What is MiscroStategy ? MicroStrategy -Objects, Schema and more -Interview Questions/Answers
What is MicroStrategy?
MicroStrategy is a leading Business Intelligence tool which existing independently by itself (for now). Business Intelligence technology providing integrated reporting, analysis, and monitoring software that helps the decision support system in an organization.
What is MicroStrategy’s Technical Definition?
MicroStrategy is a Business intelligence tool with a ROLAP engine which can connect to almost any databases.
What is MicroStrategy means?
MicroStrategy is an object oriented model with an attractive and an easy to use graphical user interface for developers and end users. MicroStrategy is a reporting tool, which is used to create and send reports, also used to create ad-hoc report and dashboards for mobiles, emails.
There are main two version of this tool Web version and Client Version.
Web version: Generally web version is used for the users.
Client version: Generally client version is used for the developer.
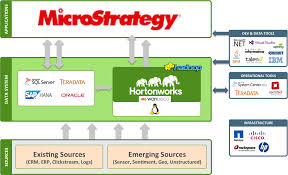
Metadata, I-server, web server, and Narrow cast Server are the main components of the MicroStrategy.
What are the main roles in MicroStrategy?
There are main three different roles on MicroStrategy.
Administrator: By default, the role/person will have full access to the environment. In other words this role has full access to all the type of objects mentioned above.
Architect: By default, access to configuration objects is restricted.
Developer: By default, no access to configuration objects, use access to schema objects and full access to public objects.
MicroStrategy Brief View
What is the RDBMS means?
RDBMS stands for: Relational Database Management Systems
What is Data modeler?
Someone who designs the project, and creates data model.
What is Heterogeneous mapping?
Heterogeneous mapping is used to map any attribute to the column which is not identical in names and but same in meaning.
What is OLTP?
OLTP stands for Online transactions Processing
OLTP is a system which deals with operation data.
OLTP is a class of program that facilitates and manages transaction – oriented application, typically for data entry and retrieval transaction in a number of industries.
What is OLAP?
OLAP stands for Online Analytical Processing
OLAP is a process where it allows its use to easily extract and view the data.
OLAP is computer processing that enables a user to easily and selectively extract and view data from different points of view.
What are the Differences between ROLAP, MOLAP and HOLAP?
MOLAP stands for Mutlidimensional Online Analytical Processing
In this form of storage, data is stored in the form of multidimensional cubes. Data is not stored in the relational database.
ROLAP stands for Relational Online Analytical Processing
As the name suggests this is a method which helps in manipulating the data using the clauses of the relational databases eg. Where clause
HOLAP stands for Hybrid Online Analytical Processing
HOLAP tries to combine the positive aspects of both MOLAP and ROLAP in order to leverage the storage and processing capability of data.
Advantages of MOLAP:
- Fast in data retrieval (recovery)
- Complex calculations can be performed very fast
Advantages of ROLAP:
- Can use the relational database functionalities
- Can handle large amounts of data
Advantages of HOLAP:
- Faster performance of MOLAP
- Drill through capabilities of ROLAP
What are the types of MSTR objects available?
There are only and only three types of object in MicroStrategy. They are same follows:
- Schema objects
- Application objects
- Configuration objects
Please also refer
- MicroStrategy
MicroStrategy brief Introduction and MicroStrategy related defiantions and explanations. (Rolls in MicroStrategy, Meta Data, Narrow Cast Server, Cube and all what you need to know about MicroStrategy) - Business Analyst
This blog is on Basic Information about Business Analyst roles and responsibilities.
Schema Objects:
A schema is a collection of database objects. Schema objects are the logical database structure that characterizes database's data. Schema objects include tables, views, sequences, synonyms, indexes, clusters, database.
Schema objects are logical structures created by users. Schema objects characterize various sections of the logical data model, including logical data model components such as facts, attributes, and hierarchies. Report designers can use these schema objects to create application objects such as metrics, filters, templates, and eventually reports. The default schema objects in the Schema Objects folder are populated when you create a new project. The Schema objects are grouped into the following subfolders (types of Schema Objects).
- Attributes
- Facts
- Functions and Operators
- Hierarchies
- Partition Mappings
- Tables
- Transformations
A schema is owned by a database user and has the same name as that user. There is no relationship between a tablespace and a schema. Objects in the same schema can use storage in different tablespaces, and a tablespace can contain data from different schemas.
Schema objects can be created and manipulated using SQL. As an administrator, you can create and manipulate schema objects, just as you do with the logical and physical structures of your database using Oracle Enterprise Manager. The underlying SQL is generated for you by Oracle Enterprise Manager.
