Domain Name Services - DNS
The Internet has a plethora of different sites and to access them you have to enter an address in the corresponding field of your browser, for example: www.hubpages.com, www.youtube.com or www.wikipedia.org.
However the computer has to find these sites amongst all the others and this is when the DNS technology makes all the difference.
DNS is the acronym for Domain Name System.
This is a resource used in TCP / IP (the protocol used on the Internet and in most networks) that allows to access computers without the user or the computer itself being aware of the IP address.

Each web site is accessible by an IP address (a group of numbers). The problem is that there are so many of them that it is almost impossible to memorize each IP.
Imagine that instead of typing www.hubpages.com to access this site you had to tell the browser the IP address (66.211.109.13). Now think that you had to do the same for each and every site you visit...
As you may have noticed it would be very difficult to access each of these sites by IP address. It would be necessary to memorize them as well as you had to see a list of IP addresses every time you wanted to access a new site.
DNS was created to deal with this problem. That is what allows the use of names (also called labels) instead of IP to access the websites.
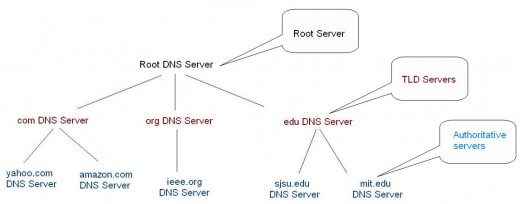
Basically DNS can be seen as a collection of large servers databases distributed around the world showing which IP is associated with a name (like www.sitename.com).
DNS "Domain Name System" Basics
These data banks have the responsibility to indicate which IP is associated with a name of a site.
When you type an address in your browser, like www.sitename.com, your computer asks the DNS servers of your Internet provider to find the IP address associated with that site.
If the servers do not have this information then it communicates with others who may have.
A domain name usually consists of two or more parts which are conventionally written separated by dots.
- The rightmost label conveys the top-level domain (for example, the address www.sitename.com has the top-level domain com).
- Each label to the left specifies a subdivision or subdomain of the domain above it. In theory this subdivision can go down 127 levels. Each label can contain up to 63 octets. The whole domain name may not exceed a total length of 253 octets. In practice, some domain registries may have shorter limits.
- A host name refers to a domain name that has one or more associated IP addresses (e.g., the www.sitename.com and sitename.com domains are both host names, on the other hand the com domain is not).
Who controls DNS?
The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) has the responsibility of assigning and coordinating all DNS Roots, IP addresses, and other Internet protocol resources.
==============================================================