How to control Bleeding
Bleeding and Wounds
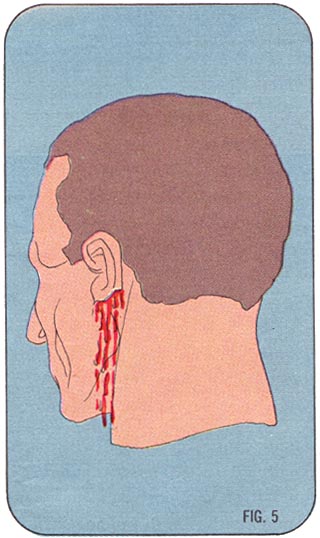
Wounds are of different kinds. However, any kind of wound may tend to bleed most especially if the vessels are injured. The amount of blood or pressure would depend on the vessels involve.
The different kinds of vessels are as follows:
- Capillaries
- Veins
- Arteries
Capillaries are minute vessels and naturally would be easy to control when it is wounded.
Veins although are bigger, have lesser pressure and are therefore easy to control
Arteries are almost of the same caliber with veins with respect to size but has greater pressure since it is connected direclty from the left side of the heart.




Different Kinds of Wounds
Now that we have an understanding on the different kinds of vessels, it is important that we should also be familiar about the different types of wounds.
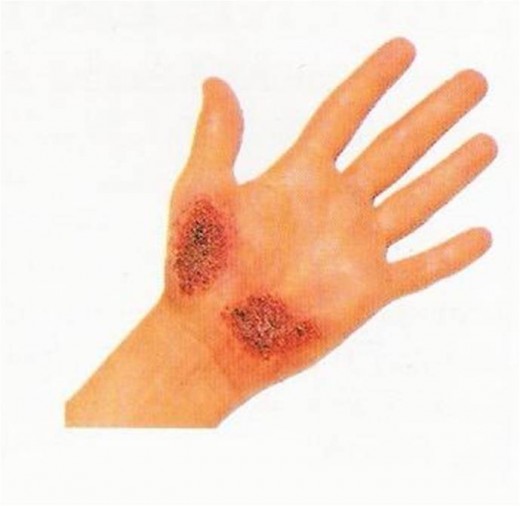
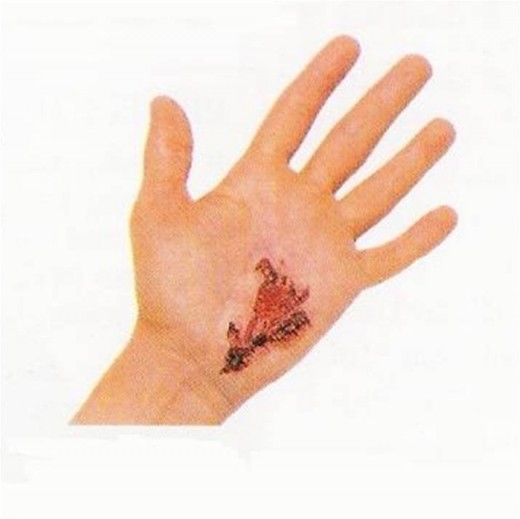
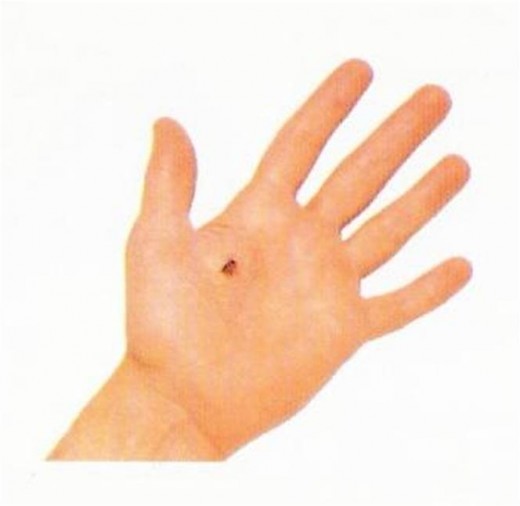
- Abrasion
- Incision
- Laceration
- Punctured
- Avulsion

