Materials Selection versus Manufacturing Process
Materials selection versus manufacturing processes is not the whole story
Material selections can determine what manufacturing processes are available, form can determine what materials can be used and manufacturing processes can determine what form can be created.
So what you have is a merry go around of decisions and compromises to make in order to elicit the best choice. It also goes a little deeper than that, because its also about the physical properties of the material and of course the design specifications that have to be met.
Often the decision process that has to be made is simpler than it might first appear, there will be required properties that will rule out certain materials for example. Something like a need to be non-magnetic would rule out a good deal of metals (not all) and might lead the designer towards a plastic. Then the next requirement might be that it has to conduct electricity which in turn would rule out most plastics and so the process goes on. It is natural for most of the decisions regarding material type selections to be done without too much thought, intuitively engineers and designers will know from past experience or training which groups of materials to consider.
Anyone with basic engineering training will be aware of the different types of materials that are generally available and what groups they fall into. Typical groupings for materials are metals, ceramics, polymers and composite materials.
Metals form a significant proportion of the materials chosen during the selection process because of the ability to manipulate their physical condition during various manufacturing process stages. They offer a very flexible and attractive solution to a material choice decision at an affordable price.
One example of this is producing aircraft parts made from aluminium alloy, the manufacturing process will nearly always consist of an annealing stage, maybe several while the material is being worked into a complex shape. After which it would receive a solution treatment to introduce changes at the atomic level that result in a high strength condition. Finally it is common to apply a precipitation treatment which is in effect an accelerated age hardening process to quickly strengthen the component ready for final function. These are relatively straight forward heat treatments that allow the manufacturer to get the shape, when the material is soft, and required physical properties from the material, when it is hardened and aged, that will allow the end item to meet the design specification.
Ceramics are one of the most difficult materials to process with only a few limited techniques being available usually involving some form of powder processing, very high pressure and temperature being applied. Ceramics tend to be brittle and/or porous but they still have their uses, a common one is to utilise them as a hard wearing coating. Components that could potentially erode, for example under flow conditions when drilling an oil well, can be protected to an extent with a carbide coating. Even better would be the use of a solid carbide component and this is often possible if the designer arranges the assemblies so that there are only compressive forces present and no tensile forces.
You will probably have realised from the dialogue that the use of ceramics is fairly specialised in whatever form they are used and as such this tends to be an expensive option, which, on occasion, is unavoidable.
Polymers, more easily recognised by most as 'plastics', are also widely used and versatile in nature. Particularly the thermoplastic plastics which can be reused time and time again as they can be melted and re-used without degradation, unlike the thermosetting plastics which once formed will degrade if subsequently remelted. These characteristics raise a further potential requirements criteria, that is asked for more and more these days, of being able to be recycled. A consideration that every manufacturer now has to take into account.
Plastics generally suit moulding processes very readily and consequently are adopted frequently for components with complex shapes. The price that can be paid for that level of flexibility is strength and resistance to high temperature. The strength drawback can be overcome by introducing structural elements utilising alternative materials, often metal. But for high temperatures the solution has been to develop specialist compounds that will withstand high temperature up to 200C. They are typically produced at a very high cost however and are more difficult to mould, although not impossible.
Composites this is where a mix of two or more base elements are used to provide properties that the base elements cannot provide standalone. There are a huge range of materials that could be considered composites, one example was alluded to previously where a ceramic coating was used to provide a hard wearing surface on a component to prevent erosion. Together these could be considered a composite material where each element solved a different problem. Another example was the plastic reinforced with metal to provide structural strength.
Composites are widely used in order to ensure that products can be made using manufacturing processes that are available and result in components that will meet the design specifications using materials that are often also commonly available.
The primary manufacturing processes fall into 4 general categories:
- Machining
- Casting
- Forming
- Joining
Not every material will be able to be processed with every manufacturing process available, so again you can see that there are a set of inter-dependencies that determine the way forward.
