- HubPages»
- Technology»
- Computers & Software»
- Computer Science & Programming»
- Programming Languages
Class in Java: Learn More about Java Classes with Sample Java Codes
Get A Website Plus a Free Domain Name in Just 1 Hour!
Bring the new technology in your hands! Share your skills, improve and impress. Get Your Own Website and a Free Domain Name Here!
What to learn about Java Classes? Questions to be answered in this hub.
1. How to make a Java Class?
2. How to access a Java Class?
3. What is a method or a Function?
4. What are the method or function parameters?
5. How to access a method by another method of the same class?
6. What is a Static class?
7. How to overload a method or function Name?
8. What are constructors (constructor, empty constructor, copy constructor)?
9. How to overload a constructor?
How to make a Java Class?
Answer: Make a New Project. Click the Project Source Packages, right click the project name folder,mouse Over New and click Java Class. If you do not have any idea on how to make a new project in Java, here is a tutorial on how to make a new project in Java using netbeans editor.
How to Access a Java Class?
Answer: To access a Java Class and its methods or functions you must declare an object under the java class name you want to access.
Syntax:
ClassNameYouWantToAccess objectName = new ClassNameYouWantToAccess(); //this is how you instantiate an object to access a certain class objectName.ChosenMethodInTheClassYouWantToAccess(); //this is how the object can access the public method of the class
For Java Source Code Example: See the Java Source Code of Binary Search and read through comments.
What is a method or a function?
Answer: A method or a function is a block of code inside a class that is intended to perform a specific task. The Binary Search in the above example has an example of a method. Please check it out again and read the comment to know more about a class method or function.
What is a Method or Function Parameters?
Answer: Parameters are variables declared inside a method or class. The example of a method with its parameters in binary search is this:
public int binSearch(int[] arr, int fIndex, int lIndex,int search) //int[] arr, int fIndex, int lIndex,int search are the parameters of the method binSearch.
Related Hubs
How to Access a Method to Another Method of the Same Class?
Answer: Just copy the method name and put the same type and number of parameters. In accessing a method with another method of the same class, there is no need to declare an object. To see how it is done, See this Java Source Code on Diamond Asterisk Shape and read through comments.
What is Static in a Class?
If you use a static type in a public method of a class, you do not need to declare an object to access that method in the main class. Refer to the next java source code example.
Syntax for a static and Syntax for accessing static method.
public static dataType methodName()//this how to make a static method
{
}
className.staticMethodName(); //this is how to access a static methodHow to Overload a Method or a Function Name?
Answer: Overloading a method or a function is just making a method/function with the same name as the other. However to overload them, they must have a different parameters.
Java Source Code Example:
//java class
package samlejava;
class javaClass {
public String Schedule(String room, String section)//method1
{
return room +" "+" "+ section + " "+" ";
}
public String Schedule(String subject,String day, String time)//overloaded methodName
{
return subject +" "+" "+day+ " "+" "+ time+" "+" ";
}
public static String Schedule(String teacher)//overloaded methodName with a type static
{
return teacher;
}
}
//main class
package samlejava;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner readInput = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter your Name: ");
String name= readInput.nextLine();
System.out.print("Add a Subject: ");
String subject= readInput.nextLine();
System.out.print("Add a Section: ");
String section= readInput.nextLine();
System.out.print("Add a Room for the Section: ");
String room= readInput.nextLine();
System.out.print("Add Day for the Subject: ");
String day= readInput.nextLine();
System.out.print("Add time for Subject: ");
String time= readInput.nextLine();
System.out.print("Add teacher for the Subject: ");
String teacher= readInput.nextLine();
javaClass iAccess = new javaClass();//access javaClass class,instamtiate object
System.out.println();
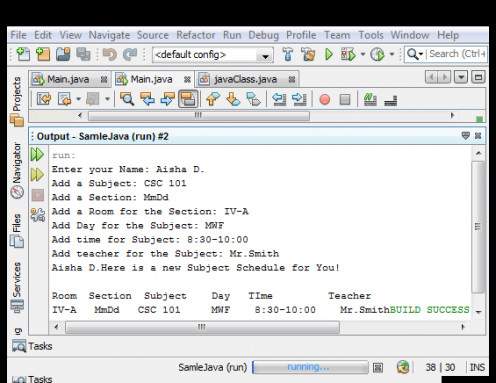
System.out.println(name + "Here is a new Subject Schedule for You!");
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Room" + " " + " " + "Section" + " " +" " +
"Subject" + " " +" " + "Day" + " "+" " +
"TIme" + " " + " " + "Teacher" );
System.out.println();
System.out.print (iAccess.Schedule(room, section));//access method1
System.out.print (iAccess.Schedule(subject, day, time));//access method2
System.out.print (javaClass.Schedule(teacher));//this is how static works
}
}
Sample Output:
What are constructors (Normal Constructor, Copy Constructor, Empty or default Constructor)?
