Kingdom - Monera

- It was first created by Copeland in his 4 - Kingdom classified. Later it was also opted by R.H. Whittaker in his 5 - Kingdom classification.
- It includes unicellular or multicultural prokaryotic organisms
- All of them have cell wall. Hence all belongs to plants. The only exception is that Mycoplasmas included in Monera do not contain cell wall.
- These are the most primitive anaerobic organisms.
- In the place of nucleus, cell has single, circular, naked, double stranded DNA. Nuclear wall is absent. So it is considered as incipient nucleus or nucleoid or prokaryon or gonophores
- Nucleolus is absent. Histones are absent.
- Membrane bounded organelles like plastids, Mitochondria, Golgi, ER etc are absent.
- Cells consist 70 S Ribosome’s only.
- Cells show Amitosis.
Kingdom Monera includes
1) Archaebacteria
2) Eubacteria
3) Cyanobacteria
4) Mycoplasmas
5) Actinomyeetes
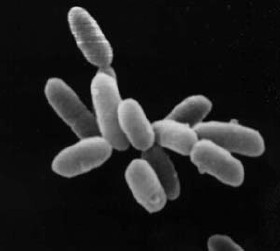
1.Archaebacteria
These are unusual, special, unique group of bacteria. These are also called as oldest living fossils. The cell is made of pseudomurein. The cell membrane is made of branched chain of lipids due to which they, survive in extreme conditions and become immune to most antibiotics.
Some of the archaebacteria show various kinds of occurrence as follows. (Habitats).
Salty areas or pools - Halophiles -Example: Halobacterium.
Sulphur rich hot acid springs - Thermoacedophiles - Example: Sulfolobus.
Marshy, swampy & Cattle rumen - Methanogens.
Methanogens are obligatory anaerobic and produce Methane (Bio gas) from dung and CO2.
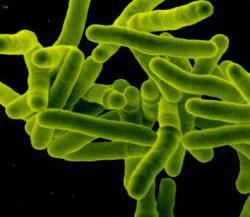
2. Eubacteria
They were first discovered by Antony von Leeuwenhoek (Dutch) in 1675. He named them as Animalecules.
The term Bacteria was coined by Ehrenberg.
They are unicellular, microscopic, prokaryotic, omnipresent or ubiquitous, most versatile, adaptable.
They live everywhere i.e. soil, water, air, inside the plant, animal, ice, hot water etc.
They may be autotrophic (Photoautotrophic or Chemosynthetic) heterotrophic (saprophytic or parasitic) or they may show symbiosis.
Chemosynthetic bacteria participate in inorganic oxidative, exothermic chemical
reactions and obtain energy to produce food. Bacteria like Rhizobium shows symbiosis in the root nodules of Leguminaceae (Fabaceae).
Photosynthetic bacteria do not evolve oxygen.
The shapes of bacteria may be spherical (Coccus), rod (Bacillus), Comma (Vibrios) or spiral (Spirillum)
The cell wall is made of peptidoglycan or murein or Mucopeptide. They may bear pili, flagella and sex pili. Cell membrane in some forms Mesosomes.
Nucleus is indistinct.
Membrane bounded organelles are absent.
The only organelleles present in theme are 70 S Ribosomes. These are naked.
Some bacteria may consist plasmids. Bacteria are friends and as well as foes to man. Saprophytes are decomposers. They are useful in recycling. Bacteria are useful in conversion of milk to curd, fermentation nitrogen fixation and production of antibiotics. Some bacteria cause TB, Cholera, Plague, Typhoid, Leprosy, Tetanus in human beings. Some bacteria cause Blight of Rice, Citrus Canker and Fire blight of Apples.
Reproduction
1. Asexual reproduction occurs by endospores when conditions are unfavourable. Endospores are highly resistant and everlasting generally Bacillus bacteria form endosphores.
2. Vegetative reproduction occurs by binary fission when conditions are favourable. It is the most common kind of reproduction.
3. Sex organs are absent. Gametes are absent - Zygote is not formed. But sexual reproduction occurs by the incomplete transfer of genetic material from one bacterium to the other. It is rare.
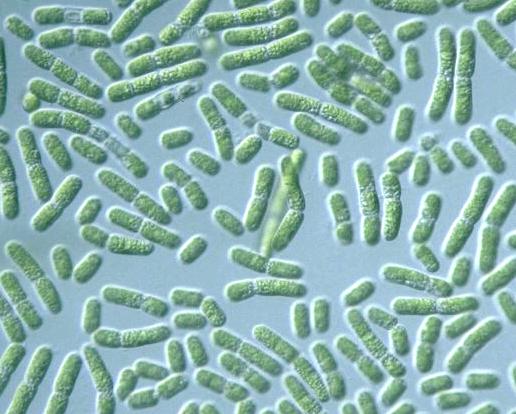
3. Cyanobacteria
These are also called Blue Green Algae (BGA). They belong to Cyanophyceae (Class in Algae). Now they are included in Eubacteria in Whittaker Classification.
