What are the Chemical Hazards of Food?
Chemicals in Food
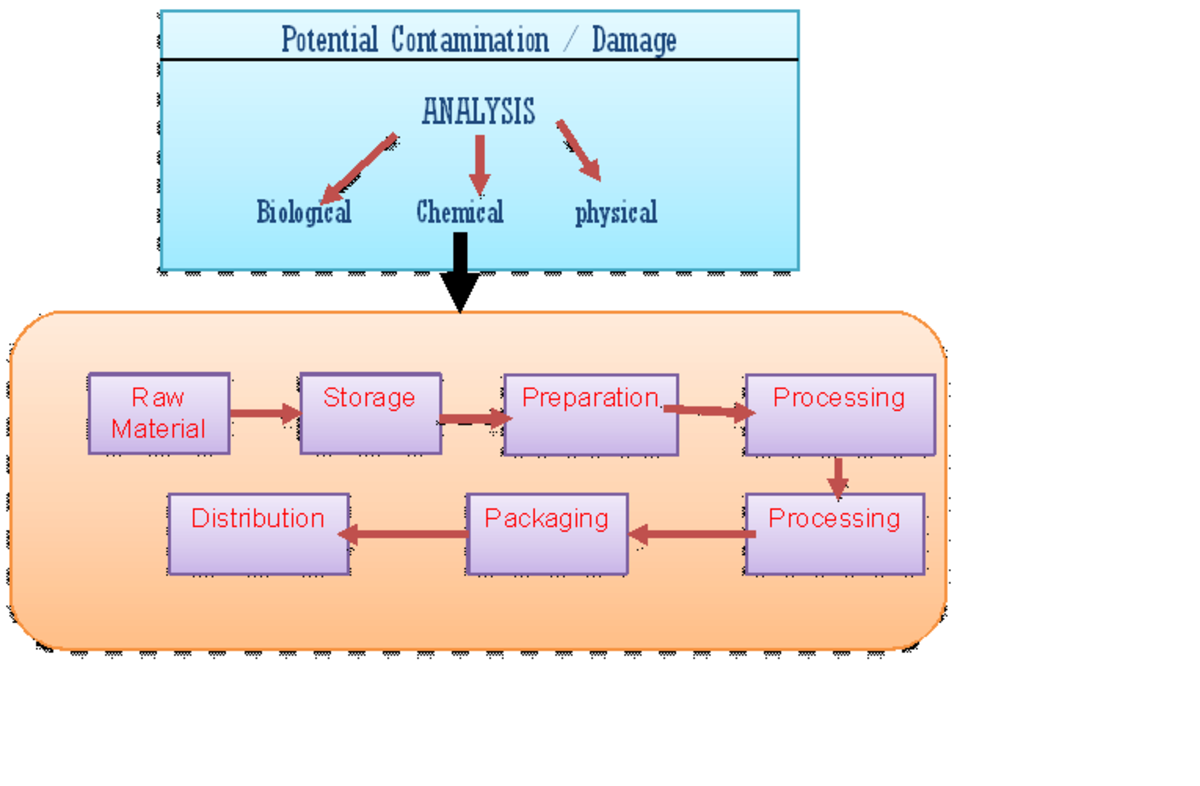
CHEMICAL HAZARDS
Chemical contamination of foodstuffs can happen at any stage of their production, from growing of the raw materials through to consumption of the finished product. The effect of chemical contamination the consumers can be long term (acute) such as the effect of allergenic foods.
The current main chemical hazards issues in food products are as follows;
· Cleaning chemicals-from food preparation area e.g. detergents
· Pesticides – fungicides, insecticides, herbicides, rodenticides
· Toxic metals
· Nitrites, nitrates and N-nitrogen compounds
· Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs)
· Plasticizers and packaging migration
· Veterinary residues – antibiotics, hormones, ectoparasiticides
· Phyllotoxins – Cyanide, Estrognes
· Zootoxins
Cleaning chemicals
In any food preparation or production operation, cleaning chemicals are one of the most significant chemical hazards. Cleaning residues may remain on offenses or with pipe work and equipment and be transferred directly onto foods, or they may be splashed onto food during the cleaning of adjacent items.
It is therefore vitally important that the HACCP Team members consider the implications of the cleaning procedures in their operation. Problems can be prevented by the use of non-toxic cleaning chemicals where possible, and through the design and management of appropriate cleaning procedures. This will include adequate training of staff and may involve post-cleaning equipment inspection.
Pesticides are any chemicals which are applied tocontrol or kill pests and include the following;
· Insecticides
· Herbicides
· Fungicides
· Wood preservatives
· Masonry biocides
· Birds & animals repellent s
· Foods storage protectors
· Rodenticides
· Marine anti-fouling paints
· Industrials/domestic hygiene products
Pesticides are used in a wide range of applications all over the world, in agriculture, industry, shipping and the home. The use most relevant to food safety is in agriculture but contamination from other sources must also be considered.
