Collision on a Galactic Scale
As in the past, so is the future as Andromeda has a fateful encounter with the Milky Way galaxy.
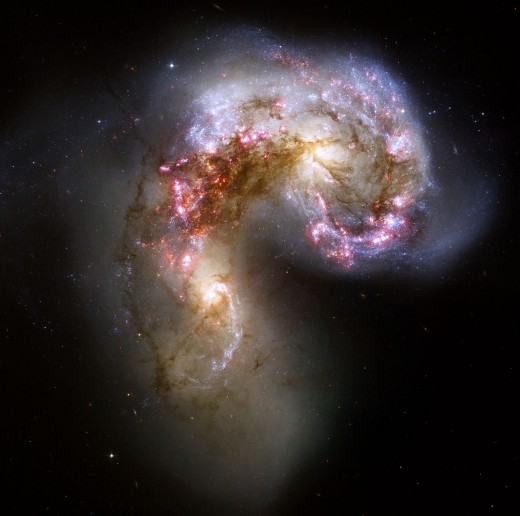





Mega Apocalypse in the Future
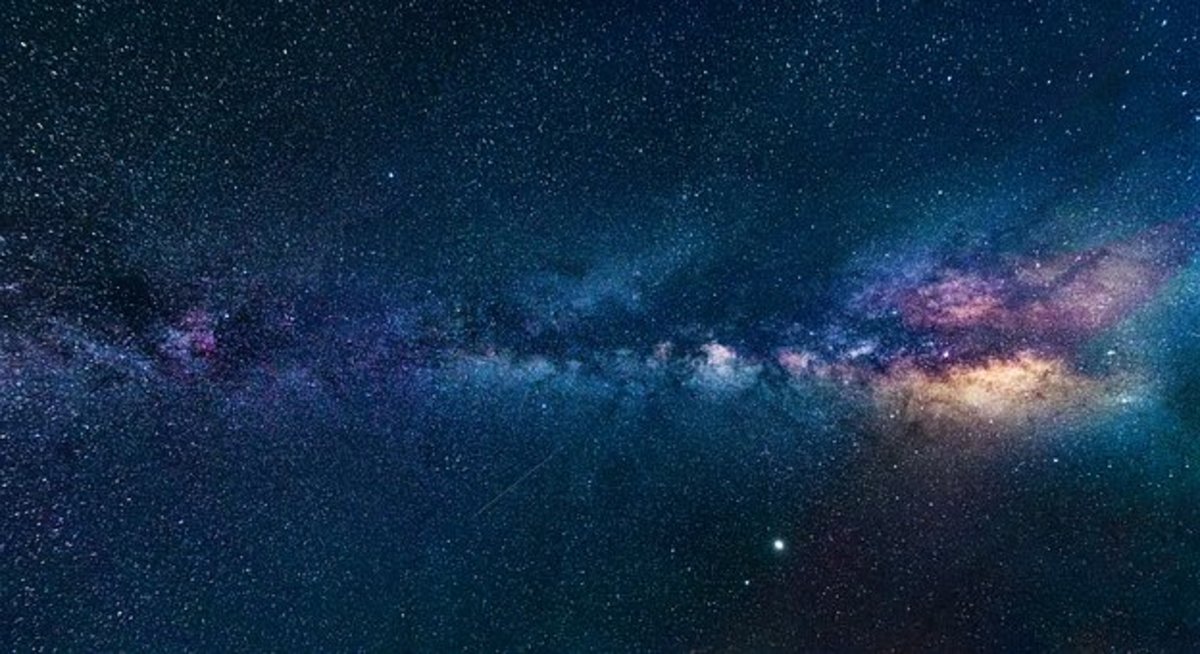
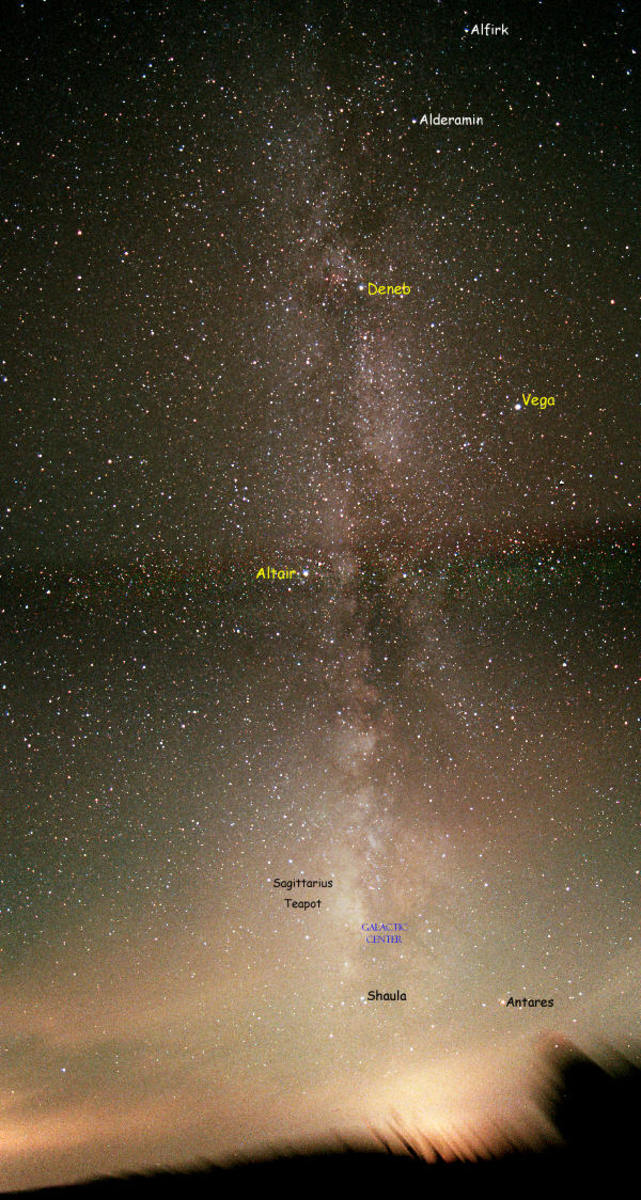
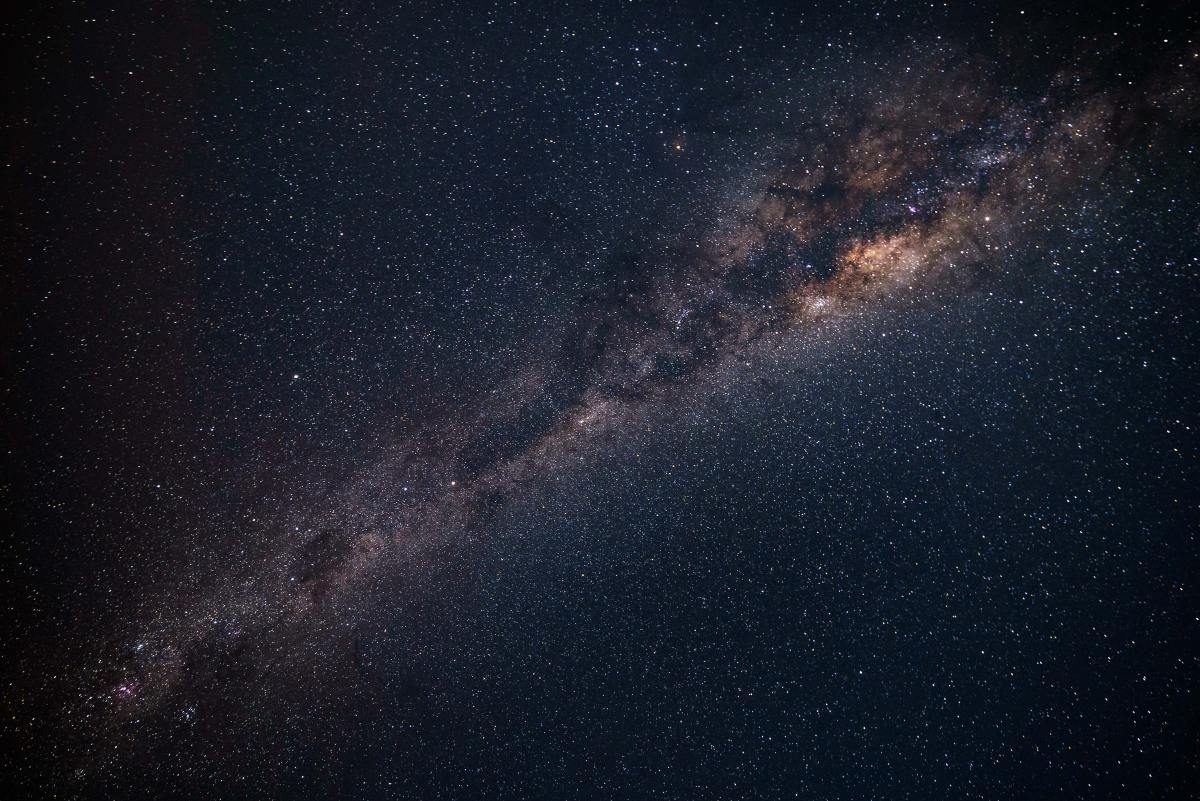
It is thought that the massive Andromeda galaxy is on a collision course with ours, but that appears to be 4.5 billion years in the future, long after the earth and sun are evolved well beyond the capability to support life. We know that galaxies cannibalize one another to form larger ones as we have found from sky surveys of various sources including the Hubble telescope. There is strong evidence that our galaxy got to its present size by this process and it is evidenced by a number of facts. These are;
-
The uneven rotation of the various arms of our local galaxy suggesting clumps of mass. Outer regions move faster than inner regions
-
More than one central black hole with a 26 million year orbit
-
Speculation that a small galaxy is already embedded in the far side hidden from our view
-
The overall structure is a barred spiral.
