MCQs - Organs of Mixed Function
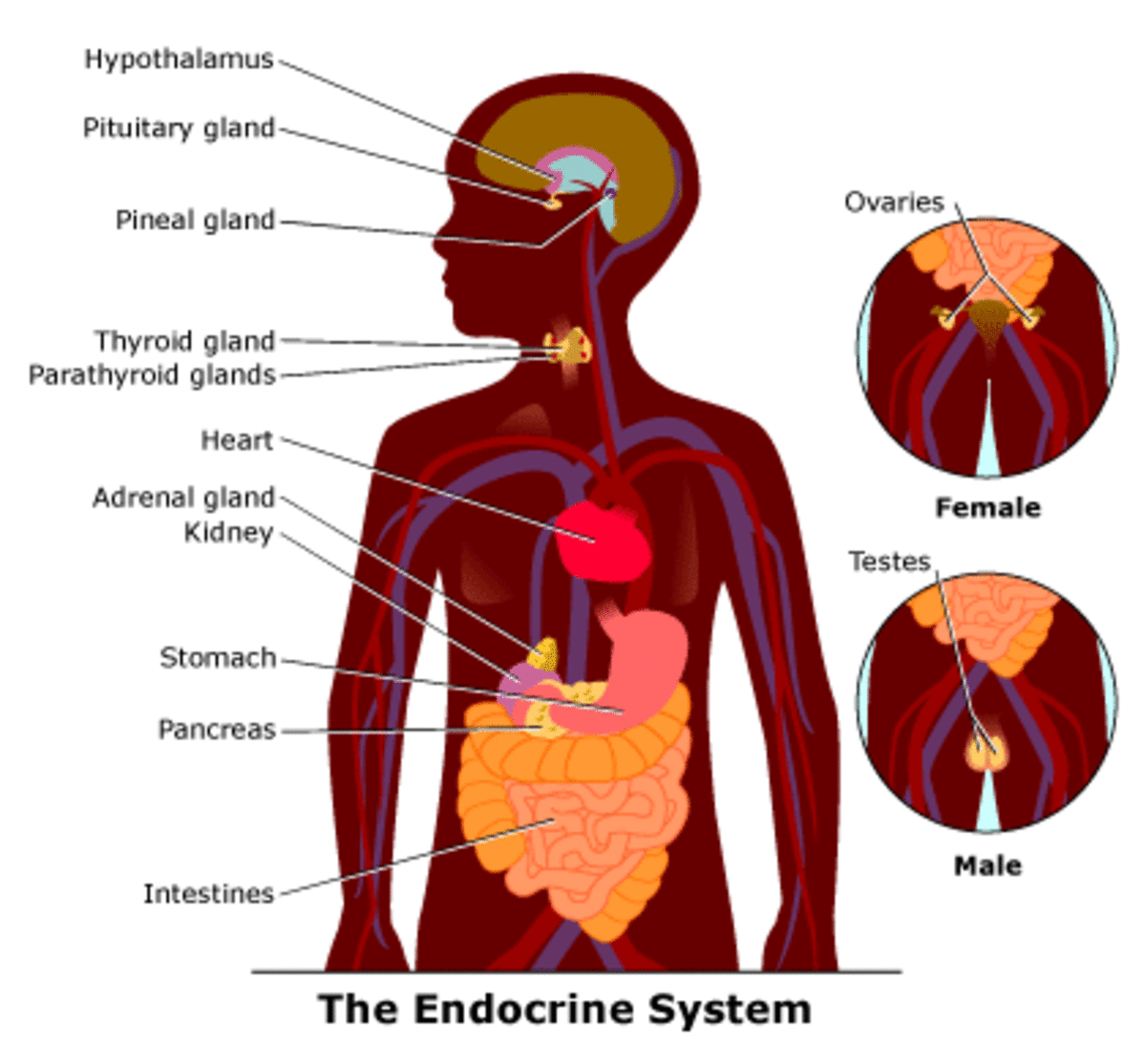
Organs of Mixed Function
You got confused? Here we are talking about the organs which have endocrine function in addition to the other bodily functions.
Hypothalamus is situated below the thalamus and above the brainstem inside the brain.
