Effectiveness of Chelation Therapy for Heart Disease Is Proof of Free Radical Theory of Heart Disease
Build up of plaque in the arterial wall
A scientific study has proven chelation therapy as effective for heart disease
Chelation therapy is effective as treatment for heart disease
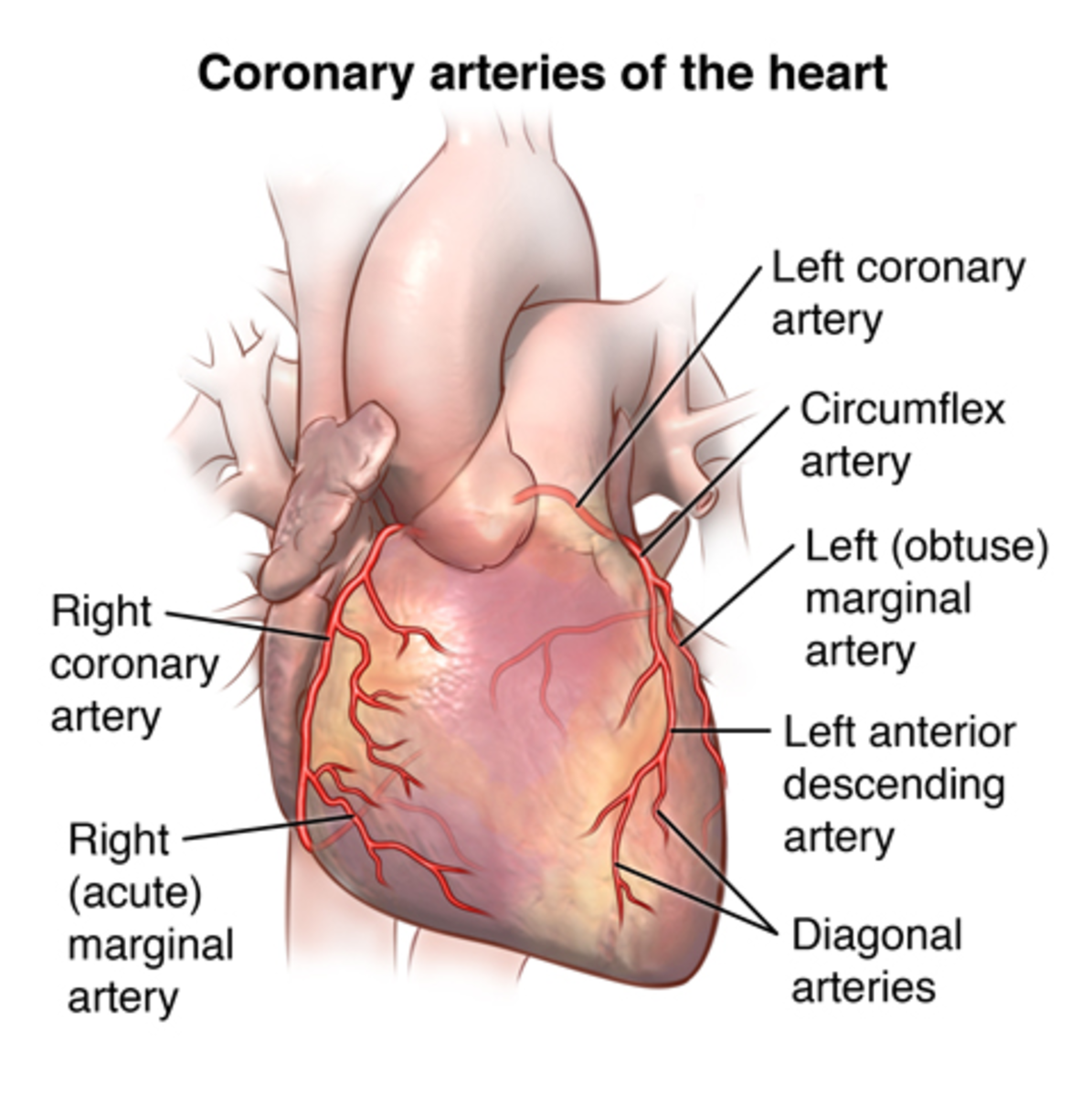
This diseases consists of narrowing of at least one of the coronary arteries that supply blood to the heart. Such narrowing results in a limited supply of blood to heart muscles and an accompanying limited supply of oxygen as the blood is the carrier of oxygen. Starvation for oxygen turns into lack of energy for heart muscles as oxygen is involved in the metabolism of glucose that provides energy.