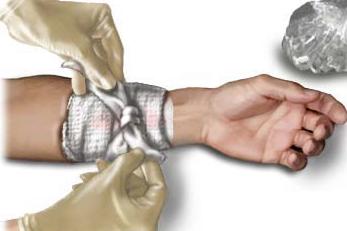
Direct Pressure
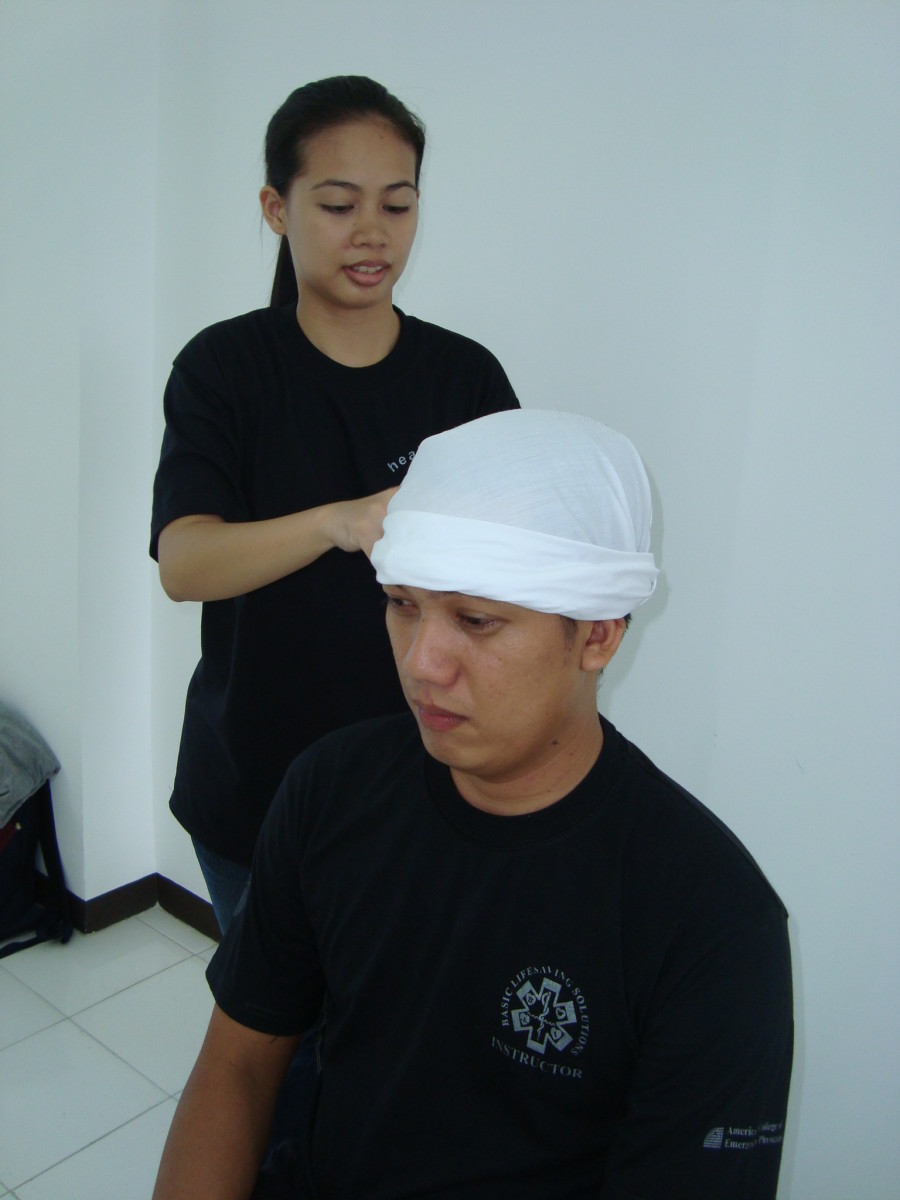
The first and foremost method in controlling bleeding may not be as difficult as you think. It is simly putting pressure directly over the wound. This can be done with the use of gauze or any cloth available directly over the wound with constant pressure.
Remember that a what we are up to is to stop the bleeding so continuesly apply the pressure over the wound. This will also allow the blood to clot and will aid in cotrolling the bleeding. Any gauze or cloth applied to the wound is what we call a dressing. Even your bare hands can be used as a dressing.
You can also apply a bandage to hold the dressing in place.
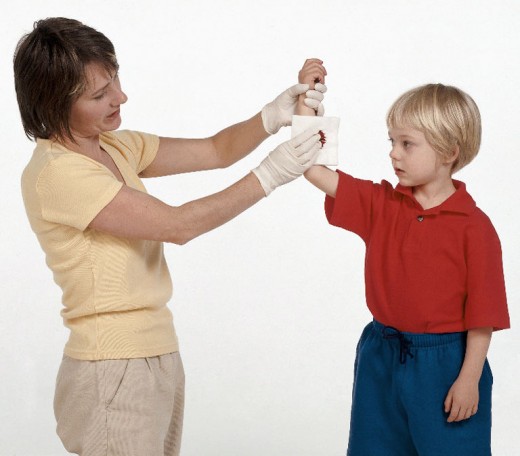

Pressure on Supplying Artery
You may also apply Pressure on the Supplying Artery. This is done by pressing the brachial artery or the femoral artery should the wound involves the extremities. But again bear in mind that direct pressure is always the first and foremost method in controlling bleeding.
Elevation
If there is no fracture in the area of the wound and the wounded part can be elevated, then apply the second method, Elevation. But you have to remember that elevation should be done when direct pressure has been applied already.
Elevate the wounded part above the level of the heart. This will lessen the amount of blood heading to the wound and lessen the flow of blood.

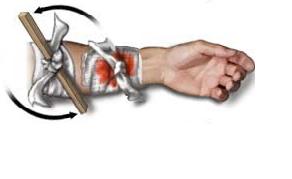
Torniquet
This is the last resort in controlling bleeding. In fact, in some states, torniquet is discourage and in some is no longer applied due to the dangers that it poses.
Torniquet is applied in between the heart and the wound. Placing a constricting band on the area and twisting the band until bleeding is controlled.
It is very importatn that the torniquet should be released every 15 minutes for 2 minutes time. This will re supply the muscles and tissues with oxygenated blood to prevent permanent damage.

Prevention Infection
For minor wounds where there is no severe bleeding. The important thing to do would be to prevent infection. This is done by washing the wound with soap and water.
Afterwhich, antibiotic or antiseptic solution should be applied. Cover the wound with a sterile dressing to prevent the wound from getting infected.
- First aid Guidelines
First aid Guidelines for Common Emergencies - CPR Training Guide
Guidelines of Cardio Pulomary Resuscitation