- HubPages»
- Technology»
- Computers & Software»
- Operating Systems
How to Mount a Windows Partition in Ubuntu or Xubuntu
I use a dual boot system with both Windows XP and Xubuntu Linux installed on different partitions. You cannot access the Linux partition from Windows, but you can access the Windows partition while running Xubuntu or Ubuntu Linux.
The process of accessing an internal or external drive in Ubuntu is called mounting. You have to mount the drive to be able to read and write its content.
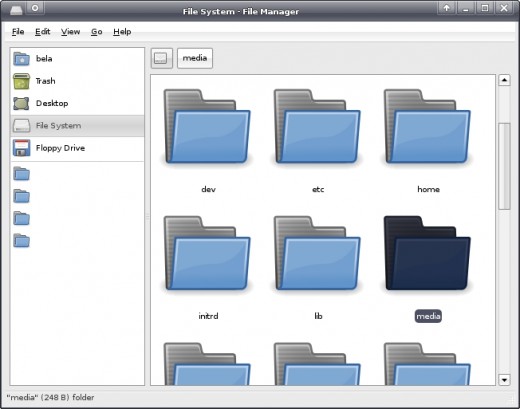
Using Ubuntu it's easy to mount your Windows partition (an internal drive). All you need do is access it via the 'Places' menu usually found in the top sidebar on the desktop. When I switched from Ubuntu to Xubuntu in order to make a slow computer run faster, however, I realized that the icon of the Windows partition has gone missing from the 'Places' menu.
I'm writing this guide for any beginner Ubuntu or Xubuntu user to teach you how to mount (access) your Windows or any internal drive in Ubuntu Linux. Along the way, you'll also learn a few more helpful commands from checking out partition details to becoming the superuser.
How to mount Windows partition in Ubuntu
To mount the Windows partition in Ubuntu you need to open the terminal and type a few simple commands. Go to Applications -> Accessories -> Terminal. Your terminal opens and looks something like this (with the prompt containing your username):
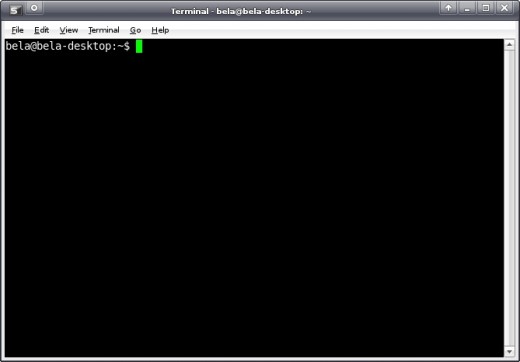
Becoming the superuser in Xubuntu
Type the command:
sudo /bin/bash
When you're asked for your root password type it and press enter. You'll notice that the prompt changed to reflect that you are now accessing the system as root. This means that you are now the superuser and have the power to do whatever you want. Any command you type in the terminal now can potentially harm the system.
You see, one of the good things about Linux is that as a normal user you have absolutely no way to damage the system. Commands that could do that will not be executed because you have no right to execute them. As the superuser, however, be very careful with what you type as your authority is no longer questioned.
Now, you see something like this:
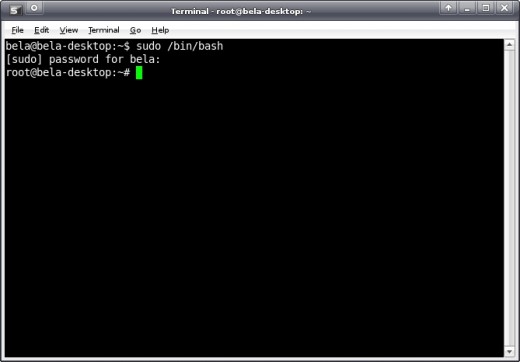
Creating a folder in Xubuntu
Next thing you need to create a new folder under /media directory that will be used to mount the Windows partition. Note, partitions in Ubuntu are treated as folders.
Type in the terminal:
mkdir /media/wdisk
You've just created a folder named 'wdisk' using the mkdir (make directory) command. This folder will be used to mount your Windows partition. Don't worry if you don't get any confirmation that your command was successfully executed. In Linux you usually don't.
The terminal window looks like this:
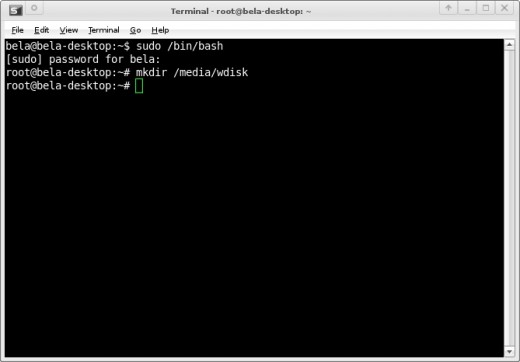
Finding out about your partitions in Xubuntu
Before we run the actual command that will mount the Windows partition, we need a bit more information about the partition itself. We have to find out the name of the Windows drive as well as the file system used on the drive.
In terminal type this command:
fdisk -l
In the picture below, you can see that in my case the Windows drive is /dev/sda1 and the file system is FAT32. Chances are your file system will be NTFS.
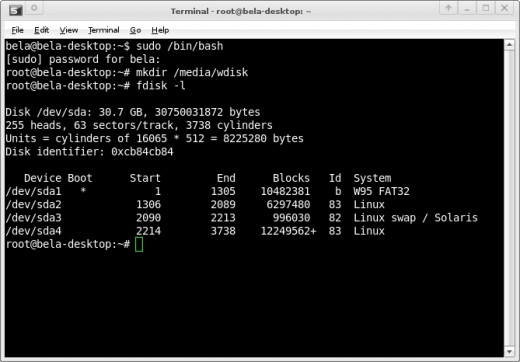
Mounting an NTFS drive in Xubuntu
If your drive uses NTFS file system, type this command in the terminal substituting the /dev/sda1 parameter appropriately based on your findings:
mount -t ntfs-3g /dev/sda1 /media/wdisk -o force
Mounting an FAT32 drive in Xubuntu
If your Windows partition uses FAT32 file system, type this command in the terminal substituting /dev/sda1 appropriately based on your findings:
mount -t vfat -o umask=000 /dev/sda1 /media/wdisk
Success!
Congratulations! You have successfully mounted your Windows partition in (X)ubuntu.
Now, go to Places -> File System -> Media -> wdisk to find and access the drive. Also, make sure you close the terminal to terminate the root access.