These are unicellular or multicellular, filamentous, unbranched or colonial.
They may aquatic or terrestrial. They are photo autotropic and consist pigments like Chl-a, Carotenes, Xanthophyll, Phycocyanin and Phycoerythrin. Branching is absent. Flagella are absent. Filaments are called Trichomes. They are covered by gelatinous mucilage sheath.
They are photosynthetic and oxygenic. They are the oldest, first, primitive plants to release oxygen in photosynthesis.
Some of these algae form blooms and pollute the water bodies.
Example: Microcystis. Protoplasm of the vegetative cells is divided into
1) Outer, peripheral, pigmented chromoplasm.
2) Central, colourless centroplasm
The colour of the red sea is due to Trichodesmium erythrium. Vegetative reproduction occurs by fragmentation. Fragments are called Hormogonia.
Asexual reproduction occurs by Akinetes.
Sexual reproduction is absent.
Some Cyanobacteria show symbiosis and fix nitrogen.
Example: Nastoc and Anabaena, Aulosira etc.
These algae consist Heterocyst.
Spirulina is the richest source of single cell proteins. Some Cyanobacteria also form lichens with the association of Fungi. It is also an excellent example of symbiosis.
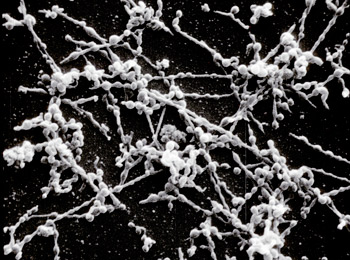
4. Mycoplasmas
This term was first coined by Nowak to PPLO
The term PPLO (Pleuro-Pneumonia like (organisms) was coined by Roux and Nocard for the disease (Pleuro-pneumonia) causing agent in cattle.
These are the smallest prokaryotic living cells
Cell wall is absent. So they show Pleomorphism. These are also called as jokers of micro biology. They are obligatory, intracellular, pathogenic, parasites. They are obligatory anaerobic.
Notable pathogenic Mycoplasmas cause the following diseases
1. Mycoplasma hominis causes urethritis in human beings.
2. M. Salivarium causes disease in upper respiratory tract in man.
3. Witches broom disease in Alfa alfa.
4. Pleuropneumonia in cattle.
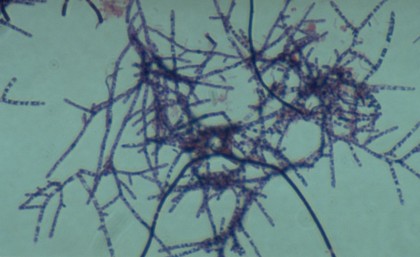
5. Actinomycetes
- These are Monerans.
- They include filamentous, branched, prokaryotic bacteria.
- They form colonies.
The cell wall consists Mycotic acid.
They may be saprophytic, parasitic or may show symbiosis
Saprophytic- Example:- Streptomyces
Parasitic-Examples:- Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Mycobacterium leprae, Mycobacterium bovis, Corynebacterium diphtheriae
Symbiosis- Examples:- Frankia shows symbiosis in the root nodules of Casuarina by fixing nitrogen.
Pathogenic- Examples:- Leprosy, Tuberculosis
Antibiotics- Examples:- Waksman discovered Streptomycin (first bacterial antibiotic) from Streptomyces
You Might Also Like
- The Living World
Living organisms can be easily identified and distinguished from non-living objects. A virus shows both the characters of living and non-living. - Delicious Fleshy Fruits
Formation of seeds inside the fruit is the characteristic feature of angiosperms. Fruit is regarded as a ripened post fertilized product of the ovary. The fruit has tow parts namely, the fruit wall (pericarp) and the seed. The nature of pericarp... - Solanceae and Liliaceae
Tomato, potato, brinjal, chilly, onion and garlic are some important vegetables which are used in the preparation of almost in every food item. They will provide the tasty, hot, spicy ad delicious diet. For e.g. slices of potato are used in making... - The Fragrance of Flowers
In evolved plants, the body is more complex and shows various levels of organization such as cells, tissues, tissue systems and organs. Tissues are functional units of organ. A tissue is a group of similar or dissimilar cells that have a common origi - Reproduction in Angiosperms
Development of male and female gametophytes, formation of gametes is pre requisite for sexual reproduction in angiosperms. In angiosperms the female gametophyte is produced from haploid megaspore present in the nucellus of the ovule and it is called.