Lack of energy stimulates pain receptors that is why the patient feels chest pain or angina. If the lack of oxygen is severe some heart muscles die resulting in heart attack.
The conventional treatments for heart disease are angioplasty and coronary artery bypass graft surgery.
An alternative treatment for heart disease is chelation therapy, in the form of oral chelation or infusion chelation therapy.
The Institutes of Health (National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute) of the United States launched in 2002 a study called “Trials to Assess Chelation Therapy” or TACT. The experimental design of TACT was double blind randomized with control. Results of TACT were presented on November 4,2012 in a meeting of the American Heart Association held in Los Angeles, California.
Chelation therapy is safe and effective for the treatment of heart disease. These are the findings of TACT. I have a Hub “USA has announced chelation therapy as safe and effective for heart disease and diabetes."
The treatment solution and protocol of chelation therapy so assessed were those that are already being administered by chelationist in USA and other countries like the Philippines.
Treatment solution
- 3 gram EDTA or less, based on GFR
- Vitamin C, MgCl (magnesium chloride), KCl (potassium chloride), bicarb, procaine, heparin
- B1, B6, pantothenic acid, to 500 cc with sterile water
- No oral nutriceuticals except multivitamins were in the study
- Placebo infusion - 6 gm dextrose per week
Primary end point and sample size
- Composite of death, stroke, MI (myocardial infarction or heart attack), new revascularization (necessity of new surgery for angioplasty or bypass surgery), hospitalization for angina (chest pain)
- Original plan 2372 patients, follow up for 1 year or more, 85% power to detect a 25% difference. (Follow up ended in October 2011).
- There were 222 cardiac events (26.5%) in the EDTA group and 261 (30.0%) in the placebo groups
- This was a statistically significant difference with a P-value of 0.036
- The largest difference came in the need for subsequent cardiac revascularization [27 fewer in the group given EDTA]
- The longer the patients were followed, the greater the difference between the treated and the placebo groups.
[That means those treated with EDTA got better through time.]
Summary of improvement with TACT
Record of those who were given chelation therapy versus patients in the control group (given water and glucose).
6 fewer death; 15 fewer heart attacks; 3 fewer strokes; 27 fewer revascularization surgeries (angioplasty and arterial bypass graft surgery). Reference: TACT: A research result on EDTA treatment (Internet. March 27,2014).
Theory is true
The above is a review of the findings of TACT and the methods employed. In our discussion we will focus on: What is proven by the finding that chelation therapy is effective for heart disease.
That chelation therapy is effective for heart disease proves that its theoretical basis is true.
To explain this, let’s use E = mc2 as an example. This formula when it was first issued by Albert Einstein in 1906 was only a prediction. Einstein derived it from his special theory of relativity. (At that time, the proper term to use was hypothesis that is a guide in conducting an experiment. A hypothesis when proven true graduates into a theory.)
Being a prediction, the formula was not yet verified. In fact, it was considered as a physical fiction until stumbled upon by Enrico Fermi in 1936 and Fermi's experiment was verified by Lise Mietner and company in 1938.
The special theory of relativity was couched in mathematical language that it is said only Max Planck understood it. Among several reasons, Einstein derived the formula to pave a way to verify that the special theory is true.
We are reminded that mathematics is different from science. Each has a test of its own. That science uses mathematics is another story.
The special theory was couched in mathematics. The special theory in mathematics was valid. The test of mathematics is validity (Russell, B. Human Knowledge: Its Scope and Limits. 1947). Einstein wanted to pave a way to prove that his theory is true. That he did by deriving a statement of fact (E = mc2) from his mathematical formulations. That way it would belong in science. The test of science is truth, according to Russell. (To recall, it was still a prediction up until 1938).
When the formula was verified true in 1938, it proved that the special theory of relativity is true. (The special theory deals with two coordinate systems, like galaxies, that are in uniform motion. The generalized theory of relativity deals with coordinate systems that are in relative motion.)
The atomic bomb is based on the special theory of relativity. Of course, the explosion of the atomic bomb proves that this theory is true.
We are making a parallel between the special theory of relativity and the free radical theory of heart disease.