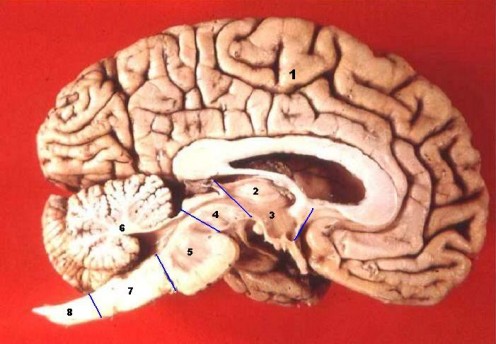
Pituitary gland
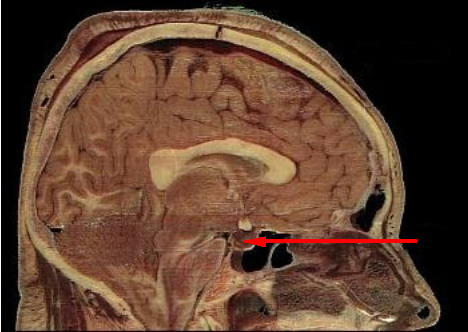
The endocrine organs in the body can be classified as
- Solely endocrine function –Pituitary, parathyroid, thyroid and adrenal gland
- Mixed function – Hypothalamus, thymus, heart, stomach, pancreas, duodenum, kidneys, skin, ovaries and placenta
- Complete function uncertain – Pineal body
Solely endocrine function:
They are the glands with only endocrine function. They release hormones into the blood stream as the need arises and helps in processes such as growth, metabolism and sexual development.
- Pituitary gland: Pituitary glandis situated within the brain. It has got two parts; the anterior pituitary and the posterior pituitary. The anterior pituitary is known as the “master gland” and controls the functions of other endocrine glands. It releases the stimulating hormones for other glands in the body depending on the blood level of their secretions. The posterior pituitary secretes vasopressin and oxytocin. Vasopressin causes the blood pressure to increase and controls the amount of water in body cells. Oxytocin causes uterine contraction during child birth and initiates lactation.
- Parathyroid gland: Parathormone is the hormone secreted by parathyroid gland. It controls the blood level of calcium and phosphate.
- Thyroid gland: Thyroid gland secretes thyroxin. Thyroxin plays a vital role in the body’s metabolism.
- Adrenal glands: Adrenals are also known as the suprarenal glands as they are situated on the top of the kidneys. It has got two parts; the inner adrenal medulla which secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine and the inner adrenal cortex which secretes cortisol, aldosterone and androgens.
How the Brain Works: Hypothalamus
Mixed Function
These organs perform their endocrine function in addition to the other bodily functions.
- Hypothalamus: Hypothalamus is situated below the thalamus and above the brainstem inside the brain. It secretes certain hormones called the hypothalamic releasing hormones which control the functions of the pituitary gland.
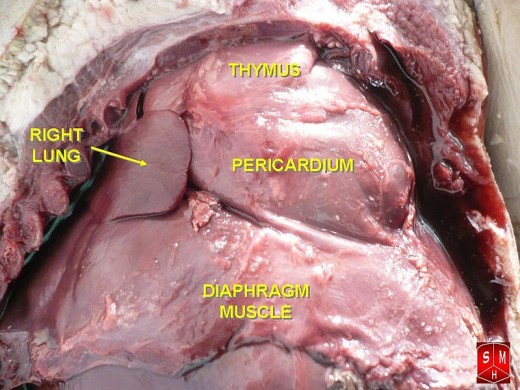
- Thymus: Thymus gland is situated in the upper chest cavity. Its main function is maturation of T lymphocytes as part of the immune system. Thymus also secretes humoral factors which help in the development of lymphatic system.
-
Heart: As you know heart’s main function is to provide oxygen and nutrients to all tissues in the body through blood. Heart also secretes a hormone atrial natriuretic peptide in response to certain stimulus from the body.
Thymus gland is situated in the upper chest cavity.
Complete function uncertain
- Pineal body: Pineal gland is situated inside the brain. Its functions are not really clear. It secretes a hormone called melatonin which controls the sleep-wake patterns. Be careful not to confuse the pigment ‘melanin’ with melatonin.
Multiple Choice Questions
view quiz statistics- Multiple Choice Questions on Neurons
A compact article on information about neurons and multiple choice questions on neurons to prepare for competitive exams. - MCQs on Eye, Ear and Taste
An article explaining the impportant points in normal anatomy and physiology of eye, ear and tongue. Useful for premedical, medical and nursing students - MCQs on muscle stretch reflexes; tendon stretching
MCQs on muscle stretch reflexes; tendon stretching; a guide for students - MCQs on Cerebral Cortex and Subcortical Structures
Review questions (multiple choice) to prepare for medical entrance exams - Multiple choice questions on the functions of cell o...
Multiple choice questions for premedical competitive exams
Fill in the blanks
- Skin converts ............. into ............ or vitamin D on exposure to UV rays
- Renin converts angiotensin I to ...................
- The thymus gland produces .............. which helps in maintain the T lymphocytes
- .............. in pregnant women is a significant source of estrogen and progesterone
Answers
- 7 - dehydrocholesterol into cholecalciferol
- angiotensin II
- thymosin
- Placenta