Ergonomics at Work and the Computer
What is Ergonomics?
According to the Merriam-Webster dictionary, ergonomics is "an applied science concerned with designing and arranging things people use so that the people and things interact most efficiently and safely —called also biotechnology, human engineering, human factors."

IEA Mission & Goals
- International Ergonomics Association
To elaborate and advance ergonomics science and practice, and to expand its scope of application and contribution to society to improve the quality of life, working closely with its constituent societies and related international organizations.
Goals of Ergonomics
Ergonomics aims to fulfill the goals of health and productivity. Ergonomic design is applied to products to optimize the interaction between humans and other elements of a system. An ergonomics professional will examine things such as equipment fit, size, and shape for the individual completing the required task. In order to avoid things such as repetitive strain injury, an ergonomist will evaluate workstation setup unique to each individual. Things examined may include computer monitor, keyboard, mouse, chair, and desk. The ergonomist works to optimize the adjustment of each piece of equipment as well as recommend different equipment in order to keep the programmer safe and productive.
There are other ergonomic considerations besides workstation optimization. According to the International Ergonomics Association, specializations generally include the following:
Physical ergonomics is concerned with human anatomical, anthropometric, physiological and biomechanical characteristics as they relate to physical activity. (Relevant topics include working postures, materials handling, repetitive movements, work related musculoskeletal disorders, workplace layout, safety and health.)
Cognitive ergonomics is concerned with mental processes, such as perception, memory, reasoning, and motor response, as they affect interactions among humans and other elements of a system. (Relevant topics include mental workload, decision-making, skilled performance, human-computer interaction, human reliability, work stress and training as these may relate to human-system design.)
Organizational ergonomics is concerned with the optimization of sociotechnical systems, including their organizational structures, policies, and processes.
Stretching at Your Desk to Avoid Injury

Why Ergonomics?
Ergonomics can be important in any job to maintain safety, avoid injury, and optimize productivity. Ergonomics is most frequently associated with people who occupy desk and sitting jobs. However, ergonomics is also important to consider when operating machinery, driving, and moving any sort of load, either manually or using equipment. Any time an individual interacts with a system, ergonomics should be considered.
One of the biggest reasons individuals or companies utilize an ergonomics professional is to avoid injury. Common injuries may include carpal tunnel syndrome, repetitive strain injury, low back pain, neck stiffness, nerve compression, and muscular soreness in various locations. These types of injuries occur because of improper equipment use, poor fitting equipment, or poor body position. An ergonomic assessment will address any faults discovered by providing new equipment such as chairs and desks and also instruct an individual on proper use. It is important tom realize that although proper equipment is necessary, the individual must also be trained in its proper use.
Links for Posture
- Posture for a Healthy Back
Posture is the position in which you hold your body upright against gravity while standing, sitting or lying down. - Safety and Health Topics: Ergonomics
Safety and Health Topics: Ergonomics - Office Chair, Posture and Driving Ergonomics
Guidelines and helpful tips for prevention of back pain and neck pain at the workplace using ergonomic concepts. - Best Ergonomic Office Chairs 2011
As you are interested in the best ergonomic office chairs you already know what it is all about as much as I do. The pain of perching on a stiff piece of furniture...
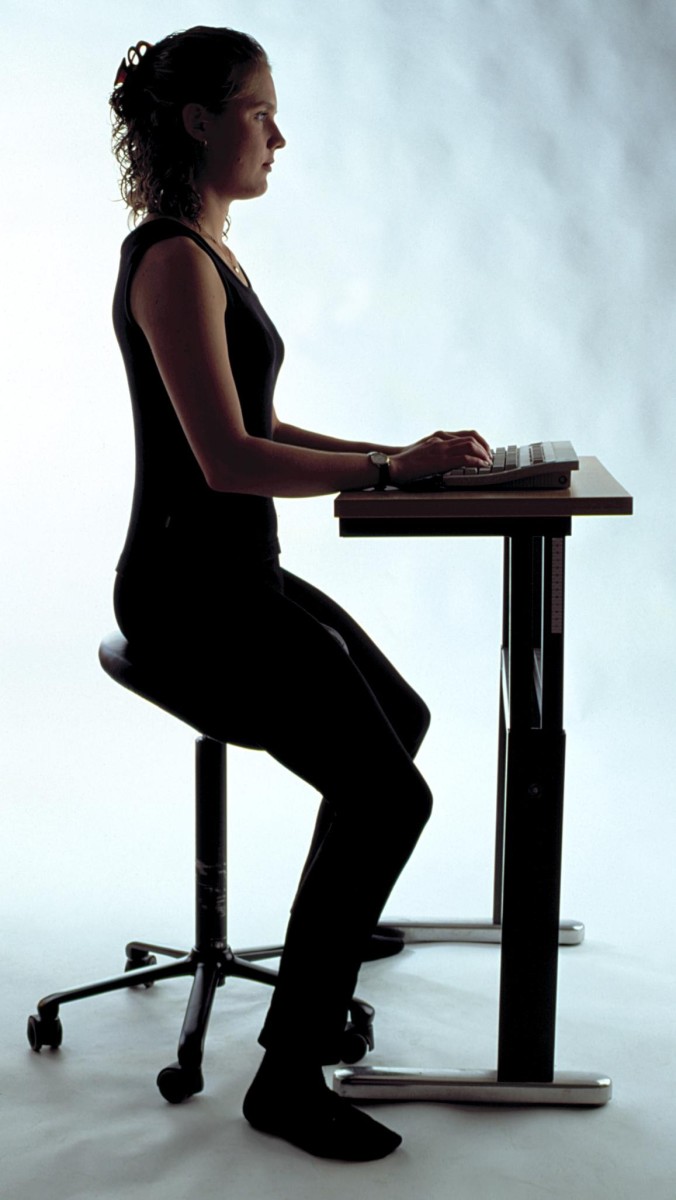
Correct Way to Sit