That chelation therapy is effective for heart disease proves that its basis, the free radical theory of heart disease, is true.
Cure versus treatment
Chelation therapy cures heart disease. This is different from "chelation therapy treats heart disease." Cure is different from treatment. In cure, a disease that is cured will not recur, assuming that there had been no reinfection or no repeat of the circumstances that brought on the disease.
In treatment, a disease that is treated can recur. For example, the application of angioplasty for heart disease. It is probable that a person who had an angioplasty will have angina or heart attack. The reason is mainly that the causes of heart disease (free radicals and ROS) are still around and not dealt with. They can cause plaque in another artery. The same is true for heart bypass surgery.
There is a need for maintenance after being cured with chelation therapy. For one, change in life style like halt in drinking alcohol, halt in drinking coffee, and halt in smoking. Antioxidants must also be taken because the body keeps on producing free radicals and ROS. Built-in antioxidants like superoxide dismutase and supplement antioxidants (vitamins A, C, and E) balance out the population of free radicals and ROS such as to prevent oxidative stress.
Free radicals and ROS are unlike bacteria. Our body produces the first two continuously. We also get them from the environment like pollution, pesticides, meat treated with nitrite, nitrosamine, ractopamine, and many more.
Unfortunately a person who stops smoking now will still have X-rays and free radicals in his body from polonium 210 and lead 210 that tobacco contains. Polonium lasts for over a hundred days but lead 210 lasts for 44 years which means that lead 210 stays in the body for 44 years. They must be neutralized for the same period..
Bacteria like tetanus come from outside the body. Once the tetanus bacteria had been killed by antibiotics, if there is no reinfection, the patient is cured.
Free radical theory of heart disease
Let’s get to preliminaries. Free radical theory is a short label, for the purpose of brevity. The full term should be “free radicals and reactive oxygen species theories of heart disease.” Each free radical and reactive oxygen species can cause injury that is why we say "theories."
[There is also a free radical theory of cancer; a free radical theory of lupus; a free radical theory of diabetes; a free radical theory of arthritis..... Free radicals and ROS cause a lot of disease otherwise called degenerative diseases.]
Examples of free radicals are atomic oxygen, molecular oxygen, ozone, singlet oxygen and superoxide.
A free radical is any atom or molecule or fragment of a molecule with at least one unpaired electron its its outermost orbital. That unpaired electron is unstable and to stabilized itself it grabs another electron from a neighboring molecule resulting in injury. If that injury were inflicted on DNA it would result in mutation, resulting, in turn, into an atheroma.
Examples of reactive oxygen species (ROS) are hydroxyl radical, alkoxy radical, hydrogen peroxide, nitric oxide, peroxynitrite, nitrous oxide and many more. They are derived from free radicals. A ROS acts like a free radical in causing injury.
A hypothesis or theory consists of concepts and relationships among concepts (Einstein, A. Ideas and Opinions. 1954). A hypothesis is a guide in the conduct of research; a proven hypothesis graduates into a theory. Here then is the theory:
“Free radicals and reactive oxygen species injure the inside wall of artery. This injury results in atheroma.”
The concepts are free radicals, reactive oxygen species, inside wall of artery, injury and atheroma. The relationships are injure and results.
Atheroma is a benign tumor. The body attempts to repair the injury with patches of collagen, elastin, fibrin, bad cholesterol, and other debris. Calcium joins in later that cements the mixture (Cranton, E., MD. Bypassing Bypass. Updated second edition. 1995). However, the attempt at repair turns awry. The mixture turns into a mound that grows in size as more deposits like bad cholesterol pile up.
The injured artery leaks copper and iron that accelerate the production of ROS. Iron accelerates the production of hydroxyl radical; copper accelerates production of alkoxy radical.
The mixture grows into a mound then to a plaque that blocks, partially or completely, an artery. The symptom is angina. Blockage of blood to heart muscles may result in heart attack.
For more details, you may review my Hub "A theory of heart disease as guide in treatment.
It is expected that some people will doubt the effectiveness of chelation therapy. The same holds for the free radical theory of heart disease.
Such doubts are legitimate in science. However, some detractors are goaded by profits.
The proof of the free radical theory of heart disease is no longer anecdotal but a double blind randomized with control study.
Let those who are benefited by chelation therapy speak.