In agriculture pesticides are used during production to protect crops and improve yields, and after harvest they are again used to protect the crops in storage. However, not all pesticid4s are safe for use on food production (for example, some of those used for the treatment of timber) and even those that are safe for food ;use may leave residues which could be harmful in high concentrations. To overcome these problems most countries have very strict control on the pesticides which can be used and on the residue limits which are acceptable. These are set through expert toxicological studies and are normally set down in legislation.
From the food safety point of view you need to know which pesticides have been applied to all your raw materials at any stage in their preparation. You must also understand which pesticides, are permitted for use and what the maximum safe residue limits are in each case. Control can be built in to your HACCP System to ensure that the safe levels are never exceeded in your products.
In addition to raw materials which have direct pesticide contact, you must also consider the possibility of cross-contamination with pesticides at any stage in food production. This could be cross-contamination of your raw materials or it could happen on your site, e.g. from rodenticides. These issues should again be considered as part of your HACCP study.
Allergens
Some food components can cause an allergic or dood intolkerance response in sensitive individuals. These reactions can range from mild to extremely serious, depending on the dose and the consumer’s sensitivity to the specific component.
The control options open to the food processor manufacturing products with allergenic components are effective pack labeling, control or rework and effective cleaning of equipment. The label must accurately describe the product components. Special care must be taken when declaring a generic category of ingredient such as ‘flash’or ‘nuts’, where certain individuals may be allergic to specific species of fish or type of nut. A manufacturer or caterer who produces several different products must also consider the chance of cross-contamination of allergenic components into the wrong product where they will not be labeled. This is particularly important in the case of recycling loops and rework of product, and these issues souls be considered as part of the HACCP Study.
Toxic Metals
Metals can enter food from a number of sources and can be of concern in high levels, the most significant sources of toxic metals to the food chain are:
· environmental pollution;
· the soil in which food stuffs are grown;
· equipment, utensils and containers for cooking, processing and storage;
· food processing water ; and
· chemicals applied to agricultural land.
Particular metals of concern are tin (from tinned containers), mercury in fish, cadmium and lead, both from environmental pollution. Also significant are arsenic, aluminum, copper, zinc, antimony and fluoride, and these have been the subjects of research studies.
As for the other chemical hazards, you need to understand the particular risk of toxic met also your products and this is likely to be product packaging. Control can be built in as part of your HACCP System.
Nitrites, Nitrates and N-nitroso Compounds
Nitrate occurs naturally in the environment and is present in plant foodstuffs. It is also a constituent of many fertilizers, which has increased its presence in soil and water.
Nitrites and nitrates have historically been added to a number of food products as constituents of their preservation systems. This deliberate addition of nitrite and nitrate to food is closely governed by legislation as high levels of nitrites and N-nitroso compounds in food can produce a variety of toxic effects. Specific examples include infantile methaemoglobinaemia and carcinogenic effects.
N-nitrose compounds can be formed in foods from reactions between nitrities or nitrates with other compounds. They can also formed in vivo under certain condition s when large amounts of nitrites are present in the diet. Nitrate can cause additional problems in canned products where it can cause lacquer breakdown, allowing tin to leach into the product.
The HACCP T eam must ensure that nitrite and nitrate being added to lproducts do not exceed the legal, safe levels and must give appropriate consideration to the risk of contamination from other sources and otgher ingredients, giving an increased overall level.
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs)
PCBs are members of a group of organic compounds which have been used in a number of industrial application. Because these compounds are toxic and environmentally stable, their use has been limited to closed systems, and their production has been banned in a number of countries. The most significant source of PCB s in foodstuffs is through absorption from the environment by fish. PCBs then accumulate through the food chain and can be found in high levels in tissues with high lipid content. This issue should be considered by HACCP Team dealing with raw materials of marine origin.
Plasticizers and Packaging Migration
Certain plasticizers and other plastics additives are of concern of they are able to migrate into food. Migration depends on the constituents present, and also on the type of food, for example fatty foods promote migration more than some other foodstuffs.
The constituents of food contact plastics and packaging are normally strictly governed by legislation, along with the maximum permitted migration limits in a number of food models. The HACCP Team should be aware of current issues for both food packaging and plastic utensils, and should build control into the HACCP system. This might mean the requirement for checks on migration at the packaging concept stage.
Watch what are you eating

Food Safety
- Top Ten List of Food Additives to Avoid
What are the top ten food additives that should be avoided? This article takes a look at why we use additives and which additives should be eliminated from our diets. - List of Safe Foods For Acid Reflux
Have you been in pain recently because of acid reflux? Most people have suffered from heartburn, a major symptom of acid reflux disease, at least once in their life. Those who suffered from this condition will know how uncomfortable and painful it...
Food Safe