection to function.
| They hold the ability to run offline.
|
Monetizing the App
| A payment or subscription gateway has to be setup, to monetize the app.
| Native apps are easier to monetize. A price is set, app is listed on an app store, and when users buy it, the developer makes money.
|
Speed of the App
| Are generally slower than the native apps
| They are extremely fast when compared to a web app.
|
So while choosing which type of app is the suitable for you, analyze all the factors that are mentioned above before selecting the right type for your desired function.
Which type of application do you prefer?
© 2017 PGupta0919