How chelation therapy works
I will give a summary of the mechanism of chelation therapy. I have a detailed discussion of this in my Hub "A theory of heart disease as guide in cure."
The primary objective of cure is to remove or neutralize the cause of disease. In the free radical theory of heart disease, the causes are free radicals and ROS. A free radical can be neutralized by providing the electron it needs to stabilize. This vitamins C, A, B1, B6 and E can do. It is the electrons from their hydrogen components that satisfy the hunger of free radicals and ROS.
Some minerals like iron and copper accelerate the production of free radicals. An injured arterial wall leaks them. They can be chelated by EDTA (ethylene-diamine-tetra-acetate). Chelation is like a a crab pinching on a prey. EDTA has six pinchers, as it were, that pinch iron, copper and calcium and dispose off them through the urine. Vitamins A, C, E and magnesium are also chelators (Walker, M. MPD. The Miracle Healing Power of Chelation Therapy. 1986).
Neutralization is not always by disposal. Stem cells are involved. As the chelation solution circulates in the blood, the level of calcium goes down. This stimulates the parathyroid gland to secrete more parathormone that stimulates the osteoblast. This is a stem cell that produces bone cells, getting calcium from any source including the plaque.
Some calcium can be found in the urine owing to chelation therapy, according to Dr. Arturo V. Estuita, a Filipino internist and chelationist. But the decrease in the amount of calcium in the plaque cannot all be found in the urine; they find their way in new bone cells (Cranton, E. MD. Bypassing Bypass. Updated second edition. 1995).
As the arterial wall gets well from atheroma, its capability to produce endothelium nitric oxide (eNO) returns. An injured wall cannot produce eNO (Ornish, D., MD. Dr. Dean Ornish Program for Reversing Heart Disease. 1996). eNO signals the dilation of artery to allow more blood flow that alleviates angina and prevents heart attack.
The endothelium progenitor cell (EPC) also joins in. EPCs are stem-cell like cells circulating in the blood; they heal injuries of the arterial wall. This healing takes time. That is why the full benefit from chelation therapy comes 90 days after the last chelation session (Cranton, 1885). Cranton calls it "90 day syndrome."
The mode of chelation therapy is not to eliminate free radicals and ROS, called oxidants. The reason is that the body is continuously producing them. Besides, to repeat, we get them from the environment. The mode is to establish a balance between oxidants and antioxidants resulting in absence of oxidative stress.
Take molecular oxygen that we breathe and use in the metabolism of glucose. A molecule of glucose splits into two, each going through a pathway likened to a waterfall. At the head of the waterfall, one atom of hydrogen is involved in each pathway. The electron of this hydrogen falls down in what is called, technically, as electron transfer, while its partner proton floats around waiting for use. In three spots in its fall, the electron produces adenosine triphosphate (ATP) a currency of energy. At the foot of the waterfall, molecular oxygen is waiting, partially pulling down the electron. Molecular oxygen designated as O2 2- has two atoms of oxygen and two negative charges. One negative charge will catch the falling electron joined in again by the floating proton. Together, they make up a molecule of water. The other part of molecular oxygen remains as O2- which is now a superoxide, a free radical.One molecule of glucose produces 38 ATPs, with water and superoxide as by-products. This metabolism shows how superoxides are produced. Millions of ATPs are produced because our body needs million of them. One brain cell consumes 10 million ATPs per second. So millions of superoxides are also produced. Superoxide is a master free radical that produces a lot of ROS like nitrous oxide, peroxynitrite, hydroxyl radical.
[When oxygen is lacking, the electron transfer in the waterfall chokes up. No energy is produced that brings on angina. Heart muscles starved for oxygen, thus energy, die resulting in heart attack.]
The are several reactions in the body that produce superoxide. For one, cyclooxygenase acts on arachidonic acid and produces prostacyclin and thromboxane with superoxide as by-product.
How is a superoxide dismantled? Superoxide dismutase (SOD), an enzyme, attaches one proton and one atom of hydrogen and the mixture turns into hydrogen peroxide, a ROS. It looks like SOD makes the situation worse. Our body has a remedy. The built-in glutathione peroxidase donates one electron to hydrogen peroxide and turns it into safe water.
However, we have a super abundance of superoxide and hydrogen peroxide that the built-in antioxidants are overwhelmed. Chelation therapy and supplement antioxidants come to the rescue.