History has shown over the years that the use of materials required to resolve engineering problems can sometimes only be achieved by the development of new or improved manufacturing processes or equipment. Modern electronics is a great example of this, excuse the pun, but miniaturization has grown at an exponential rate. Massive amounts of memory can now be stored on tiny chips as a result of process improvements and changes in manufacturing techniques that allow these components to be manufactured. A significant impact on this technology has been the improvement of the viewing equipment used to allow operators to work with microscopic components.
Materials Selection for Micro Electronics
Manufacturing Processes and Materials Selection
- Manufacturing Processes and Methods
The selection of a manufacturing process is done very much on the basis of a manufacturer choosing the process that best suits his needs. Consideration must be given to a number of factors before deciding on... - Manufacturing Processes - Surface Treatments
Examining and explaining the use of the manufacturing process for surface treatment of industrial components. - Manufacturing Processes - Vapour Deposition
Surface engineering processes includes both chemical vapour deposition CVD and physical vapour deposition PVD - Manufacturing Processes - Joining Techniques
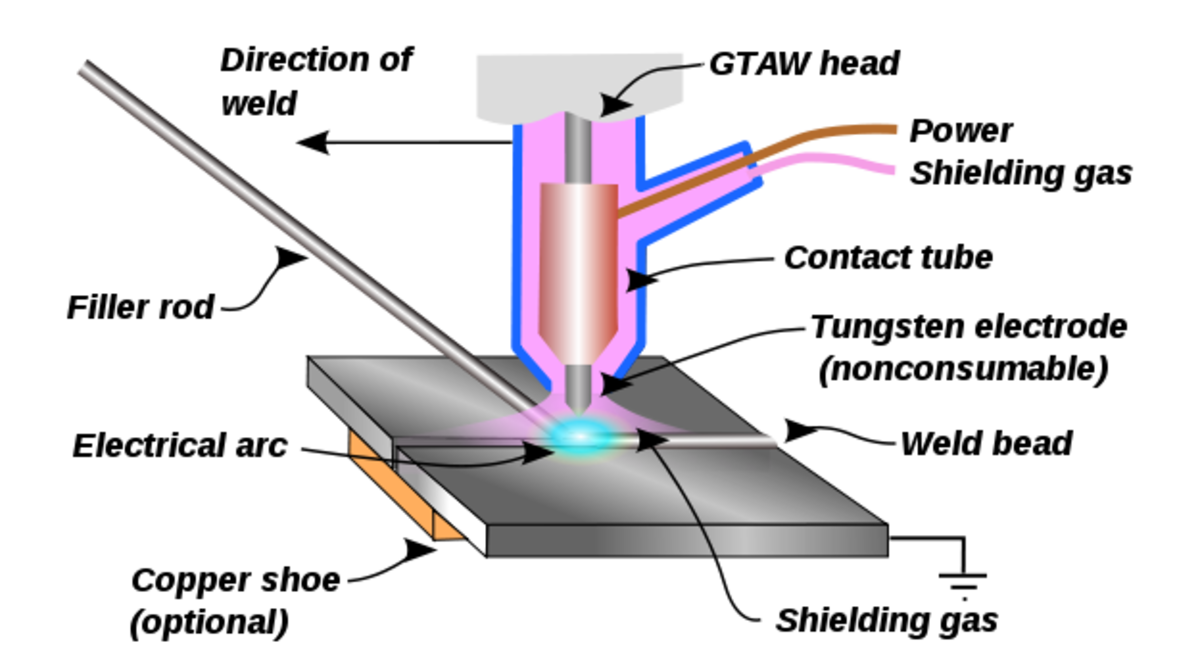
Adhesive bonding and mechanical fastening with rivets or nuts and bolts. - Manufacturing Processes - Fusion Welding
Fusion welding belongs to the general manufacturing processes category of joining. One of the original welding techniques used was gas welding the best known of which is called Oxy- Acetylene welding. The... - Manufacturing Processes - Brazing and Soldering
Brazing and soldering comes under the manufacturing processes category of joining. The process in both cases involves introducing a low temperature alloy into a controlled gap between metal surfaces. An... - Manufacturing Processes - Friction Welding
Most commonly described as welding, this process which is more accurately described as a forging process, is used typically for the joining of dissimilar metals and thermoplastics. - Manufacturing Processes - Blow Moulding
The blow moulding process fits in the general manufacturing processes category of 'forming'. A heat softened hollow plastic blank, sometimes referred to as a 'parison' is clamped between two mould halves. Air... - Manufacturing Processes - Pressing and Sintering
Pressing and sintering is a powder processing process that falls in the general category of forming under the manufacturing processes umbrella.The powder is pressed in closed dies to form a green compact that... - Manufacturing Processes - Forging
The metal forging process comes under the category of forming as a manufacturing process. It involves the forming or shaping of bulk metal between dies which mirror the shape of the component or section of a... - Manufacturing Processes - Sheet Metal Forming
The sheet metal forming process comes under the category of forming as a manufacturing process. There are a number of sheet metal forming methods available which all consist of some form of deformation of the... - Manfacturing Processes - Rolling And Metal Forming
Metal rolling is manufacturing process that falls under the general category of forming. It facilitates the continuous forming of bulk metal between two rotating roller tools. It is a 2 dimensional process... - Manufacturing Processes - Extrusion Process
Extrusion fits under the general category of forming in manufacturing processes. The term applies to a variety of processes that involve confining a material in a container and applying a force to push the... - Manufacturing Processes - Superplastic Forming