Sitting Posture
Optimal sitting posture can ensure there is symmetry and balance throughout the body and ensure that irritation does not occur from compression or overuse. From the ground up, here are some suggestions that one may utilize to optimize their posture:
- Feet Flat on the Floor - It is important to have your feet flat on the floor, or if your feet do not reach the floor, they should be on a foot rest. Having weight through your legs takes some load away from the spine as well as make it easier to maintain upright sitting posture. When your feet are stretched out or curled under the chair it is more likely for your low back to round out and you begin to slouch. This can affect the low back but also your neck.
- Knees Bent 90-110 Degrees- It is important to have your knees bent between 90 and 110 degrees. This will ensure your feet stay flat.
- Hip Position- When sitting, your hips should be slightly higher than your knees. If they are not, your knees will bend further than the above recommendation and your low back is more likely to round out.
- Shoulder Position- Your shoulders should be at rest with your elbows at your side. This means you should try to avoid slouching and try to keep your shoulder blades touching the chair back. This position ensures good posture and many neck and shoulder muscular pain can be avoided.
- Elbow Position- Your elbow should remain next to your body at all times. If the keyboard or mouse are too far away and you have to reach for them, the muscles of your upper back, shoulder, and neck are likely to be overused and can become painful. Try to sit close to your work so that your elbow can remain in a relaxed position at your side.
- Wrist Position- To avoid wrist injury such as carpal tunnel syndrome, try to keep your wrist in a neutral position. This can be accomplished with a wrist pad in front of your keyboard while typing. Proper chair and desk height can also influence wrist position.
- Neck Position - Keeping your head over your shoulders is very important to neck safety. Ideal position is to have your ears over the center of your shoulders. Once in this position, keep your eyes straight forward. Your head weighs 10 pounds, so keeping it balanced over your center is important. With poor posture the head comes forward due to gravity and you are forced to extend your neck to maintain forward gaze. For every 1 inch your head moves forward, it is an extra 10 pounds that your neck has to support. So if you slouch with your head forward 3 inches, that's 40 pounds your neck feels.

Ergonomic Chair
For a sitting job, like so many people have, an ergonomic chair is required. Often a company will provide a new chair if discomfort develops or injury ensues. The following are several adjustments that can be made to a chair in order to optimize sitting posture:
- Seat Height- Seat height must be adjusted to allow for a 90-110 degree knee bend, feet resting on ground or foot rest, keyboard at elbow level, and desk items within reach.
- Seat Pan- This is the part you sit on. It can often slide front to back to adjust the depth of the seat, and also tilt front to back. When sitting all the way back in a chair, it is best to have about 3 fingers width between the front of the seat pan and the back of your knees. The angle should be slightly forward to ensure good low back position.
- Back Rest- The back rest should provide support for your trunk when you lean into it. It should be firm enough so that you cannot recline in the chair. The height should be adjusted in order to fill in the natural curvature of your low back. Ideally the back rest is tall enough to support your shoulders also.
- Arm Rest - The arm rests should be adjusted so that your arms can hang at your side in a neutral position, but provide enough support through the elbow to avoid muscle strain. If your shoulders feel shrugged up near your ears, the arm rests are likely too tall.
Desktop Ergonomics
With computers a staple in almost every profession, it is important to understand proper computer setup and body position in relation to the computer. The monitor height should be adjusted so that when sitting in proper posture, the top of the monitor is even with your line of sight. This ensures that when looking at the center of the monitor, you are looking slightly downward and avoiding neck extension. The monitor should also be roughly 2 feet from your eyes. The keyboard and mouse should be close enough to reach without having to pull your elbows away from your body. Ensure your chair fits under your desk or use a pullout keyboard tray. Everything you use frequently should be within short reach such as the phone, pens, stapler, etc. If entering data from a printed document, please the document close to the monitor to avoid excessive and repetitive neck movement. In general, think of keeping your joints in neutral positions and setting up your workstation to minimize effort.
Useful Ergonomic Equipment
Equipment
There are several pieces of equipment that can help optimize your workstation setup. An adjustable chair is a good place to start. There are several types of keyboards to help neutralize wrist position. There are also several types of mouses that allow for various hand positions. If on the phone frequently, use a headset.
General Considerations
In general, it is best to think about keeping your spine neutral and sitting tall. Ergonomics are a big piece of the puzzle, but do not take the place of training your body to be stronger and move better. In addition to the above suggestions, take frequent breaks at work by stretching briefly every hour, walk during your lunch break, and manage your workload differently when possible by dispersing repetitive tasks throughout the day.