Other theories of heart disease
The most prevalent theory is the cholesterol theory. It asserts that the low density lipoproteins are small enough to be able to penetrate the inner wall of the artery and built up a plaque there. However, there is a flaw in this theory. Dr. Estuita points out one. The same blood flows through the vein and the artery carrying cholesterol. But veins do not develop plaque. Another flaw is that one may have a persistently high cholesterol level but does not develop heart disease.
Conventional medicine does not have a theory but forwards risk factors (DeBakey, M. MD and A. Gotto, Jr. The Living Heart. 1977). In the second edition of their book "They New Living Heart" published in 1997, they did not tackle any theory of heart disease. The concession they gave is that the plaque can be reversed by change in life style and cholesterol-lowering drugs. Dr. DeBakey is considered the father of coronary arterial bypass graft surgery.
Risk factors are obesity, age, hypertension, cholesterol, smoking, diabetes and stroke. The presumption is that if any or all of these risk factors were addressed heart disease would not occur. However, a large study conducted in Finland for 10 years where one group of participants were given cholesterol-lowering drugs and another group given anti-hypertensive drugs gave results contrary to expectations. Participants in the control group (without medication) gave a lower mortality rate owing to heart disease than those in the treatment group.
Dr. Dean Ornish, MD has another belief of the cause of heart disease. It is a modification of the conventional risk factors, cholesterol excluded (Ornish, D. MD. Dr. Dean Ornish Program for Reversing Heart Disease. 1996). Dr. Ornish has devised a protocol based on his hypothesis, treating heart disease without drugs. It has reduced plaque by 8% in four years.
Dr. Ornish was a medical adviser of Pres. Clinton in his last term who banned smoking in the White House. However, neither Dr. Ornish nor Pres. Clinton has affirmed if Pres. Clinton followed the advise of Dr. Ornish. After his last term Pres. Clinton underwent a 4-artery bypass. You can access an account of this in "The Last Heart Attack" hosted by Dr. Gupta, produced by CNN (Youtube).
The key concept in any theory of heart disease is the cause of the injury of the inner wall of the artery. Free radicals or ROS or both have been caught red-handed with electron spin resonance spectroscopy (Cranton, E. MD Bypassing Bypass. Updated second edition. 1995; Sharma, H. Freedom from Disease. 1993).
Dr. DeBakey and Dr. Gotto abandoned the pursuit for cause and settled for risk factors.
Added background reading
What follows could be considered as TMI or too much information. The concern is how molecular oxygen that we use in generating energy is turned harmful.
Molecular oxygen does not react with non-free radicals that is why it does not burn (oxidize) the inner wall of an artery. Molecular oxygen does not start the harm it inflicts; it is initiated by other free radicals and ROS. (Halliwell, B. “The Proteosome: Source and A Target of Oxidative Stress.” Stefanis, L. and J. B. Keller. Editors. The Proteosome in Neurodegeneration. 2006:86).
To start with, a fat combined with a ROS (hydrogen peroxide) forms a carbon-fat plus ROS and atom of hydrogen. The reaction continues this way:
Carbon-fat plus molecular oxygen form fat and superoxide. This compound of fat and superoxide is called peroxyl radical.
Peroxyl radical plus fat form lipid peroxide that engulfs a molecular oxygen with two unpaired electrons. The macrophage, component of the immune system, engulfs lipid peroxide and turns foamy then clings to the atheroma (Sharma, H. MD. Freedom from Disease. 1993). That is how lipid peroxide adds to the plaque of arteries. That is one kind of harm molecular oxygen participates in.
In another way, molecular oxygen as part of lipid peroxide turns harmful in that its two unpaired electrons grab other elections of other molecules causing injury. The low density lipoprotein (LDL) is the kind of fat that is commonly involved in lipid peroxidation. This peroxidation usually occurs in membranes of cells and mitochondria, the energy factory.
Hubs on chelation therapy by conradofontanilla:
http://conradofontanilla.hubpages.com/hub/Why-Is-Heart-Disease-The-Number-One-Killer-In-the-World
http://conradofontanilla.hubpages.com/hub/What-For-Is-A-Theory-of-Heart-Disease
http://conradofontanilla.hubpages.com/hub/How-To-Treat-Stroke
http://conradofontanilla.hubpages.com/hub/What-Would-I-Do-If-I-Had-a-Heart-Attack