Superplastic forming as the name suggests falls in the manufacturing processes category of forming. The process works under closely controlled conditions of temperature and strain rates which allow certain... - Manufacturing Processes - Vacuum Forming
The vacuum forming process comes under the general manufacturing processes category of forming. The process involves producing components that are formed by heat softening plastic sheet and forcing it against... - Casting Process Problems
The main problem to overcome in a casting process is porosity, of which there are 2 types - Manufacturing Processes - Sand Casting
Sand casting comes under the general category of casting as a manufacturing process and is a permanent pattern process.In other words the sand moulds are produced using a reusable pattern that is removed... - Manufacturing Processes - Investment Casting
Investment casting comes under the general category of casting as a manufacturing process and uses expendable moulds and patterns.This process is sometimes referred to as the lost wax process and is one of... - Manufacturing Processes, Full Mould Evaporative Pattern Casting
Full mould casting, otherwise known as full mould evaporative pattern casting, comes under the general category of casting as a manufacturing process and is an expendable mould and pattern process.... - Manufacturing Processes - Gravity Die Casting
Gravity die casting is a simple casting process which utilises reusable metallic moulds. The process is primarily used for simple shapes with some basic coring possible. It is mostly suited to casting light... - Manufacturing Processes - Squeeze casting
Squeeze casting fits in the general category of casting as a manufacturing process. Casting has been around for approximately 6000 years, so squeeze casting is a relatively new development.being introduced... - Manufacturing Process-Centrifugal Casting & Rotational Molds
Centrifugal casting fits under the general category of casting as a manufacturing process and utilities a permanent mould. Typically this process is used for the production of long, hollow components that... - Manufacturing Processes - Injection Moulding
The injection moulding process fits under the general category of casting as a manufacturing process. This may seem surprising as the process is dedicated to the production of plastic, rubber and composite... - Manufacturing Processes - Reaction Injection Moulding (RIM)
This is a permanent mould process that fits in the general category of casting as a manufacturing process and is sometimes abbreviated to the RIM Process. The general mode of operation of this process is to... - Manufacturing Processes - Single Point Cutting
Single point cutting fits in the category of machining as a manufacturing process. It involves the removal of metal from a workpiece using cutting tools that only have one primary cutting edge. Typical... - Manufacturing Processes - EDM Electrical Discharge Machining
Wire Electrical Discharge Machining fits in the category of machining as a manufacturing process. It involves removal of material from a workpiece using spark discharges. This is achieved by connecting the... - Manufacturing Processes - Grinding Machines
Grinding machines come in many different forms and types but generally fit under the category of mechanical machining as a manufacturing process. In principle all grinding machines operate in a similar... - Statistical Process Control versus Acceptance Sampli...
There are two types of product quality control approaches that are going to be compared and contrasted in this article, namely: Acceptance Sampling Statistical Process Control. (SPC) The purpose of...