Answer: Constructors are those which are similar to the class name. Basically, constructors are used to initialize the variables. They do not have any data types.
Syntax for constructor:
public className(list of parameters here)
{
initialization here.
}
Constructors can be 1 or more in a class, however they should have different parameters. Empty or default constructor is always present in a class. You can make your own empty constructor or let the computer generate it automatically for you, as you execute the class. You can tell that the constructor is default if it do not have any formal parameters. Moreover, copy constructor, is a constructor which copy the task of an existing method.
Syntax for copy constructor:
public className(className Parameter)
{
copy code
}
How to Overload a Constructor?
Answer: Overloading a constructor is also just like overloading a function name with different formal parameters.
To understand about constructor more: Refer to the Java Source Code below and Read through the comments:
//java class
package constructor;
public class constructor {
String fName;
String lName;
String gender;
int age;
public constructor() //empty constructor initialized variables
{
fName= " ";
lName= " ";
gender = " ";
age= 0;
}
public constructor(String firstName, String lastName)//constructor1 return fName and lName
{
fName = firstName;
lName = lastName;
System.out.print(firstName+ " " + lastName);
}
public constructor(String Sex, int Age)//overloading the constructor Name return gender & age
{
gender = Sex;
age = Age;
System.out.print( Sex+ " : " + Age);
}
public constructor(String firstName, String lastName,String Sex, int Age)//overloading 2 return all
{
fName = firstName;
lName = lastName;
gender = Sex;
age = Age;
System.out.print(firstName+ " " + lastName + ": " + Sex+ " : " + Age +" yrs. old");
}
public constructor(constructor copyCons)// copy the last constructor
{
fName = copyCons.fName;
lName = copyCons.lName;
gender = copyCons.gender;
age = copyCons.age;
System.out.print(fName+ " " + lName+ ": " + gender+ " : " + age +" yrs. old");
}
}
//main class
package constructor;
import java.util.Scanner; //import scanner for input Stream
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);//instantiate object to input
System.out.print("Enter first name: ");
String fName = input.nextLine(); // read the string input
System.out.print("Enter last name: ");
String lName = input.nextLine(); // read the string input
System.out.print("Enter gender: ");
String gender = input.nextLine(); // read the string input
System.out.print("Enter Age: ");
int age = input.nextInt(); // read the integer input
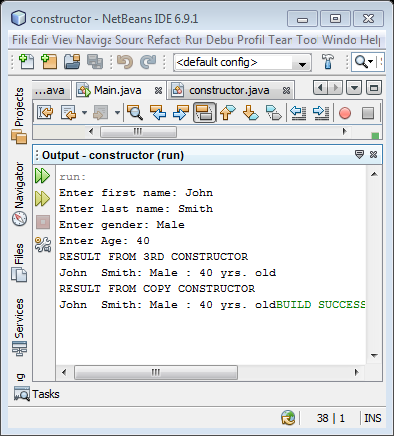
System.out.println("RESULT FROM 3RD CONSTRUCTOR");
constructor access1 = new constructor(fName, lName, gender, age); //accesslast constructor;
System.out.println();
System.out.println("RESULT FROM COPY CONSTRUCTOR");
constructor access2 = new constructor(access1); // access copy constructor
}
}
Other Java Source Code Examples
- What is a Java Scanner Class and How to Use it?
- Java Program: How to Use Switch Statement in Java
- Java source code Sample: Print Different Asterisk Shapes in Recursion
- Java Source Code: A Recursive Asterisk Diamond Shape
- Java Source code: How to Add numbers inside an Array Using Recursion
- Java Source code sample: How to Add Numbers inside an Array using For Loop
- Java Source Code: Sort Numbers in Selection Sort
- Java Source Code sample: Sort Numbers in Bubble Sort
- Java Source code on Printing the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) using Recursion
- Java Source code sample: Print String Backward using Recursion
- Java Source Code Recursion: Recursive Koch Snow Flakes
- Java Source Code in a Recursive Linear Search
- Java Source Code: Binary Search in Recursion
- Java Source Code Determine Person's Salutation and Current Age
- Java source code: Recursive function for X to the power Y