-
Very fast moving stars, like Bernard's star passing near our region.
-
The galactic halo stars
-
Massive globular clusters that behave like mini spherical galaxies.
-
Metal rich and metal poor star regions.
-
Indications of the warped structure of the disk and the center.
Our local galaxy has been absorbing smaller ones since it became organized long before the birth if our solar system. In fact, our solar system may have been born from the matter of one of the smaller absorbed galaxies, though there is no direct proof of this. It is a topic that needs further research. Though we have suspected that for a long time that the distant future of our galaxy and solar system is to merge with Andromeda, the proof has been sketchy until now. The following piece describes the most recent findings.
On Wednesday September 2nd, 2009, The Associated Press ran information on the latest findings. Some of this is detailed below.
Earth's nearest major galactic neighbour, Andromeda, is a cosmic cannibal, just our galaxy is, which is also a sizable galaxy. In fact, in the local group, Andromeda and our galaxy are the two largest in a group that consists of dozens of dwarf ones. Two dwarf irregulars are in closing orbits to our galaxy and these are the large and small Magellanic Clouds. The Andromeda galaxy is heading our way. Astronomers have long suspected that Andromeda is a space predator. It, like ours, is consuming dwarf galaxies that wander too close to it. Now, cosmic detectives are doing a massive search of the neighbourhood and have found proof of Andromeda's sordid past. They have spotted leftovers of small galaxies in Andromeda's wake.
“Early results of a massive telescope scan of Andromeda and its surroundings found about a half-dozen remnants of Andromeda's galactic appetite. Stars and dwarf galaxies that got too close to Andromeda were ripped from their usual surroundings. “What we're seeing right now are the signs of cannibalism," said the study's lead author Alan McConnachie of the Herzberg Institute of Astrophysics in Victoria, British Columbia. "We're finding things that have been destroyed; partly digested remains."
Their report was published in Thursday's edition of the journal Nature.
Andromeda and the Milky Way galaxy are the two big galaxies of our local galactic neighbourhood. Andromeda is the larger of the two and will absorb us, rather than we absorb it. Andromeda is the closest major galaxy, which is about 2.5 million light years away. The massive mapping of Andromeda has been and is still looking half a million light years around Andromeda. Astronomers have known for decades that galaxies consume each other, sometimes violently. Sometimes they create new mega-galaxies. Many large spherical galaxies, such as in the Virgo cluster are of this type. But this study is different because "of the scale of the cannibalism, and we've found evidence directly in front of our eyes," said co-author Mike Irwin, an astrophysicist at the University of Cambridge in England.
This type of galactic crash is common and we have photographs of galaxies caught in the act. “The paper makes sense”, said Harvard astronomer Mark Reid, who was not part of the Andromeda mapping team. “Just because Andromeda consumes a galaxy, it does not make the victim disappear”. he said.
The cannibalistic behaviour often just strips stars from where they had been owing to the complex interactions of gravity in a tidal fashion and this rearranges the night sky for any planets with observers to see. “Most of a galaxy is empty space, so there is little if any crashing of stars and planets going on”. Irwin said. This of course is not ruled out, as evidenced by the cratering just in our own solar system. Indeed, there are craters on the moon and Mimas that came close to destroying these bodies completely. Despite galaxies being mostly empty space, stars will be passing one another at high speed. If any have planets, these will at least be disrupted in their orbits and some even torn out of their star's gravity to become a lone wander in deep space between the stars; a rogue planet. When the two massive galaxies of our local group begin to merge, it will be interesting to witness. "It would be a beautiful night sky," Irwin said. "It would be quite spectacular."
There are accounts in myth, of battles in heaven, that could well be a memory of a past event where a rogue planet of star approached a little too close to our solar system and caused major havoc. In our immediate future measured in millions of years, several stars will approach the solar system. One of them will come within one light year and could cause a comet storm from the Oort cloud.
The main victim of Andromeda is a dwarf galaxy called Triangulum. This one is in the process of becoming absorbed. “Eventually, in about 3 billion years, Triangulam, which once came too close to Andromeda and was stripped of some stars, will spiral into Andromeda, about the same time it comes crashing into Earth's galaxy”. said study co-author John Dubinksi of the University of Toronto.
“The Milky Way and Andromeda are heading toward each other at about 75 miles per second. They are so far away from each other that the big crash is a few billion years away. And even that might be nothing more than a reshuffling of the night sky or the creation of one super-sized galaxy”. McConnachie said.
References:
Nature: http://www.nature.com/nature
The Pan-Andromeda Archaelogical Survey:
https://www.astrosci.ca/users/alan/PANDAS/Home.html
Interacting galaxies
- Interacting galaxy - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Colliding galaxies are common, but as there is a lot of space between the stars, they can interact and fuse with one another.