Application/Public Objects:
These objects are used to deliver analysis of and insight into relevant data.
Application objects are objects that a report designer can directly manipulate, such as reports, metrics, filters, and prompts.
You can use each of these objects to add different types of reporting flexibility and functionality to a business intelligence application.
Public objects are just a folder in metadata which “mainly” holds application objects, it is not a type of objects. Security Filter is a configuration object even though it is created the way application objects are created.
Common application objects include (types of Application/ Public objects)
- Reports
- Documents
- Filters
- Templates
- Metrics
- Prompts
- Custom Groups
- Searches
- Drill Maps
Configuration Objects:
Configuration objects are MicroStrategy objects which can be re used in multiple projects and they appear in the system layer. Configuration objects are MicroStrategy objects which can be re used in multiple projects and they appear in the system layer. Configuration objects are created using the Administration option in Microstrategy Desktop.
Object included in this category are:
- Connectivity information – Data base Instances
- User privileges – Users, Groups
- Project administration
- Schedules
What are the two types of schemas available in DataWare?
Star Schema and Snowflake Schema
What is Star schema?
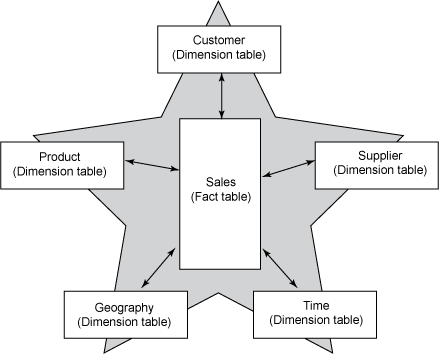
Star Schema:
One fact table surrounded by all the three or 4 or 5 any no. of dim table. Symbol looks
like star schema. This is more de-normalized data.
In the star schema design, a single object (the fact table) sits in the middle and is drastically associated to other surrounding objects (dimension lookup tables) like a star. Each dimension is represented as a single table. The primary key in each dimension table is related to a foreign key in the fact table. A star schema can be simple or complex. A simple star consists of one fact table; a complex star can have more than one fact table.
Image Example of Star schema

What is Snowflake Schema?
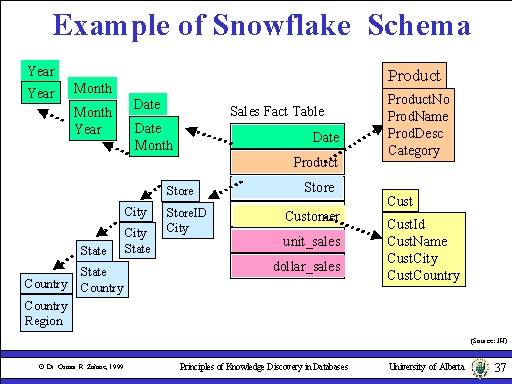
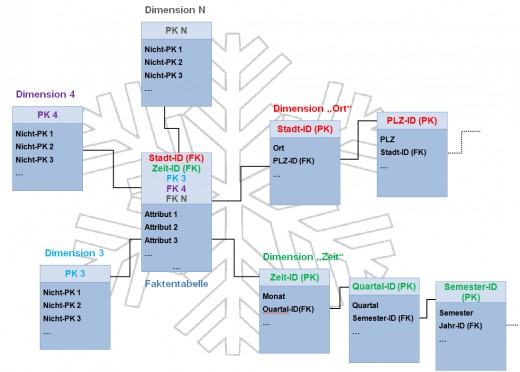
Snowflake:
The snowflake schema is an extension of the Star Schema, where each point of the star detonates into more points. In a star schema, each dimension is represented by a single dimensional table, whereas in a snowflake schema, that dimensional table is normalized into multiple lookup tables, each representing a level in the dimensional hierarchy.
One fact table is bounded by different dim table but this dim table is splited into different levels.
This is more normalized data.
Image Example of Snowflake Schema
What is the difference between Star Schema and Snowflake Schema?
Star Schema:
- De-Normalized data structure
- More data dependency and redundancy
- Query result faster
- View Star Schema structure
- Simple DB structure
- No parents table
- Category wise single dimension table
- Don’t need to use complicated join
Snowflake Schema:
- Normalized data structure
- Less data dependency and no redundancy
- Some delay in query processing
- Complicated DB structure
- View Snowflake Schema structure
- Complicated join
- Dimension table split into many pieces
- It may contain parent table